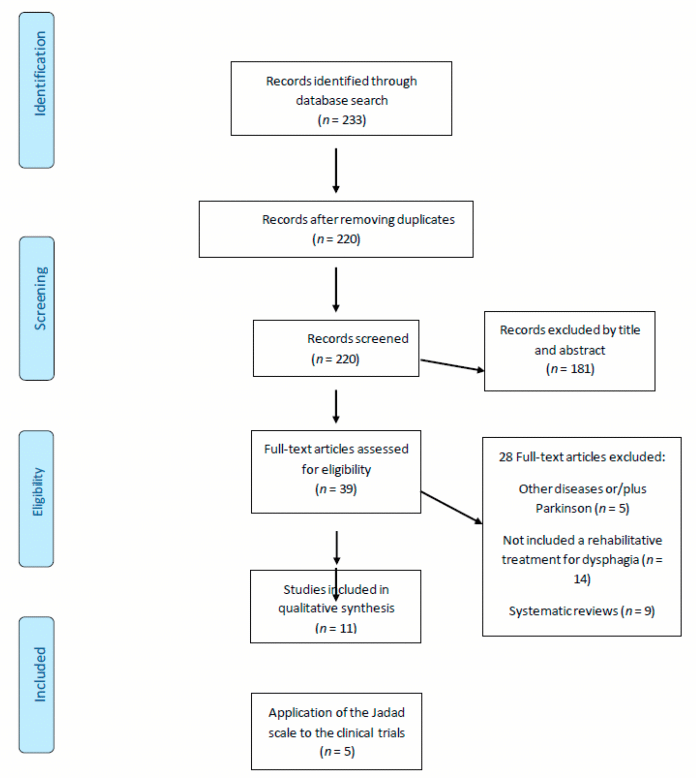
Data Collection And Analysis
The authors independently assessed the studies identified by the search strategy. Disagreements about inclusions were resolved by discussion.
All authors of eligible studies were contacted for further unpublished details of their trials. The full papers were assessed for methodological quality by recording a number of items that could either introduce bias or could affect the assessment of the data presented in the study. This included the method of randomisation and blinding, whether an intentiontotreat analysis was used and the number of patients lost to follow up.
Eligible data was abstracted by two of the authors onto standardised forms independently, checked for accuracy and amalgamated. Disagreements about inclusions were resolved by discussion.
Investment To Reclaim Your Health
Our program has specific guideline requirements to become a patient. If your case qualifies, we provide you with two options, our BEST recommendation and a second GOOD option. Our BEST recommendation is the most thorough option available at uncovering hidden past causes and providing future health direction based on your consultation, examination results, diagnostic tests, records review, biomedicine questionnaire, and health history forms. Each plan is customized and based on your unique requirements in our personalized Neurobiomedicine plans. Although we do not guarantee results, we expect results for every patient in our office.
Pathophysiology And Contributing Factors
As for dysphagia, the underlying pathophysiology of gastroparesis in PD is not fully understood but is likely to be multifactorial . Other comorbid conditions, such as diabetes, may also play a role in the development of gastroparesis in PD. It may also be due in part to Lewy body pathology in the vagus nerve, which plays a central role in the neural control of gastric emptying, and in the wider ENS, as well as alpha-synuclein deposition in the brainstem . One study in 16 patients with PD and 15 healthy controls demonstrated that delayed gastric emptying in patients with PD does not appear to be due to any functional deficits of the interstitial cells of Cajal, the pacemaker cells that cause contractions of the gastric smooth muscle .
While not a cause of gastroparesis per se, several classes of medication, including anticholinergics and some dopaminergic PD medications, may contribute to a delay in gastric emptying . The direct positive and negative effects of dopaminergic PD medications on GI function have been evaluated in a range of animal and clinical studies. Different dopaminergic medications are prescribed in PD specifically to improve motor function and reduce OFF time and are therefore hypothesized to improve GI motility . On the other hand, dopaminergic medications have been shown to alter the gut microbiota, associated with the development of GI symptoms, resulting in slowed GI transit .
