Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Via Datscan And Clinical Exam Are Similarly Accurate
Despite the DaTscan being available to help diagnose Parkinsons, in most clinical situations, a DaTscan will not add information to what can be gleaned from the clinical exam. One study actually demonstrated that the accuracy of diagnosis in early PD was the same whether the diagnosis was reached using clinical exam or using DaTscan.
Read Also: Anesthesia Drugs To Avoid With Parkinsons
How To Watch Paxman: Putting Up With Parkinsons
Paxman: Putting Up With Parkinsons can be viewed on ITV when it airs at 9pm on October 4. It will be available on ITV Hub immediately afterwards.
ITV and ITV Hub are both free to watch. To view Paxman: Putting Up With Parkinsons on ITV Hub, you just need to register for an account. There is a premium service available, entitled ITV Hub+ . This is a subscription service priced at £3.99 a month or £39.99 for a year. For this price, subscribers receive ad-free television and downloads. A 7-day free trial is available prior to any commitment.
Neurodegeneration With Brain Iron Accumulation
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation patients present with a progressive extrapyramidal syndrome associated with iron deposition in the basal ganglia. The two main syndromes are outlined here, although there are additional syndromes including neuroferritinopathy and aceruloplasminemia. The most common of the NBIA disorders is pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration , resulting from mutations on the PANK2 gene, accounting for 50%. The classic syndrome manifests in early childhood with a combination of pyramidal and extrapyramidal features . PKAN can also rarely present in early adulthood. There are typical MRI findings, with a central hyperintensity with surrounding low signal on T2 images in the globus pallidus, giving the so-called eye-of-the-tiger sign .
The second main type of NBIA is PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration . When onset occurs in infancy, PLAN causes progressive motor and mental retardation with cerebellar ataxia, seizures, and pyramidal signs. However, onset can occur later in life which leads to an atypical syndrome that may mimic PD, with rest tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia and a good response to levodopa. However, patients also exhibit additional features including eye-movement abnormalities and pyramidal signs .
You May Like: Is Difficulty Swallowing A Symptom Of Parkinson Disease
Testing For Parkinson’s Disease
The exam for Parkinson’s disease is based on the review of your medical history, but diagnostic imaging may be used to rule out other diseases that are easily mistaken for Parkinson’s disease.
CT and MRI scans can be used to rule out the possibility of other brain diseases besides Parkinson’s disease .Your doctor might also perform a test called an MIBG myocardial scintigraphy, which is used to examine the condition of sympathetic nerves in the heart. For this, you take a test agent containing a substance called metaiodobenzylguanidine, which is similar to norepinephrine . The degree to which this agent collects in the heart is then assessed using images. It is known that this agent does not collect in the heart in Parkinson’s disease patients, and this fact is used as a reference in making a diagnosis.
In January 2014, a testing procedure called dopamine transporter became available in Japan. DAT is a protein that encourages the recycling of the dopamine that is used to send signals in the brain. This test discriminates between conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies by visualizing the workings of DAT.
Parkinsons Foundation Center Of Excellence
Mount Sinai Beth Israel is designated as a Center of Excellence by the Parkinsons Foundation, specialized team of neurologists, movement disorder specialists, physical and occupational therapists, mental health professionals and others who are up-to-date on the latest Parkinson’s disease medications, therapies, and research to provide the best care.
Don’t Miss: Does Caffeine Help Parkinson Disease
Whats Hot In Pd An Update On Dat Scanning For Parkinsons Disease Diagnosis
In 2011, the FDA approved a diagnostic test for Parkinsons disease. The DaTscan is a radiopharmaceutical agent which is injected into a patients veins in a procedure referred to as SPECT imaging. DaTscan, when it was approved, was considered an important addition to the armamentarium of the bedside clinician. In 2011 I wrote a Whats Hot column on DAT scanning, and this month I will update that posting and bring everyone up to date on the impact of this test.
One of the most frequently asked questions about Parkinsons disease on NPFs Ask the Doctor web-based forum is whether or not to pursue DaT or PET scan to confirm a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. The short answer is that the DaT test is over-used in clinical practice, and is only FDA approved to distinguish potential Parkinsons disease from essential tremor. In fact, the test only tells the clinician if there is an abnormality in the dopamine transporter, and does not actually diagnose Parkinsons disease . PET is also overused, though it can be a more powerful diagnostic tool when in the right expert hands.
