Family History And Genetics
Approximately 15 percent to 25 percent of people with PD have a relative with the disease.5 People with a close family member with Parkinsons have a small increased risk of developing the disease. About 15 percent to 25 percent of people with PD have a known relative with the disease.5 A number of genetic mutations have been identified that are associated with PD. Some of these appear to be more causal, while others simply increase a persons risk for the disease.5
What Is Already Known About This Subject
-
According to an estimation, one million people have Parkinsons disease in Pakistan, and this number will increase up to 1,200,000 till 2030.
-
Both non-modifiable and modifiable risk factors such as occupation, exposure to pesticides, and depression have an association with PD.
-
PD is under research in Pakistan, and there is a need to identify the factors that increase the risk of PD.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
You May Like: How Is Parkinson Dementia Different From Alzheimer’s
Dopamine Dopamine Receptor And Dopamine Transporter Activity
A catecholamine neurotransmitter dopamine is secreted by the SN, hypothalamus and some other regions of the brain. TH synthesizes the dopamine precursor that is converted to dopamine by L-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase . In the brain, dopamine is used as the precursor of noradrenaline and adrenaline . Loss of dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain and SN of PD brains leads to the reduction of dopamine levels . The dopamine transporter controls dopamine levels by facilitating its reuptake back to the cytosol. However, free dopamine is toxic for neurons, since its oxidation creates poisonous reactive quinones. Therefore, the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 stores excess dopamine in vesicles. Thus, any change in dopamine or DAT levels may be an indicator of PD. Moreover, dopamine activates five types of receptors and the severity of PD is related to the decreased expression of the dopamine type 3 receptor , leading to more severe symptoms because of reduced dopamine signals . Therefore, D3R can be also considered as a potential biomarker for PD .
In another recent article a preclinical phase of PD is identified by analysis of dopamine metabolites in CSF. Low CSF concentrations of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and DOPA identify pre-clinical PD in at-risk healthy individuals .
Family History & Genetics
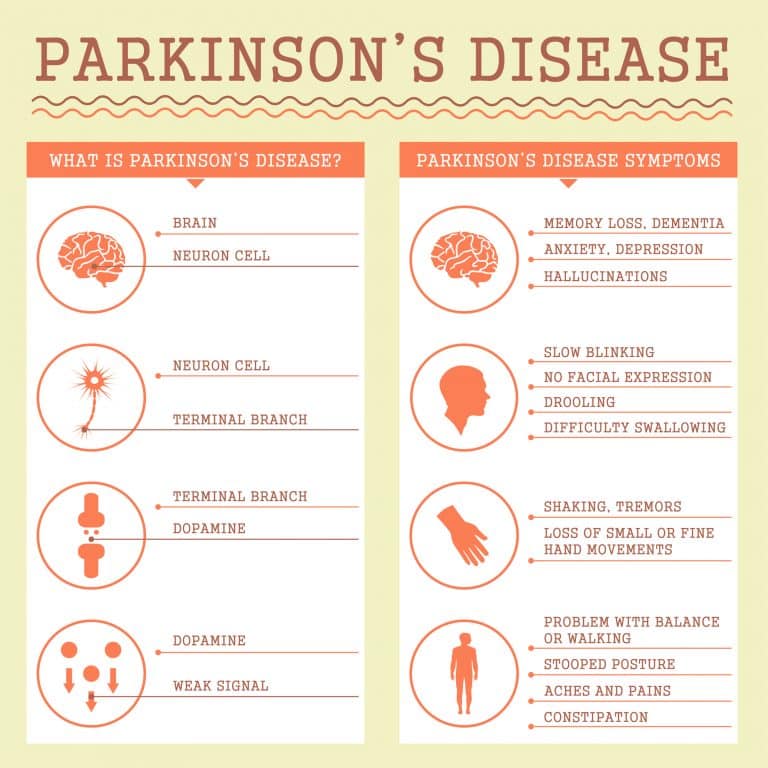
Researchers have been able to identify certain genetic mutations that can increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
These are the two types of Parkinsons disease, from a genetic standpoint:
- Hereditary Parkinsons disease: Roughly 15% of all cases of Parkinsons disease are inherited. In these cases, mutations in certain genes are passed down through families and increase the individuals risk of developing this condition.
- Sporadic Parkinsons disease: On the other hand, cases in which people dont have a family history of Parkinsons disease are referred to as sporadic cases. These cases are in fact the majority. Scientists have found that alterations in certain genes may also play a role in sporadic cases, in addition to other environmental and lifestyle-related factors.
However, the role that these genetic mutations play in the development of the condition hasnt been fully understood yet.
