Pathology Overlap Between Tbi And Pd
TBI sequalae can be divided in to 3 phases: acute , post-acute , and chronic . During the acute period cell necrosis from direct transfer of force to the brain tissue occurs, followed by secondary cell death from axonal pathology, and inflammation. The post-acute period can be characterized by neuronal remodeling, decreased inflammation, and an increase in chronic pathology . Chronic pathology of most interest here includes, neurodegeneration, protein misfolding , and persistent inflammation. Chronic TBI pathology can vary, with some patients recovering completely while others suffer physical and cognitive decline, and eventually develop neurodegenerative diseases , most notably Parkinsons Disease .
PD as well as TBI brains are characterized by neuronal degeneration, compromised blood brain barrier, infiltration and expansion of resident microglia into the affected areas, and infiltration of phagocytic cells from the periphery . In both PD and following a TBI this histological presentation is accompanied by inflammation, metabolic disturbances, and protein aggregation, making them essential factors to consider when studying the mechanisms connecting these two disorders.
Figure 1
Inflammation
Metabolism
Protein aggregation
Purpose Of Brain Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease surgery is used to treat motor effects of Parkinsons disease, such as tremor, but it does not help non-motor effects, such as reduced facial expression and dry skin.
Parkinsons disease can range from mild to severe, and it can be very disabling when the disease is severe. When high doses of medication are needed to control the symptoms, the medication can cause side effects such as dyskinesia , hallucinations, or both.
You might benefit from surgery if your symptoms do not improve adequately with medication or if you experience severe medication side effects.
What Causes The Disease
