What Is Parkinsons And What Makes You Think I Have It
Parkinsons is a progressive neurological disorder and is considered to be one of the most common neurological conditions.
Every case of Parkinsons is different and not everyone will experience the same symptoms. For example, not all people develop tremor and for some, rigidity is the major symptom. With modern medication, symptoms can be well controlled.
Our movements are controlled by nerve cells in the brain which pass messages to one another, and to the rest of the body, using chemicals called neurotransmitters. An area of the brain called the substantia nigra produces one of the neurotransmitters that controls movement: dopamine. In people with Parkinsons, 70-80% of dopamine-producing cells gradually deteriorate and are lost this is called neurodegeneration. Cell death occurs naturally with ageing, but in Parkinsons the process is much faster.
The loss of dopamine-producing neurons results in low levels of dopamine in the part of the brain that controls movement and balance. When nerve cells do not pass on brain messages properly due to a lack of dopamine, movement is no longer controlled smoothly and the symptoms of Parkinsons appear. The most common symptoms are tremor, stiffness and slowness of movement.
Difficulties that are not related to movement can also occur, such as pain, sleep disturbance and depression. These are known as non-motor symptoms.
You May Like: Caring For Someone With Parkinsons
Longitudinal Gray Matter Volume Analysis
Structural MRI data were processed using the computational anatomy toolbox and SPM 12. For each participant, T1 images from each of the four time points were first registered and bias-corrected using serial longitudinal registration in SPM 12. In this process each time point is reoriented, spatially warped, and intensity biased corrected relative to the average T1 image, resulting in four jacobian difference maps representing the extent to which voxels from each time point image expand or compress in relation to the average T1 image. Individuals average T1 images were then segmented into gray and white matter and cerebral spinal fluid using CAT12.
A group level multiple regression model was conducted in which baseline indexes for AR and tremor symptoms were used to predict gray matter changes , while age, LED at the final time point, scanner site, gender, and total intracranial volume at baseline were included in these models to control for confounding factors. Previous studies have shown that the corrected voxel peak threshold of p< 0.05, based on the Gaussian random field theory, may be too restrictive, and suggested the use of a cluster threshold,. Unless otherwise noted, we present results that satisfy both an uncorrected threshold of p< 0.001 at the voxel level and a false discovery rate of p< 0.05 at the cluster level to correct for Type I error.
Pathophysiology Of Motor Dysfunction In Parkinsons Disease As The Rationale For Drug Treatment And Rehabilitation
Stefano Tamburin
1Department of Neurosciences, Biomedicine and Movement Sciences, University of Verona, Piazzale Scuro 10, 37134 Verona, Italy
2Neuromotor and Cognitive Rehabilitation Research Centre, University of Verona, Piazzale Scuro 10, 37134 Verona, Italy
3Rehabilitation Unit, Pederzoli Hospital, Via Monte Baldo 24, 37019 Peschiera del Garda, Italy
4Neurology Unit, Pederzoli Hospital, Via Monte Baldo 24, 37019 Peschiera del Garda, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimers disease , with an overall prevalence of 300 per 100,000 that rises from 41 in the 4049 years age range to 1903 in people older than age of 80 years .
This review will summarize the evidence on the pathophysiology of PD motor symptoms and signs and give some insight into their neuropathological and neuropharmacological bases. These pieces of information may help the clinicians to better understand the rationale of current pharmacological and rehabilitation strategies for PD and encompass the large areas of uncertainty that should represent the focus for further studies.
2. The Functional Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Basal Ganglia and the Role of the Cerebellum
3. The Neuropathology of PD
4. The Neuropharmacology of PD
| Neurotransmitter |
5. Pathophysiology of Bradykinesia in PD
6. Pathophysiology of Tremor in PD
7. Pathophysiology of Rigidity in PD
8. Pathophysiology of Motor Fluctuations and Dyskinesia
Read Also: Parkinsons Prognosis
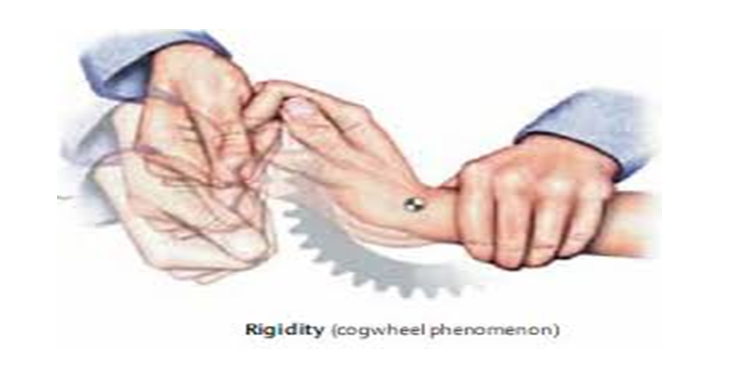
Clinical Diagnosis Of Rigidity
A doctor will test for rigidity by flexing and extending the patients relaxed wrist and elbow joint, and look for sustained rigidity or intermittent rigidity if tremors are associated with it.
