Treatment Options For Peripheral Neuropathy In Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease Patients
In our initial case series with IPD patients identified to have peripheral neuropathy , all patients identified to have one of cobalamin deficiency, methylmalonic acid elevation, or elevated homocystine levels were prescribed monthly intramuscular injections of 1000 µg of cobalamin . This was provided via intramuscular injections and not oral therapy due to concerns of potential inadequate absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. All patients initialized on therapy were subjected to repeated clinical examinations using the Toronto Clinical Scoring System and electrophysiological evaluations at 6, 12, and 24 months after diagnosis of the peripheral neuropathy when cobalamin therapy was initiated. Repeated blood tests for cobalamin, fasting methylmalonic acid and fasting homocysteine were concurrently performed.
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is named after James Parkinson. He first described the illness in 1817. PD mostly causes problems with moving around. It can cause a person to move very slowly. A person with PD appears stiff or rigid. At times, a person with PD may appear to suddenly freeze up or be unable to move for a short period of time.
A tremor of the hands is common. It is called a pill-rolling tremor because of how it looks. Many years ago, pharmacists used to make their own tablets. In order to make the medications into a tablet, they would roll the medicine into a small ball. The motion that it takes to roll a small ball looks very similar to the tremor in PD. When a person has PD, they often will have one or more of these symptoms.
Preventing Parkinsons And Neuropathy
Biggest Culprits | Digestive Health | Immune system | Movement | Optimizing Health
This article focuses on recent scientific research to isolate the actual roots of these two maladies, which interestingly have many of the same causes. It outlines the most effective ways to prevent them and maintain your health.
When doctors dont know what causes these diseases,theyre called idiopathic.
What is Parkinsons Disease?Parkinsons disease happens when nerve cells in the substantia nigra central area of the brain are damaged and can no longer produce dopamine, a nerve-signaling molecule that helps control muscle movement. People with PD have a variety of symptoms including loss of muscle control, trembling, and lack of coordination. People may also experience anxiety, constipation, dementia, depression, urinary difficulties, and sleep disturbances. Over time, symptoms intensify.
Symptoms of PD include the characteristic hand tremor, slow movement, slurred speech, small handwriting, accelerating small steps when walking, rigidity, decreased facial expression, poor balance, poor reflexes including blinking and swallowing, sleep disturbance, anxiety, depression, difficulty thinking, constipation, and skin problems.
In Parkinsons disease, dopamine-producing cells of the substantia nigra region of the brain basal ganglia slowly die. These cells normally produce dopamine, an essential neurotransmitter.
What is Neuropathy?
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
In Vivo Corneal Confocal Microscopy
All participants underwent IVCCM bilaterally, or unilaterally if one eye met exclusion criteria. The central corneal subbasal nerve plexus was imaged as previously described. Briefly, a topically anesthetized eye was examined with the Heidelberg Retinal Tomograph 3 laser-scanning confocal microscope with the Rostock Corneal Module . A single examiner performed all eye scanning, recording images of the subbasal nerve plexus across a wide area of the plexus using the built-in fixation light to access paracentral regions and continually adjusting the focus to the plexus depth. Mosaics were generated with an automated computer algorithm to select nerve plexus images from the recorded data using tissue classification and to stitch together adjacent images. Depth variations of subbasal nerve fiber paths were mapped onto a single two-dimensional mosaic image. A separate automated algorithm was used for detection and tracing of nerve paths and branching points, from which the mean values of CNFL and CNBD were calculated,. Averaged values between both eyes were used where applicable.
Potential Pathogenic Mechanisms Of Peripheral Neuropathy In Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease Patients
The studies to date have been descriptive and associative in nature only. The precise pathogenic mechanisms for the development of peripheral neuropathy in IPD patients remain speculative. Before considering the mechanisms by which methylmalonic acid and/or homocysteine may be pathogenic, other considerations require discussion.