Don’t Miss: Do Boxers Get Parkinson’s Disease
How Do I Know If I Have A Speech Or Voice Problem
- My voice makes it difficult for people to hear me.
- People have difficulty understanding me in a noisy room.
- My voice issues limit my personal and social life.
- I feel left out of conversations because of my voice.
- I cannot participate in telephone calls because of my voice.
- My voice problem causes me to lose income.
- I have to strain to project my voice.
- My voice clarity is unpredictable.
- My voice problem upsets me.
- My voice makes me feel handicapped.
- People ask, “What’s wrong with your voice?”
Motors Aspects Of Dysphagia In Parkinsons Disease
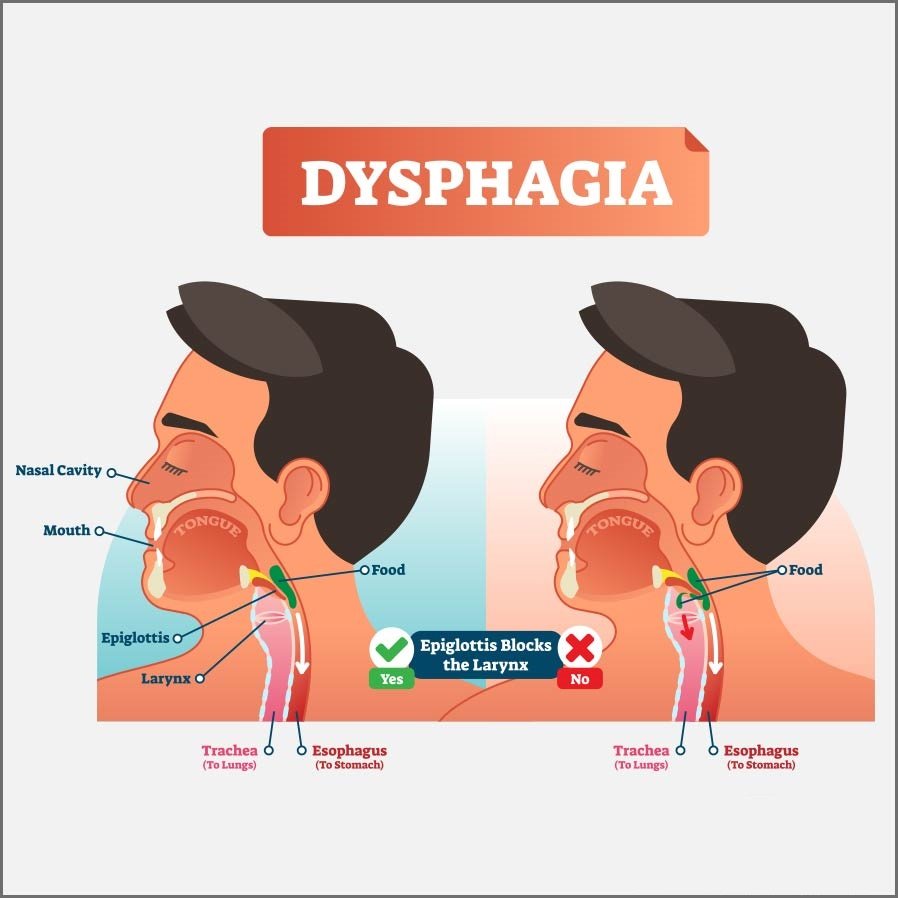
The dysphagia in PD is often associated with oral phases of swallowing because of the difficulty of bolus propulsion and tongue manipulation, slowness to initiate oral manipulation, presence of drooling and premature spillage, and presence of oral residue. Even in pharyngeal stage of swallowing abnormalities were found, such as, reduction in lower airway closure, delay in the initiation of pharyngeal phase of swallowing, residue in the valleculae or pyriform sinuses and on the aryepiglotic folds or posterior pharyngeal wall, reduction of the upward and forward motion of the hyoid that can results in abnormalities of upper esophageal sphincter opening.18 The rigidity, hypertonia, bradykinesia and involuntary movements can interfere in the motor control of swallowing, increasing the risk for penetration and laryngeal aspiration.