Clinically, Parkinsons rigidity is characterized by increased muscle tone during examination using passive movement of the affected body parts. Parkinsons rigidity is more marked in flexor muscles than extensor muscles . Rigidity may be enhanced by voluntary movement of other body parts and is more pronounced during slow stretching rather than fast stretching. These features help to differentiate Parkinsons rigidity from spasticity, which becomes worse during fast movements.
Mold Growth Might Cause Parkinsons
Just down the road at Rutgers University, a recent study has concluded that mold growth may cause similar symptoms as Parkinsons disease. The findings were recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and how this team of researchers got to this conclusion regarding these shocking mold side effects is a fascinating story, and one that starts very close to home for the team leader, Joan Bennett.
Joan Bennett is Rutgers own resident fungus expert. Being a skeptic of sick building syndrome, which has been one of the main causes in the rise in mold inspections and mold remediation, she never fully supported the idea that the air inside of the places that we dwell can make us sick. Well, she was proved wrong.
Owning a home in New Orleans, she definitely experienced one of the leading causes of severe in-home mold growth when Hurricane Katrina cause her home to flood in 2005. She did what any biologist would do, and decided to take samples of the growth in her home so she could study them in her temporary home, New Jersey. While she was collecting these samples, she noticed that she felt ill, experiencing nausea, dizziness, and headaches despite the fact that she was wearing a face mask and protective gear. This experience led to the new research discovery.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Ribbon
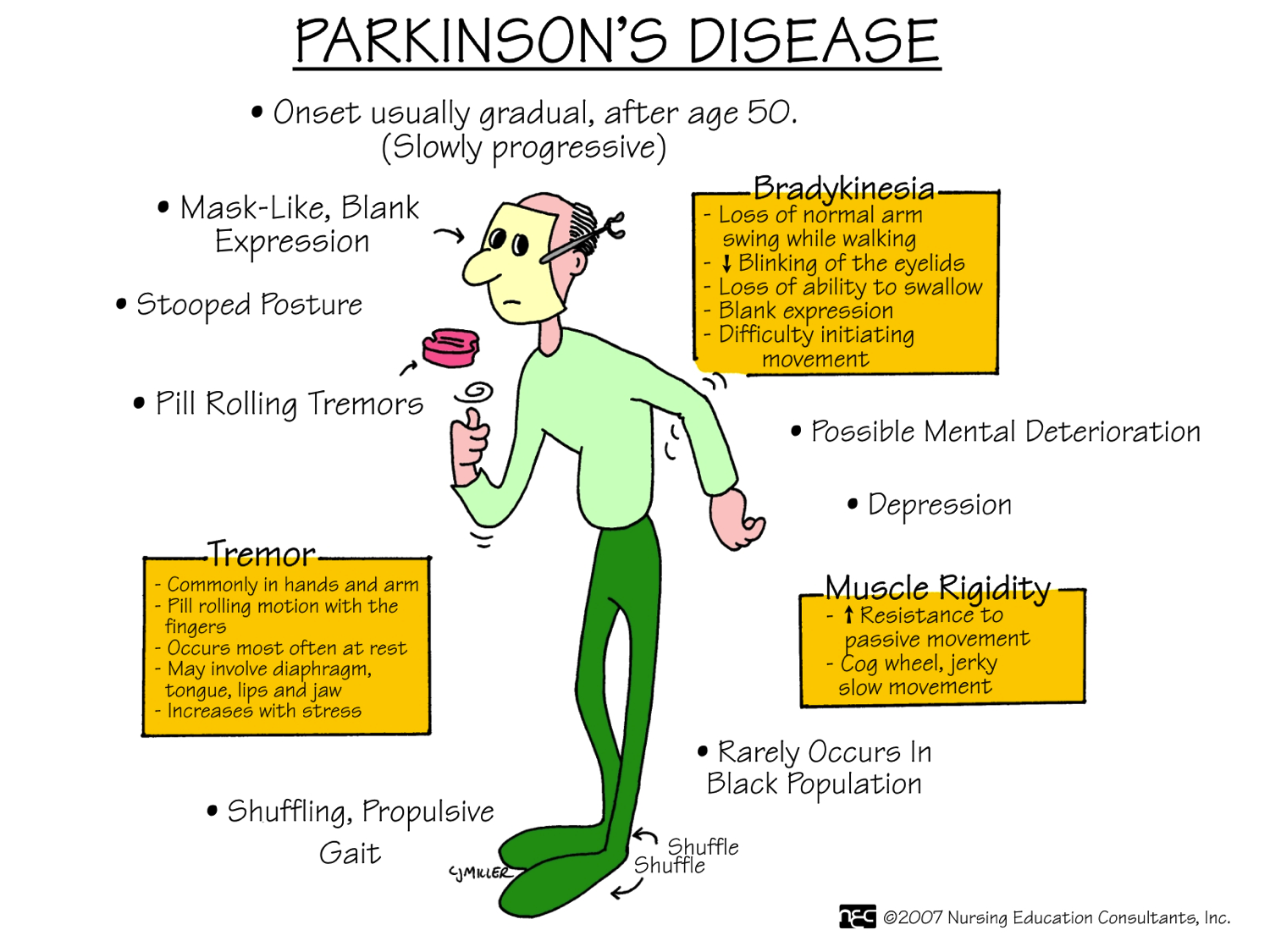
What Are The Primary Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
There are four primary motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease: tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability . Observing two or more of these symptoms is the main way that physicians diagnose Parkinsons.
It is important to know that not all of these symptoms must be present for a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease to be considered. In fact, younger people may only notice one or two of these motor symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. Not everyone with Parkinsons disease has a tremor, nor is a tremor proof of Parkinsons. If you suspect Parkinsons, see a neurologist or movement disorders specialist.
Tremors
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Postural Instability
Walking or Gait Difficulties
Dystonia
Vocal Symptoms
Functional Image Data Preprocessing
Standard image preprocessing was performed using Statistical Parametric Mapping . For each individual, functional images were corrected for slice timing and then realigned to the first image to correct for head motion between scans, while structural image was coregistered to the mean functional image. The structural image was then segmented and normalized to a template based on a sample of individuals with PD using affine registration followed by nonlinear transformation,. The resulting parameters were then applied to all functional images. Finally, the functional images were spatially smoothed with a Gaussian kernel of 6mm at full width at half maximum.