Don’t Miss: How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work In Parkinson’s Disease
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
/6symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
One of the early signs of Parkinsons disease are tremors. These usually begin in the limbs, hands or fingers. Parkinsons disease may also slow your movement, whether in walking or performing your everyday simple tasks. Muscle stiffness can happen in any part of the body, and can also be painful. You may experience decreased ability to perform unconscious movements like blinking, smiling or swinging your arms when walking. Your posture may become stooped and you may also experience problems in balancing your body. There can be changes in your speech as well.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Bike Riding
Literature Selection Data Extraction And Methodological Quality Assessment
Two review authors independently screened all of the citations for potentially eligible articles and extracted information from each included SR. Any conflicts were resolved through discussion, by referring to the original publication, or by consulting a third senior author.
The following information was extracted from each included SR: characteristics of the SR, including the first authors name, year of publication, and the number of included studies and participants characteristics of the original studies included in SRs, such as study design, the studied risk factor, methods used for exposure assessment, diagnostic criteria for PD, follow-up duration of cohort studies, and risk of bias details on participants characteristics, including age, sex, and region pooled effect estimation for each risk factor with the corresponding 95%confidence interval , and results from subgroup meta-analyses.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic, progressive neurological disease that currently affects about 1 million Americans. Parkinsons disease involves a small, dark-tinged portion of the brain called the substantia nigra. This is where you produce most of the dopamine your brain uses. Dopamine is the chemical messenger that transmits messages between nerves that control muscle movements as well as those involved in the brains pleasure and reward centers. As we age, its normal for cells in the substantia nigra to die. This process happens in most people at a very slow rate.
But for some people, the loss happens rapidly, which is the start of Parkinsons disease. When 50 to 60 percent of the cells are gone, you begin to see the symptoms of Parkinsons.
You May Like: How To Take Care Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Raises Someones Risk For Parkinsons
Its a complex picture, but you may be more likely to get Parkinsons based on:
Age. Since it mostly affects people 60 and older, your risk goes up as the years go by.
Family history. If your parent, brother, or sister has it, youre a little more likely to get it.
Job. Some types of work, like farming or factory jobs, can cause you to have contact with chemicals linked to Parkinsons.
Race. It shows up more often in white people than other groups.
Serious head injury. If you hit your head hard enough to lose consciousness or forget things as a result of it, you may be more likely to get Parkinsons later in life.
Gender. Men get it more than women. Doctors arent sure why.
Where you live. People in rural areas seem to get it more often, which may be tied to chemicals used in farming.
What Else Causes Parkinsons
- exposure to toxins
- post-infectious encephalitis
Although doctors do not know exactly what causes Parkinsons disease, they do have a good idea of whats happening inside the brain when someone has the condition.
A part of the brain called the basal ganglia houses neurons that produce dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter responsible for many functions in the body, like the smooth movement of muscles.
In people with Parkinsons disease, dopamine-producing neurons die or become impaired in their function. As a result, there is less dopamine available in the brain.
Another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine may also be affected in people with Parkinsons disease. This is a neurotransmitter that controls heart rate, blood pressure, and other bodily functions.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson Tremors Be Controlled
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
What Causes The Condition
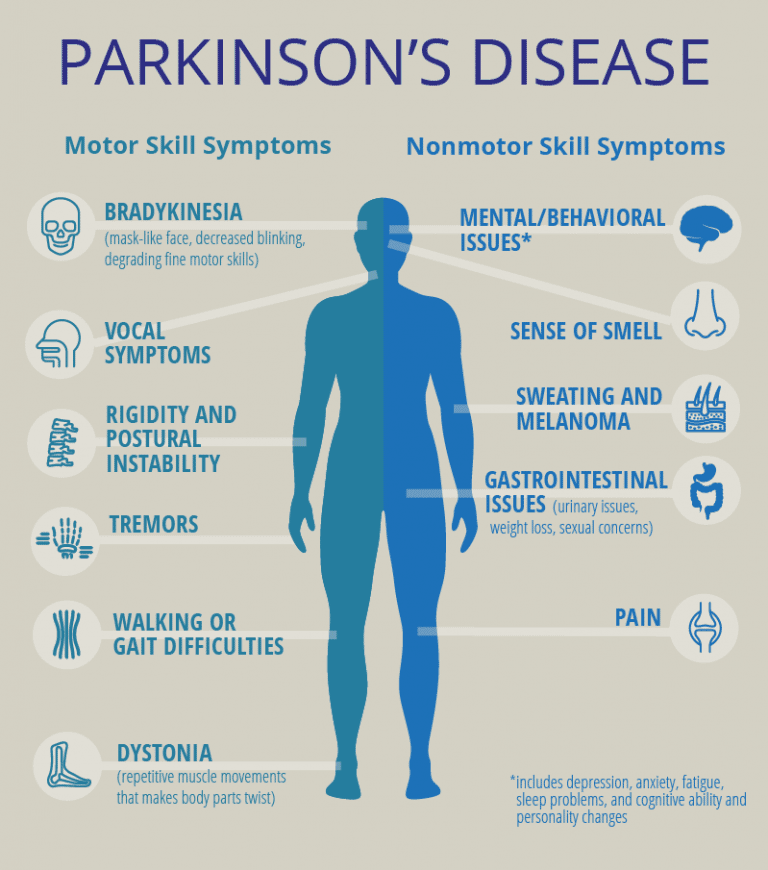
Although there are several recognized risk factors for Parkinsons disease, such as exposure to pesticides, for now, the only confirmed causes of Parkinsons disease are genetic. When Parkinsons disease isnt genetic, experts classify it as idiopathic . That means they dont know exactly why it happens.