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Disease Always Fatal
Traditional Dysphagia Assessments And Therapies In Stroke
More than 50% of stroke survivors experience dysphagia however, most of them recover their swallowing function within a week . The proportion of stroke survivors with dysphagia at 6 months is reported to be approximately 11-13% . Constant awareness and review of swallowing are needed after stroke because of the diverse course of the symptoms over the six subsequent months. The assessment and management of dysphagia are important for minimizing the risk of food and liquid aspiration as well as pneumonia.
Screening for dysphagia includes the water-swallowing test and repetitive saliva-swallowing test. To assess the swallowing dysfunction in detail and detect silent aspiration, a video fluoroscopic swallowing study or fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing should be used. A VFSS provides information on bolus flow, the movement of each organ, and the anatomy . A FEES can be performed even at the bedside and is able to detect silent saliva aspiration.
Qualified Patient Results 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 :
- 85+ new contacts per month from people desperately trying to find answers to chronic health problems
- 1,000+ total new contacts per year
- 380+/- consultations with Dr. Farley per year
- 50% of cases qualify for our program
- 91% of patients feel better in 2-4 weeks
- 95% of patients have improved Super 7 Plus testing after 10-15 weeks of care
Don’t Miss: What’s The Difference Between Ms And Parkinson’s
Directions For Future Research
- 1.investigate the optimal time in the disease to initiate intervention for swallowing and to explore the impact of the natural evolution of dysphagia in patients with PD
- 2.evaluate the efficacy and adverse effects of compensatory treatment on clinical endpoints such are nutrition, hydration, respiratory complication, hospital readmission, QOL and mortality in patients with PD and dysphagia
- 3.compare the efficacy and complications of different swallowing treatments and to evaluate their effect on the progression of dysphagia in PD
- 4.evaluate the impact of nutritional intervention for dysphagia in patients with PD, including the impact of PEG placement on nutrition, respiratory complication, QOL and mortality.
The Top Symptoms That Our Patients Report Improving:
This entire process will be completed within 5-7 days maximum. We are extremely busy, and no time can be wasted. Step 2 will be scheduled 1 or 2 days maximum after Step 1. All 3 steps are completed within 7 days. Your spouse or significant other must attend all 3 steps with you. If your case qualifies and you can personally make all decisions on treatment plans, payments, etc., then you can move on to Step 2 and 3 alone. We understand that not everyone may be on the same thought process.
Go to www.drjamesfarley.com for many testimonials.
If you follow our guidelines, we expect positive results for you!
Existing Patients Additional Services Only30 Minutes Phone Consultation $425.00For outside Labatory Blood-work Review- 30 Minutes Phone Consultation, with Interpretation, Report and Educational Video $640.00
You May Like: What Causes Dizziness In Parkinson’s
Who Are We Who Sees Your Information
We are an independent, venture-capital backed startup based in San Francisco, working hard on a mission we love. All of the features on the site are designed with one goal in mind to connect you with others who have been in your shoes. Today with millions of members, millions of conversations, and a presence in eight countries, MyHealthTeam has become the fastest growing and most engaging set of social networks for web and mobile apps in healthcare.
MyParkinsonsTeam should not only provide you emotional support through the social network, but also be a resource for practical tips, personal experiences, and even referrals to other great doctors from the community. Information shared on the site can be seen by everyone who signs up for an account. You can share as much or as little as you like.
If you ever have any concerns or questions, we can always be reached at support@myparkinsonsteam.com.
Dr Farley Is The Leading Expert In Finding Which 30 Root Functional Causes Are Primary For You
My laboratory has never had anything but an extremely professional and proficient relationship with Dr. Farley and his staff. I believe that in the future more patients will seek care that is based on root functional causes rather than just managing symptoms.
Anyone who uses Dr. Farley today is getting insight, care and a dependable trusting doctor that should be the standard in doctoring across the United States and abroad.