As mentioned, considerations for genetic influences are important. The potential implications of parkin mutations given the expression of parkin mRNA in peripheral nerve may be of importance, but only a small percentage of IPD patients with parkin mutations appear to have an axonal form of peripheral neuropathy . The relationship of concurrent peripheral neuropathy to the so called Parkinsons Plus forms of disease, such as with multiple system atrophy must also be considered patients with multiple system atrophy frequently have an axonal peripheral neuropathy present . Associations such as this may suggest a neurodegenerative pathogenesis for peripheral neuropathy rather than a deficiency. Indeed, patients with greater severity and longer duration of IPD were more susceptible to development of peripheral neuropathy in our studies as well . Further studies will be required to determine if the peripheral neuropathy present in IPD patients develops in an analagous fashion to the central nervous system neurodegeneration in IPD.
You May Like: Parkinson Disease Ribbon Color
Central Nervous System Vs Peripheral Nervous System
Neurologic control of the body is very broadly divided into two systems the central nervous system which consists of the brain and the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system which consists of the network of nerves that are outside the brain and spinal cord, and innervate the limbs and the organs of the body.
The peripheral nervous system is composed of three types of nerves: autonomic nerves, sensory nerves and motor nerves. Different types of nerves have varying diameters and are generally divided into those that are small and those that are large.
- Autonomic nerves exert control over functions that are not under conscious direction such as respiration, heart function, blood pressure, digestion, urination, sexual function, pupillary response, and much more. This information is conveyed on small fibers.
- Motor nerves carry information on limb movement from the brain and spinal cord to the limbs. This information is conveyed on large fibers.
- Sensory nerves carry information on the various sensations felt by the limb to the brain and spinal cord. There are two main types of sensory nerves:
- Pain and temperature fibers which are small fibers
- Vibration and joint position sense fibers which are large fibers
Sensory Suggested Immobilization Test
The PD+RLS group was further assessed with the sensory SIT,. Patients were observed in the evening, between 8PM and 9PM, lying down in a 45° recumbent position and instructed to move as little as possible with legs extended. Patients were asked every 10min to indicate their perceived severity of leg discomfort, using a visual analog scale of 0100, generating seven individual values for each participant. A mean leg discomfort score > 11 was used as supportive of RLS diagnosis. This cutoff value has previously been evaluated and proposed as appropriate in the context of RLS diagnosis in PD.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Parkinson Disease
Results Of Large Fiber Neuropathy Assessment
NCS/EMG was performed in 39 patients . 12 out of the 26 PD and 4 out of the 13 from the parkinsonism group had abnormal NCS/EMG results. As expected, patients with abnormalities suggestive of peripheral neuropathy on the screening neurological exam were more likely to have abnormal EMG . Neuropathy prevalence was similar in the groups with PD and parkinsonism , whether PN was assessed by SWT, NCS/EMG or clinically .
Fig. 1
Part a shows mean peroneal compound motor action potential amplitudes and mean sural sensory nerve action potential amplitudes in patients with Parkinsons disease . PD all patients refers to mean values from the whole group , PD no PN refers to mean values from PD patients without large fiber neuropathy, PD SFN refers to patients with PD and small fiber neuropathy and PD Neuropathy to mean values in patients with PD and large-fiber neuropathy. Part b shows mean values of peroneal motor and sural sensory conduction velocities in the same groups
Fig. 2
Why Does Type 2 Diabetes Cause Your Feet To Go Numb
Neuropathy can lead to complications during surgery as well, explains Highlander. That is because of a condition called Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy , in which inflammation and unaddressed injuries subject bones, joints, and soft tissues to microfractures and deformity. This is not the same disorder as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and it can have many causes, including diabetic neuropathy.
A neuropathic ankle fracture is much higher risk for complications, and so it should be treated differently. If a patient knows they have neuropathy, that should be brought up before surgery, says Highlander.
Don’t Miss: How To Donate To Parkinson’s Research
The Peripheral Nervous System And Parkinsons Disease
It is well-established that the autonomic nervous system can be significantly affected in PD causing symptoms such as constipation, urinary dysfunction and orthostatic hypotension. The autonomic nerves that bring signals to the gut for example, can be directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration.
What remains unclear is if motor and sensory nerves are also affected in PD.