Also Check: How Long Does Parkinsons Take To Progress
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Also Check: Parkinson Disease Produces Dementia As Well As:
Functional Imaging Studies Of The Effect Of Surgery And Deep Brain Stimulation On Bradykinesia
Many imaging studies have been driven by the model of basal ganglia function outlined in the early 1990s. Overactivity of the inhibitory output projections from the basal ganglia to the thalamus in Parkinson’s disease was supposed to remove facilitatory thalamocortical drive, particularly to midline cortical motor areas . PET and fMRI activation studies had shown that these areas were less activated during movement in patients, and therefore pallidotomy was expected to improve activation by restoring normal levels of basal ganglia output .
Most studies on movement-related changes in metabolic activity have reported similar findings both after pallidotomy and during subthalamic nucleus stimulation . In tasks in which a free-choice joystick movement is used, increased activation of preSMA and anterior cingulate cortex is usually accompanied by increased activation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Although most reports of activation-induced metabolism suggest that there is no change in the primary motor cortex, there are some suggestions that stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus may reduce activity in the resting state . Whether this is related to a general reduction in rigidity or other involuntary muscle activity or to reduced input to the cortex via pathways direct from the subthalamic nucleus is not known.
Dysfunctional Protein Clearance Systems
There are two central protein clearance systems within cells responsible for the removal of dysfunctional proteins: the ubiquitin-proteasome system and the autophagy-lysosome pathway. The UPS is primarily responsible for breaking down abnormal proteins, and it does so by tagging them with ubiquitin and transporting them to the proteasome for degradation. The autophagy-lysosome pathway is divided into three constituents: macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy . Briefly, in macroautophagy, intracellular components, including cytosolic proteins, are engulfed by the autophagosome, which then fuses with the lysosome, leading to the breakdown of its contents. On the other hand, in microautophagy, the lysosome alone engulfs and destroys cytoplasmic components. CMA is a more selective process, whereby molecular chaperones target specific proteins and transport them to the lysosome for degradation . Monomeric -synuclein is generally cleared by both the UPS and the autophagy-lysosome pathway , and damage in either of their machineries is implicated in the pathogenesis of PD by contributing to the accumulation of defective proteins, in particular soluble misfolded -synuclein .