Many conditions look like Parkinsons disease but are instead parkinsonism from a specific cause like some psychiatric medications.
Familial Parkinsons disease
Parkinsons disease can have a familial cause, which means you can inherit it from one or both of your parents. However, this only makes up about 10% of all cases.
Experts have linked at least seven different genes to Parkinsons disease. Theyve linked three of those to early-onset of the condition . Some genetic mutations also cause unique, distinguishing features.
Idiopathic Parkinsons disease
Experts believe idiopathic Parkinsons disease happens because of problems with how your body uses a protein called -synuclein . Proteins are chemical molecules that have a very specific shape. When some proteins dont have the correct shape a problem known as protein misfolding your body cant use them and cant break them down.
With nowhere to go, the proteins build up in various places or in certain cells . The buildup of these Lewy bodies causes toxic effects and cell damage.
Induced Parkinsonism
Recommended Reading: Medication For Parkinsons Psychosis
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Skip A Generation
Peripheral Proteasomes And Caspase Activity
Proteasomes are large protein complexes responsible for degrading and elimination of unwanted and misfolded proteins and therefore are important for cell survival. Damaged proteins that are tagged with ubiquitin molecules by ubiquitin ligase, trigger the ATP-dependent proteolytic activity of the proteasome . In PD, the accumulation of proteins within the neurons leads to the formation of pathological intracellular inclusions called LBs. Proteasome dysfunction may be involved in the formation of protein aggregates and associated with LBs . In PD mutations disturbing proteasome activity may lead to the accumulation of aggregated -syn . In some PD cases, mitochondrial deficiency causes the production of more ROS and higher -syn oxidation leading to increased ATP-independent proteasomal activity and higher -syn oligomerization. Depletion of ATP levels in this case inhibits 26S proteasome, but 20S complex still remains active and degrades oxidized -syn . In advanced PD, the severity and duration of PD correlate with reduced proteasome 20S activity and increased caspase 3 activity. The activation of caspase and thus initiation of apoptosis is the main reason of proteasome 20S activity reduction. Therefore, these proteasome and caspase components may be also considered as potential PD biomarkers .
Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Cured
No, Parkinson’s disease is not curable. However, it is treatable, and many treatments are highly effective. It might also be possible to delay the progress and more severe symptoms of the disease.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Parkinson’s disease is a very common condition, and it is more likely to happen to people as they get older. While Parkinson’s isn’t curable, there are many different ways to treat this condition. They include several different classes of medications, surgery to implant brain-stimulation devices and more. Thanks to advances in treatment and care, many can live for years or even decades with this condition and can adapt to or receive treatment for the effects and symptoms.
Also Check: Movie On Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms
The best-known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms
Motor symptoms which means movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease include the following:
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual. This is also a symptom of reduced control of facial muscles.
- Cramped or small handwriting. Known as micrographia, this happens because of muscle control problems.
- Drooling. Another symptom that happens because of loss of facial muscle control.
- Mask-like facial expression. Known as hypomimia, this means facial expressions change very little or not at all.
- Trouble swallowing . This happens with reduced throat muscle control. It increases the risk of problems like pneumonia or choking.
- Unusually soft speaking voice . This happens because of reduced muscle control in the throat and chest.
Non-motor symptoms
Several symptoms are possible that aren’t connected to movement and muscle control. In years past, experts believed non-motor symptoms were risk factors for this disease when seen before motor symptoms. However, theres a growing amount of evidence that these symptoms can appear in the earliest stages of the disease. That means these symptoms might be warning signs that start years or even decades before motor symptoms.
Non-motor symptoms include:
Stages of Parkinsons disease
Comparing Risk Factors Of Incident Pd And Coronary Events
With respect to the effects of the risk factors, the differences between PD and coronary events are shown in Table and Fig. . Smoking and LDL were positively associated with risk of coronary events but were inversely associated with risk of PD . Hypertension, lipid-lowering drugs, BMI, ApoB/ApoA1 ratio, and ApoB were positively associated with the risk of coronary events but were not associated with PD . In addition, ApoA1 was inversely associated with the risk of coronary events but was not associated with PD . By contrast, age, male sex, diabetes, NLR, and FBG were common risk factors for coronary events and PD .
Also Check: Physiotherapy For Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: What Age Does Parkinson’s Disease Usually Start
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Medicines For Parkinsons Disease
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists to stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors to increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Don’t Miss: Can Tbi Cause Parkinson’s