Small Fibre Neuropathy In Parkinsons Disease: Comparison Of Skin Biopsies From The More Affected And Less Affected Sides
Article type: Short Communication
Authors: Jeziorska, Mariaa | Atkinson, Andrewa | Kass-Iliyya, Lewisb c | Kobylecki, Christopherb c | Gosal, Davidb | a | Malik, Rayaz A.a d | Silverdale, Montyb c *
Affiliations: Division of Cardiovascular Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK | Department of Neurology, Manchester Centre for Clinical Neurosciences, Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust, Salford, UK | Division of Neuroscience and Experimental Psychology, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK | Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar, Doha, Qatar
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Monty A. Silverdale, PhD, Department of Neurology, Manchester Centre for Clinical Neurosciences, Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust, Salford, UK. Tel.: +44 1612062574 E-mail: .
Keywords: Parkinsons disease, peripheral neuropathy, intraepidermal nerve fibre
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-191697
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 761-765, 2019
Abstract
The study was approved by NRES committee/North West .
Thirty-three patients fulfilling the UK Brain Bank criteria for the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease were recruited from neurology clinics. Ten patients were excluded after screening for other causes of peripheral neuropathy . Unified Parkinsons disease Rating Scale-III was used to determine the more affected and the less affected side. Specifically, parts 38 and parts 1517 were compared.
Fig.1
Table 1
Read Also: Life Expectancy With Parkinson Disease
What Does This Mean
Rajabally and Martey found that people with PD were more likely to have a polyneuropathy than people with other neurologic illnesses. There was a relationship between low vitamin B12 levels and the presence of the nerve problem. There also seemed to be a relationship between the duration of PD and the neuropathy. However, they did not find a clear link between the duration of treatment with levodopa and the occurrence of the neuropathy. Because of this, they were unable to conclusively prove that levodopa causes a polyneuropathy. However, their findings are very important because they showed that more people with PD have polyneuropathy and low vitamin B12 levels. This suggests that doctors need to check vitamin B12 levels in each person with PD.
Clinical And Demographic Features
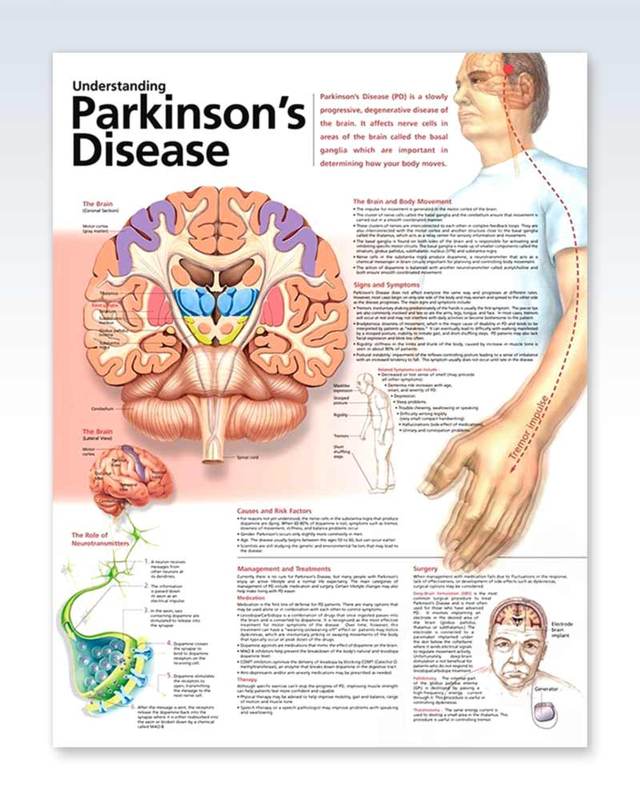
Table compares the demographic characteristics of the 38 patients with PD and 16 patients with other forms of parkinsonism that completed our work-up. Patients with PD were older than patients with parkinsonism . However, age of onset, disease duration and gender distribution were similar in both groups, despite a trend for higher percentage of women in the parkinsonism group and for older age of onset and longer disease course in the PD group. Mean Hoehn and Yahr scores in the PD group were 2.6±0.1 . Most of the PD patients were treated with levodopa and 68.8 % of the parkinsonism group were taking levodopa. A third of the PD patients and 31 % of the parkinsonism group were treated with pramipexol while 38.9 % of the PD and none from the parkinsonism group were treated with amantadine and only 8.3 and 18.8 were treated with biperiden.