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Run In Families
What Causes Muscle Rigidity In Parkinson Disease
RigiditymusclessymptomsParkinson’sMuscles
Muscle rigidity is often triggered by stress. Stress can adversely affect your body’s nervous system â including your nerves â and how they function. Your nervous system may respond to stress by putting additional pressure on the blood vessels, which results in reduced blood flow to the muscles.
Beside above, is stiffness a sign of Parkinson’s? Rigidity Stiffness can occur on one or both sides of the body and contribute to a decreased range of motion. Rigidity is one of three telltale symptoms that help doctors make a Parkinson’s diagnosis. The other two are slowness of movement and tremor.
how is Parkinson’s rigidity treated?
Initial therapy is usually levodopa , dopamine agonists, and/or monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors. The combination of levodopa and carbidopa is the most effective treatment available for the management of motor symptoms of PD, including rigidity.
Does Parkinson’s cause muscle wasting?
Causes of fatigue in Parkinson’s diseaseMany of the symptoms of PD, including slow movement, muscle stiffness, depression, and changes to sleep quality can cause or worsen the symptom of fatigue. In addition, some people with PD experience muscle atrophy, in which the muscles shrink and weaken due to lack of use.
Make Commercial Breaks Movement Breaks
If youre watching TV, stand up and march while you swing your arms during the commercials. To increase your muscular strength, lift soup cans or a do a few downward dogs.
Moving more every day is easier said than done. Remember, even small changes can make a big difference. Pat yourself on the back for all of the movement activities you do each day. Every victory counts!
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Mold Health Impact : Bipolar And Schizophrenic Tendencies
Glutamate is an amino acid found throughout every part of the body. In the nervous system, however, glutamate is used as a neurotransmitter. When patients are exposed to extreme levels of mold toxins, glutamate levels rise dramatically, causing patients to exhibit bipolar and schizophrenic tendencies. The sad reality is that most psychiatrists will not link their behavior to a mold toxicity issue leaving thousands of patients misdiagnosed. In fact, if a patient whose bipolar tendencies are a result of mold toxicity is prescribed bipolar medication, the result wont be a normalization of mood. Instead, it will result in a feeling of emotional numbness or detachment. Fortunately, when Dr. Sponaugle identifies mold toxicity in a patient who exhibits bipolar tendencies, he can utilize intravenous toxin removal to help resolve these symptoms.
Also Check: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinson
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Were The Basic Results
Exposing wild Drosophila flies to low dose 1-octen-3-ol caused movement problems within the first 24 hours and 50% to die by 16.9 days. The control group all survived for at least 27 days, by which time the entire 1-octen-3-ol group had died.
In the second part of the study, exposure to 1-octen-3-ol reduced the number of all types of dopamine nerves except for one. This caused a reduction in dopamine levels of 28% compared to flies that were not exposed. It also increased the level of the waste product of dopamine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid by 40%.
In the human embryonic kidney cells, very low levels of 1-octen-3-ol did not have an effect, whereas low and higher levels caused a difficulty in transporting dopamine into the cells.
They found that overexpression of a different genetic neurotransporter cell in flies brains was protective against the effects of 1-octen-3-ol.
Bradykinesia And Other Basal Ganglia Diseases
In Parkinson’s disease, slowness of movement occurs in conjunction with a reduction in the amount of spontaneous movement . However, in two other basal ganglia diseases, Huntington’s disease and dystonia, bradykinesia co-exists with hyperkinesia. One conclusion from this is that bradykinesia has a different mechanism from hypo- or hyperkinesia. However, analysis of the nature of the bradykinesia indicates that even this one symptom may have more than one cause. The maximum speed of simple voluntary arm movement is slower than in healthy subjects in patients with either Huntington’s disease or dystonia , but the pattern of EMG activity underlying the slowness of movement in patients with either of these conditions differs from that in patients with Parkinson’s disease. In Huntington’s disease and dystonia, the EMG bursts are often prolonged and the final position and peak velocity are more variable than in Parkinson’s disease.
Patients with Huntington’s disease are also abnormal in executing simultaneous and sequential movements and, like patients with Parkinson’s disease, have difficulty in performing a sequence of movements without external cues .
Read Also: Can Essential Tremor Turn Into Parkinson’s