The new DaT scans use a substance that tags a part of a neuron in the brain where dopamine attaches to it, thus showing the density of healthy dopamine neurons. Thus, the more of the picture that lights up, the more surviving brain cells. Dark areas could mean either Parkinsons disease or parkinsonism.
Selected References
Animal Toxicology And/or Pharmacology
Single- and repeated-dose intravenous toxicity studies have been performed using ioflupane in rats, rabbits, and dogs. Additionally, single-dose acute toxicity studies have been performed in cynomolgus monkeys. No mortality or other toxicity was observed at doses up to 5,500 times the maximum clinical dose of DaTscan at doses greater than 1,500 times the maximum clinical dose, pharmacological responses such as mydriasis and hyperactivity were seen in some species.
Dont Miss: What Can You Do For Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: Can You Stop Parkinson’s From Progressing
Living With Parkinson’s Disease
Coming to terms with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s and living with the disease is challenging and will take a lot of adjustment. There are still things you can do that can help you to feel more in control of your situation and to stay positive. Some things that might help could include:
- choosing to lead a healthy lifestyle
- making informed decisions related to your treatment
- keeping a diary of your symptoms in preparation for meetings with health and social care professionals
- attending a self-management course
Testing For Parkinsons Disease
There is no lab or imaging test that is recommended or definitive for Parkinsons disease. However, in 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved an imaging scan called the DaTscan. This technique allows doctors to see detailed pictures of the brains dopamine system.
A DaTscan involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug and a machine called a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner, similar to an MRI.
The drug binds to dopamine transmitters in the brain, showing where in the brain dopaminergic neurons are.
The results of a DaTscan cant show that you have Parkinsons, but they can help your doctor confirm a diagnosis or rule out a Parkinsons mimic.
Read Also: What Treatments Are Available For Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by nerve cell loss in the area of the brain called the substantia nigra.
According to the NHS , this part of the brain is responsible for producing dopamine, which acts as a messenger between parts of the brain and areas of the nervous system that control and co-ordinate movement. Damage to the substantia nigra nerve cells results in the amount of dopamine in the brain being reduced. Therefore, the part of the brain controlling movement doesnt work efficiently and movements become slow and abnormal.