The precise cause of PD is unknown, although some cases of PD are hereditary and can be traced to specific genetic mutations. Most cases are sporadicthat is, the disease does not typically run in families. It is thought that PD likely results from a combination of genetics and exposure to one or more unknown environmental factors that trigger the disease.
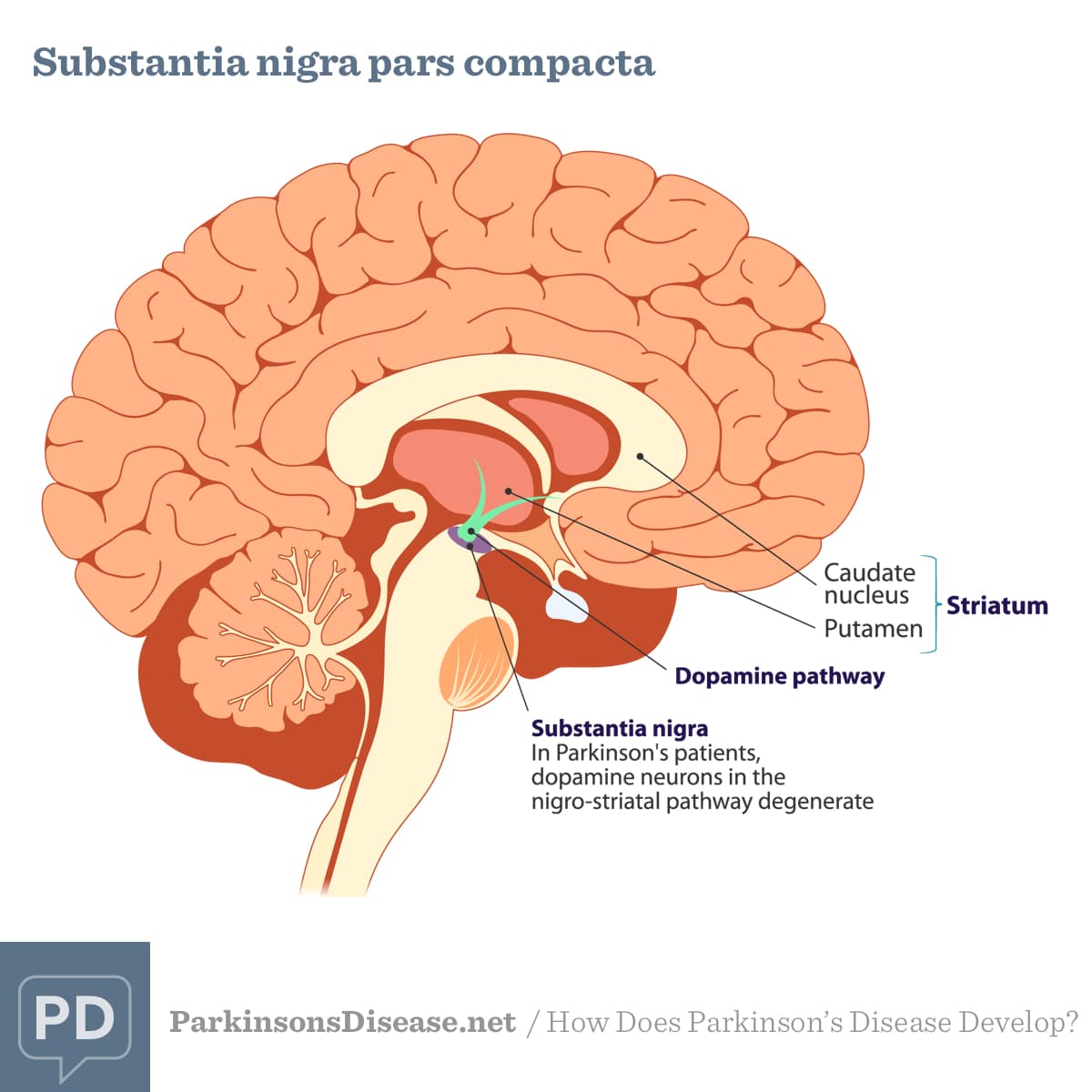
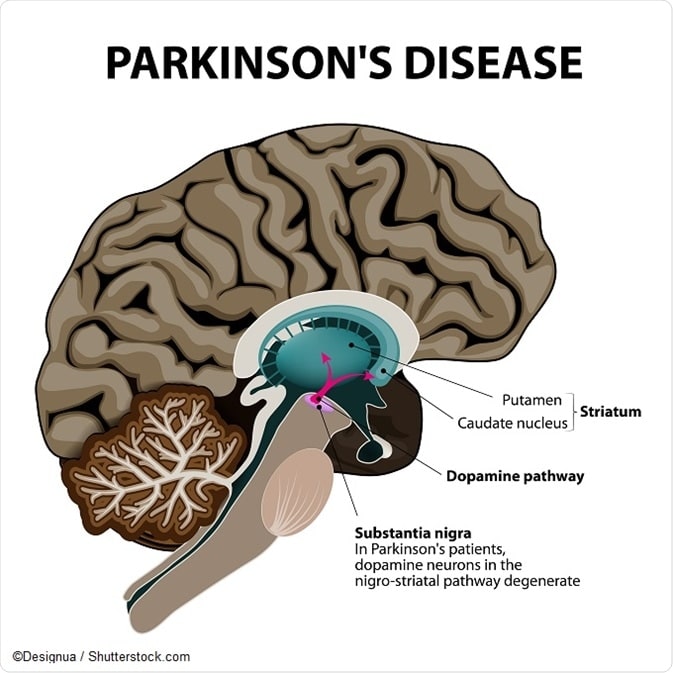
The protein alpha-synuclein. The affected brain cells of people with PD contain Lewy bodiesdeposits of the protein alpha-synuclein. Researchers do not yet know why Lewy bodies form or what role they play in the disease. Some research suggests that the cells protein disposal system may fail in people with PD, causing proteins to build up to harmful levels and trigger cell death. Additional studies have found evidence that clumps of protein that develop inside brain cells of people with PD may contribute to the death of neurons.
Genetics. Several genetic mutations are associated with PD, including the alpha-synuclein gene, and many more genes have been tentatively linked to the disorder. The same genes and proteins that are altered in inherited cases may also be altered in sporadic cases by environmental toxins or other factors.
Environment. Exposure to certain toxins has caused parkinsonian symptoms in rare circumstances . Other still-unidentified environmental factors may also cause PD in genetically susceptible individuals.
Also Check: Tips For Parkinson’s Patients
Support For People Living With Parkinsons Disease
While the progression of Parkinsons is usually slow, eventually a persons daily routines may be affected. Activities such as working, taking care of a home, and participating in social activities with friends may become challenging. Experiencing these changes can be difficult, but support groups can help people cope. These groups can provide information, advice, and connections to resources for those living with Parkinsons disease, their families, and caregivers. The organizations listed below can help people find local support groups and other resources in their communities.