I hope that patients can open their minds to understanding these concepts and not dismiss them because their doctor doesnt know about them. This healABILITY approach is an old and new evidence scientific based approach that frankly most doctors have absolutely no training in. Dr. Farleys office is run like a fine hotel that provides excellent customer service. So not only will you get exceptional care, but youll also be treated with a kind, warm and dependable staff. This book can aid anyone in getting insight into Dr. Farleys method of functional physiological based approach that has the potential to really help almost any condition. There are 30 key hidden root functional causes. Dr. Farley will help find which one of these 30 root functional causes are most important to correct for you to get well. Each person is unique in their physiology and biochemistry. Dr. Farley is the leading expert in finding which 30 root functional causes are primary for you.
Dr. Naveed Ashfaq MD emphasizes how powerful Dr. Farleys methods are and the impact they have.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Disease Run In Families
Prevalence Of Dysphagia In Parkinsons Disease
In the last 5years, the prevalence of dysphagia in Parkinsons disease has been reported with a wide range, from 11% to 100%.416 The procedures used to assess the presence of dysphagia and its severity it also differs in studies. All the data from the studies, here considered, reporting the prevalence of dysphagia in PD, can be found in the Table 1. The study of Aydogdu et al.,4 assessed the prevalence of dysphagia using the Video fluoroscopic Study of Swallowing and the United Kingdom Parkinsons Disease Brain Bank guidelines to diagnose Parkinsons disease. In that study, 23 patients were identified with PD and underwent VFSS evaluation, from the total sample, 16 patients were diagnosed with dysphagia. However, Han et al.,5 study, which observed the prevalence of dysphagia considering Hoehn and Yahr stages of PD, using a questionnaire to assess dysphagia, the Swallowing Disturbances Questionnaire in 127 patients diagnosed with PD, revealed in stage 1 the prevalence was of 14.3% in the stage 2 was of 16.7% in the stage 3 was of 33,3% in the stage 4 was of 50.0% and in the stage 5 the prevalence of dysphagia was in 100.0% of the patients.
|
Questionnaire |
32.0% had dysphagia |
Table 1 Prevalence of dysphagia in patients with Parkinson’s disease, considering publications of the last 5 years in PubMed database
Manage Swallowing Problems With Parkinsons

You can do many things to manage swallowing problems associated with Parkinsons. As the Parkinsons Foundation notes, the first step to treating dysphagia is telling your neurologist about the problem. They can refer you to a specialist, known as a speech-language pathologist , for treatment.
The SLP will begin by asking you about the swallowing difficulties youve been experiencing. They will evaluate your symptoms and medical history. In most cases, they will order a video X-ray or an endoscopy to see how your swallowing muscles are functioning as you eat and drink.
After identifying the cause of your swallowing problems, the SLP will recommend one or more approaches to help you start swallowing and drinking as normally as possible. Some interventions may work for some people but not for others. You may have to try several before you find one that improves your swallowing.
Read Also: What Are The Early Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Management Of Dysphagia In Patients With Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment of PD has traditionally been pharmacologic and was revolutionized by the discovery that levodopa is able to penetrate the blood–brain barrier and be converted to dopamine in the central nervous system. However, the effect of pharmacologic treatment on oral communication and swallowing is still controversial.
Drug treatment appears to have little effect on speech and swallowing disturbances compared with the major effect it has on motor symptoms in the trunk and limbs. In a study on voice and swallowing, when patients were asked about the effects of medication, all reported clear improvements in general physical symptoms, but only three out of twenty-four patients reported improvements in oral communication and swallowing symptoms. This suggests that both dysarthrophonia and dysphagia are related to dysfunction of nondopaminergic neuronal pathways .
Although the subject of much controversy in the past, the value of speech therapy has been confirmed in several objective studies . The effects of speech therapy on voice and swallowing were analyzed in a study, which showed that there was a 100% improvement in symptoms after therapy, particularly increased sphincteric action of the larynx .