Nerve cell loss is a slow process, with symptoms of Parkinson’s disease usually developing when around 80% of the nerve cells in the substantia nigra have been lost. It’s currently unknown why the loss of nerve cells associated with Parkinson’s disease occurs, although available research points to a combination of genetic changes and environmental factors acting to cause the condition.
Related ITV Features:
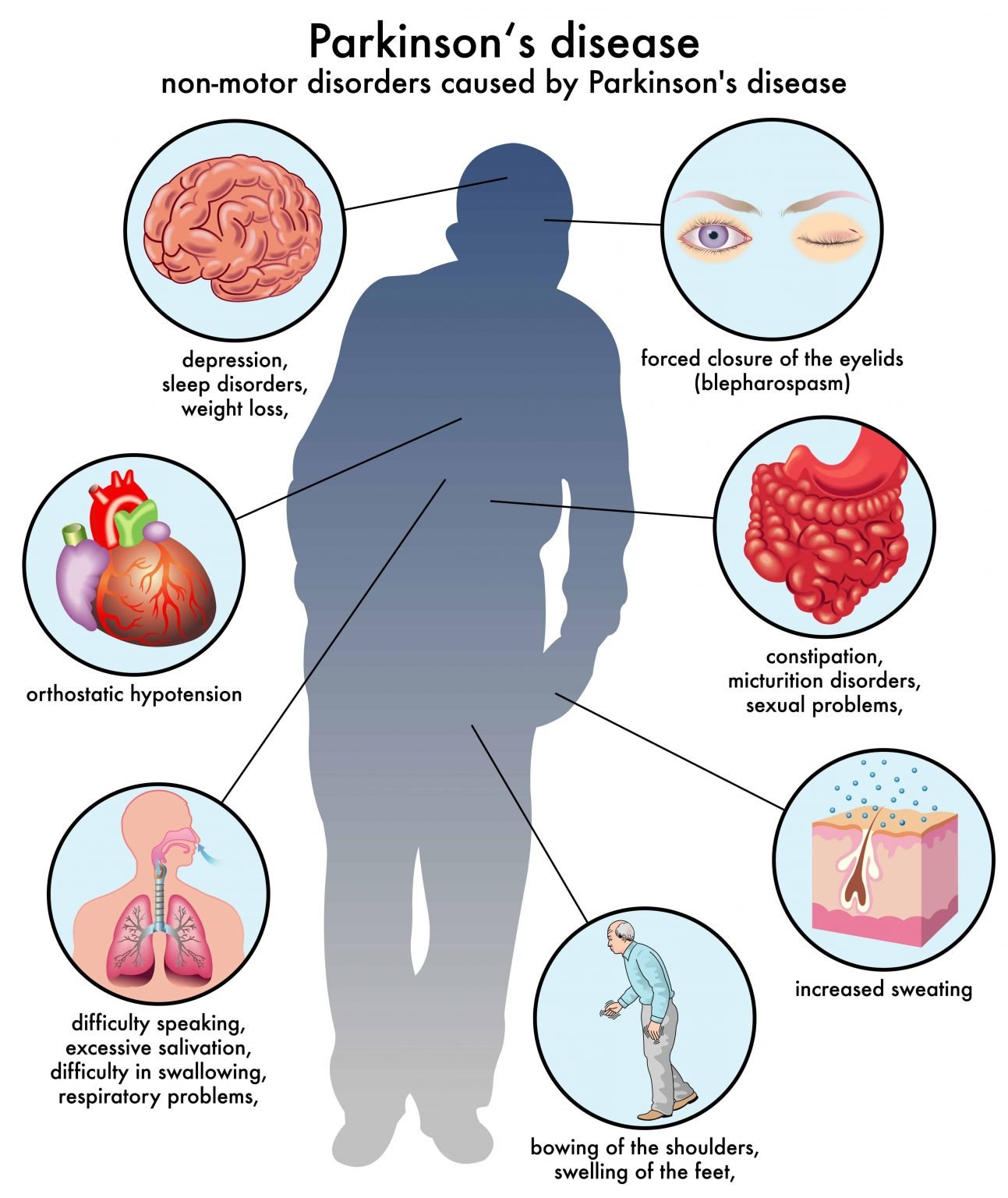
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
The main symptoms of Parkinsons disease are:
- tremor or shaking, often when resting or tired. It usually begins in one arm or hand
- muscle rigidity or stiffness, which can limit movement and may be painful
- slowing of movement, which may lead to periods of freezing and small shuffling steps
- stooped posture and balance problems
The symptoms of Parkinsons disease vary from person to person as well as over time. Some people also experience:
- loss of unconscious movements, such as blinking and smiling
- difficulties with handwriting
- drop in blood pressure leading to dizziness
- difficulty swallowing
Many of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease could be caused by other conditions. For example, stooped posture could be caused by osteoporosis. But if you are worried by your symptoms, it is a good idea to see your doctor.
Also Check: Tea For Parkinsons Disease
Recommended Reading: Does Roundup Cause Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
Mayo Clinic Q And A: Diagnosing Parkinsons Disease
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: My mother was recently diagnosed with Parkinsons, but she doesnt have many symptoms. I would like her to get a second opinion. Is there a blood test that can determine if the diagnosis is accurate?
ANSWER: Theres no one test that can be used to diagnose Parkinsons disease. Instead, the diagnosis is based on a persons medical history and symptoms, along with a neurological and physical exam. If your mother has doubts about her Parkinsons diagnosis, getting a second opinion from a neurologist who specializes in the disease would be reasonable.
Parkinsons disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects movement. In people who have this disease, certain nerve cells in the brain, called neurons, gradually die.
Many Parkinsons symptoms are related to the loss of brain neurons that produce a chemical messenger called dopamine. Loss of dopamine can lead to a variety of symptoms. Those symptoms can vary widely from person to person. Parkinsons develops slowly over time. In the diseases early stages, symptoms may be very mild and barely noticeable.
Parkinsons typically impairs a persons normal spontaneous body movements, such as blinking, smiling or swinging the arms while walking. The loss of dopamine that happens in Parkinsons may sometimes trigger sleep disorders, panic attacks, anxiety or insomnia.
If your GP suspects Parkinsons disease, youll be referred to a specialist.