Table 1 Demographic characteristics and risk factors for neuropathy in patients with Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonism
Read Also: Can You Die From Parkinson\’s Disease
Peripheral Neuropathy And Parkinsons Disease
A number of studies have tried to determine if PN is more common among people with PD as opposed to people without PD. PN is a relatively common condition in the general population, which makes it difficult to ascertain whether or not it is even more common among people with PD.
The available studies have varying results and are difficult to compare with each other as they:
- Include different types of populations of people with PD
- Assess peripheral neuropathy differently
- Assess for causes of peripheral neuropathy differently
A recent review looked at all the available data and determined that large fiber neuropathy was present in 16% of patients with PD, about double the prevalence of this condition in the general population. Skin biopsy-proven small fiber neuropathy was present in over 50% of people with PD, although this result was based on a small sample of patients.
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition in which there is damage to peripheral nerves. Symptoms depend on which type of nerves are affected and can result in:
- Weakness
- Numbness
- Pain or paresthesias in the limbs
The legs are more commonly affected than the arms because the nerves to the legs are longer than the arms and therefore more prone to damage.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Favorite Resources For Online Support
If you’re active on social media, stop by the Our Neuropathy Friends Facebook page and join the discussion. Comprising more than 4,000 members, this website is an excellent place to connect with people who understand your situation firsthand. Ask questions, share tips, or relate your personal experiences.
Youve come to the right place if you need help finding a support group for neuropathy. This site provides information about online and local support groups in your area, and you can read articles on neuropathy and get information on clinical trials.
Clinical And Demographic Data Of Pnp Subgroups
Fifty PD patients were included into the analysis with a mean disease duration of 6.5 ± 5.1 years, mean levodopa dosage of 590 ± 391, and mean MDS-UPDRS III of 31.2 ± 16.6. Of the 50 patients, 31 patients fulfilled the electrodiagnostic criteria for PNP. Fourteen patients had a mild, sensory PNP, 11 patients had a moderate, sensorimotor PNP. Six patients had a severe, sensorimotor PNP.
Importantly, concerning PNP subgroups, there were no statistically significant differences between sexes, age of onset or for LED observed .
| Total PD patients | PD patients without PNP | PD patients with PNP | PD patients with mild/sensory PNP | PD patients with moderate/sensorimotor PNP | PD patients with severe/sensorimotor PNP | Healthy controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age at evaluation ± SD | 67.8 ± 10.4 |
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Related Conditions And Causes Of Neuropathy
Following diabetes, idiopathic neuropathy, chemotherapy, and HIV/AIDS, other types of neuropathy make up the remaining 5 percent of cases, according to the Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy. These are caused by:
- Metabolic disorders such as hypoglycemia or kidney failure
- Certain nutrient deficiencies or excesses
Small Fiber Neuropathy In Early Parkinsons Disease
- Parkinsonism & Related Disorders
You’ve saved your first item
You can find your saved items on your dashboard, in the “saved” tab.
You’ve recommended your first item
Your recommendations help us improve our content suggestions for you and other PracticeUpdate members.
You’ve subscribed to your first topic alert
What does that mean?
Read Also: Parkinson\’s Plus Syndrome Life Expectancy
Black And Hispanic People And Neuropathy
Determining which racial and ethnic groups experience neuropathy the most may be complicated by the type of neuropathy, as well as the differing ways that people communicate their pain to others, including their healthcare providers.
The FDA reports that American Indians/Alaska natives , Hispanics , Black people and Asian Americans have higher rates of diabetes than white people .
Yet in a December 2017 study of more than 1,900 people who had painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy symptoms, which was published in Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology, Black and Hispanic participants were less likely than white participants to rate their pain as moderate or severe. Also, significantly fewer Black and Hispanic individuals reported having received a painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy diagnosis. However, higher proportions of those who were Black and Hispanic reported difficulty communicating with their healthcare provider about their pain symptoms, and feeling less comfortable about doing it. They were also younger, on average, than white participants. Researchers said more research in diverse populations is needed to understand the disparities.
However, a November 2015 study published in Clinical Cancer Research found that women of African descent being treated for breast cancer with specific chemotherapy drugs known as taxanes were more likely to report painful neuropathy symptoms than women of European descent.