Change How You Eat And Drink
There are a number of changes that you can make to how you eat and drink that may make swallowing easier. These include:
- Taking small sips of drinks and small bites of food
- Changing the thickness or texture of the foods you eat
- Eating and drinking when your medication is most effective, rather than right after you take it or when it wears off
- Sitting up as straight as possible when drinking and eating
- Reducing distractions, like conversations, during mealtimes
- Making sure you swallow saliva regularly to control excess saliva or drooling
- Focusing on keeping your mouth closed while eating and drinking
Read Also: Parkinson’s Awareness Day 2022
Compensatory And Therapeutic Swallowing Techniques
Compensatory strategies control the flow of food and help to eliminate symptoms, but do not alter the swallow physiology. Compensatory strategies used in the treatment of PD to be discussed include postural changes, increasing sensory input, and altering food consistencies. Eating while upright with the chin tucked to the chest or the head tilted forward at a 45 degree angle may be helpful for patients with a delay in triggering the pharyngeal swallow, reduced tongue base retraction, or reduced airway entrance closure or protection.43 Increasing sensory input may benefit patients who are delayed in triggering the pharyngeal swallow. Foods that help to increase sensory input include highly seasoned food, cold foods, sour foods, and possibly carbonated beverages. Altering food consistencies or elimination of consistencies from the diet should be explored only after other compensatory strategies have been examined.43 In general, thick viscous consistencies will be difficult for patients with PD to swallow who experience reduced tongue base retraction and pharyngeal contraction. Emphasizing foods that are moist and form a cohesive bolus has been suggested for patients with poor pharyngeal contraction, and blenderized food that requires minimal chewing may be necessary for patients with severe dysphagia.2 Similarly, thin liquids are typically the most difficult consistency for patients with reduced laryngeal closure.
Developing A Management Plan
Once a diagnosis of gastroparesis is confirmed, an appropriate management plan can be considered for the patient. Management of gastroparesis is focused on improving gastric emptying itself and methods to circumvent the inconsistency in drug absorption that may result from gastroparesis. A range of gastroparesis treatment guidelines are available to help guide therapeutic choices, although these have not been developed specifically for gastric motility issues arising in patients with PD . As a result, implementing clinical guidelines for gastroparesis in patients with PD is not that straightforward, as certain recommendations are not applicable in PD, for example the use of metoclopramide.
The management of gastroparesis in patients with PD, just as in the case of dysphagia, will ideally need a multidisciplinary approach with input from both the neurology/movement disorders team and gastroenterology colleagues . Management options for gastroparesis in patients with PD generally fall into three categories: dietary modifications, medical management, and physical/mechanical interventions.
Dietary modifications
Physical activity
Regular physical activity has been shown to have substantial overall benefits for patients with PD . However, studies in healthy subjects have shown that exercise can also be an important management tool for gastroparesis , so this is something that should be considered in the overall management of patients with PD who experience gastroparesis.
You May Like: Sudden Onset Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment And Therapy Options
If you are worried about dysphagia, a good first step is to speak with your neurologist. Your neurologist can recommend a speech-language pathologist . The SLP will examine you and recommend therapy or treatment options.1
An examination will likely include a questionnaire and imaging test. During the imaging test, the SLP will use a video X-ray or a small camera in your nose to watch you eat and drink. Your SLP may also give you a water swallowing test. In this test, your SLP determines how much water you can easily drink. These exams show your SLP where problems are happening and help them recommend options for you.2
There are different types of therapy your SLP may recommend. One method is the Lee Silverman Voice Technique . The LSVT was first designed as a therapy to help people with speaking difficulties from PD. However, the therapy can also help people swallow safely. The LSVT is a regular regimen that emphasizes exaggerated swallowing and speaking. This helps people practice swallowing hard, which can help move food down the throat.4,5
Another therapy option is called Expiratory Muscle Strength Training . This training focuses on strengthening the muscles that help you breathe. During EMST, your SLP may have you use a handheld tool. This tool trains and strengthens your breathing muscles, just like how someone might lift weights at the gym. Training these muscles also impacts swallowing and makes it safer and easier.6