This will usually be:
Read Also: Hospice Care For Parkinsons
You May Like: What Is Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease
Paxman: Putting Up With Parkinsons: Release Date
Paxman: Putting Up With Parkinsons will be released on Tuesday October 4, 2022, at 9pm.
The documentary will follow Paxman in the months after his Parkinsons diagnosis 18 months ago, charting how he adapts and comes to terms with the illness. The presenter has never before allowed such unprecedented access to his life, but wanted to show others how the disease impacts him. Throughout the 60-minute special, Paxman speaks to other high profile people living with Parkinson’s – including chatting to Sharon Osbourne caring for husband Ozzy, who shares the same diagnosis. Together, he and Sharon try CBD oil as a potential treatment for the condition.
He also meets the President of Parkinsons UK, Jane Asher, and tries different therapies for his symptoms – including attending an English National Ballet therapy dance class, and learning to play bowls. He will meet experts who are at the leading edge of research, including observing a brain dissection, and even meets a woman claiming to diagnose Parkinsons by smell.
With 1 in 37 people in the UK diagnosed in their lifetime, Paxman aims to investigate and bust myths surrounding the illness. He said I dont want to be involved in a production of a film that is in any way encouraging of the poor little me syndrome, about what he was hoping to get from making the documentary.
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Also Check: Parkinsons Disease Education Handout
You May Like: Exercise For Parkinson’s Disease Video
Idiopathic Basal Ganglia Calcification
This is a heterogenous disease associated with mineral deposition in the basal ganglia, as well as in other brain structures. There is a strong familial component, with causative mutations identified in SCL20A2 and PDGFRB. Patients commonly have a movement disorder, with parkinsonian features of akinesia and rigidity which show a variable response to levodopa. Other features include cognitive impairment, gait disorder, pyramidal signs, and a psychiatric presentation. Imaging is crucial in diagnosis to identify the areas of calcification, with CT imaging being more useful than MRI .
Parkinsons Is Easily Identified By A Pathologist But Is Difficult To Diagnose For A Clinician
When I state that Parkinsons Disease is well defined, I mean that the pathologist, looking at slides of the brain under a microscope, can say, knowing nothing about the patient, that the person had PD. Parkinsons Disease causes certain, easy to detect changes that are seen under the microscope. This, of course, requires that the person is dead, which isnt much use to that particular person or his family. The absence of a reliable test, in life, means then that there is room for mistakes. And, in fact, we make a fair number of mistakes, and Ill discuss below the types of cases in which we are most likely to make mistakes. Unfortunately, we are never in the position of being 100% certain that weve diagnosed someone correctly, until the autopsy.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Eyesight
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Its a good idea to ask questions as you and your doctor discuss a treatment. Asking questions can help you make sure you understand your condition and the benefits of treatment. Here are some sample questions to ask your doctor:
- Is it possible something other than Parkinsons is causing my symptoms?
- Do I need additional tests?
- How will my condition progress?
- What can I expect as my condition progresses?
- How will Parkinsons affect my other medical conditions?
- What treatments are available?
- Which treatments are best for me?
- How will treatments help my current symptoms?
- Will treatment slow down the progression of Parkinsons?
- What side effects do your recommended treatments have?
- What happens if these treatments dont help?
- Can you recommend any resources or educational material for me?
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Parkinsons is generally diagnosed by a primary care physician or internist who may than refer the patient to a neurologist of movement disorder specialist.
There are no standard diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. Rather, the diagnosis is a clinical diagnosis based on findings of a neurological exam and information provided by the person with Parkinsons disease.
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s A Form Of Cancer
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Driveable Cognitive Assessment Tool
Is an in-office assessment of cognitive abilities essential for safe driving. This includes tests of motor speed and control, attention, judgment, memory and decision-making, and making judgments of driving situations.
The DCAT measures only the specific cognitive functions needed for safe driving. It does not measure a persons overall cognitive functioning or intelligence.
No knowledge of computers or their applications are needed an individual only needs to touch the screen and press a button to complete the tasks. A mouse and a keyboard are never used.
A trained healthcare professional, typically an occupational therapist or kinesiologist administers the DCAT and guides the individual.
Read Also: Does Parkinsons Make You Sleepy
Don’t Miss: Are Bananas Good For Parkinson’s