How Will The Disease Affect My Life
Most people who have Parkinsonâs live a normal to a nearly normal lifespan, but the disease can be life changing.
For some people, treatment keeps the symptoms at bay, and theyre mostly mild. For others, the disease is much more serious and really limits what youre able to do.
As it gets worse, it makes it harder and harder to do daily activities like getting out of bed, driving, or going to work. Even writing can seem like a tough task. And in later stages, it can cause dementia.
Even though Parkinsons can have a big impact on your life, with the right treatment and help from your health care team, you can still enjoy the things you love. Its important to reach out to family and friends for support. Learning to live with Parkinsons means making sure you get the backing you need.
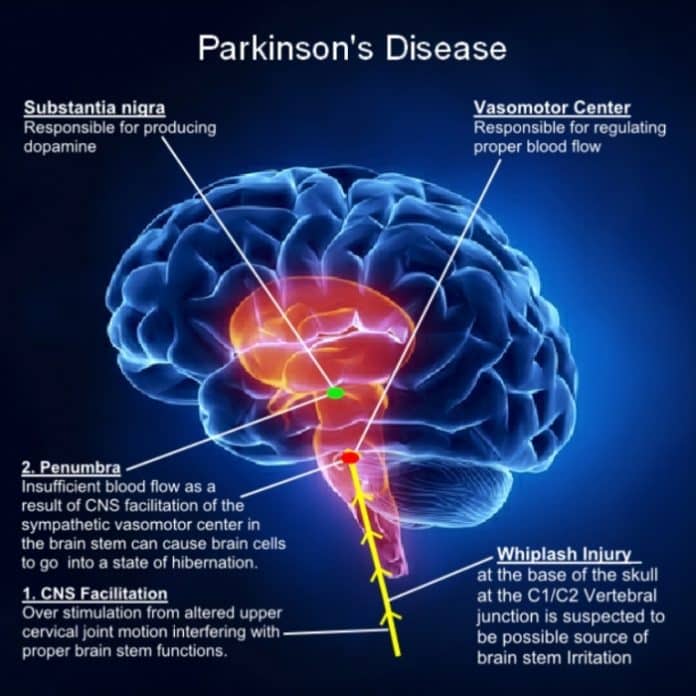
Location of the substantia nigra. FrozenManCC BY-SA 4.0
The substantia nigra is an area of the mid brain located at the top of the spinal cord, which has been the focus of much work into how Parkinsons affects the brain.
There are a right and a left substantia nigra, and often one side is affected before the other. Because of this, people with Parkinsons often experience symptoms primarily on one side of their body, particularly in the early stages. Indeed, this common feature of the condition often helps to distinguish Parkinsons from other similar conditions.
You can read more about the alpha-synuclein protein, and how it plays a role in the spread of Parkinsons, in a previous blog post:
Recommended Reading: Psychotherapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Establishing Pd Research Priorities
The NINDS-organized Parkinsons Disease 2014: Advancing Research, Improving Lives conference brought together researchers, clinicians, patients, caregivers, and nonprofit organizations to develop 31 prioritized recommendations for research on PD. These recommendations are being implemented through investigator-initiated grants and several NINDS programs. NINDS and the NIHs National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences held the Parkinsons Disease: Understanding the Environment and Gene Connection workshop to identify priorities for advancing research on environmental contributors to PD.
Research recommendations for Lewy Body Dementia, including Parkinsons disease dementia, were updated during the NIH Alzheimers Disease-Related Dementias Summit 2019 .
Related Diagnosis: Lewy Body Dementia
Current research is helping to differentiate dementia related conditions in relationship to Parkinsonâs disease. Doctorâs use a 12-month arbitrary rule to aid in diagnosis. When dementia is present before or within 1 year of Parkinsonâs motor symptoms developing, an individual is diagnosed with DLB. Those who have an existing diagnosis of Parkinsonâs for more than a year, and later develop dementia, are diagnosed with PDD.
In the simplest terms, Lewy bodies are abnormal clumps of proteins that develop in nerve cells. Cholinesterase inhibitors, medications originally developed for Alzheimerâs disease, are the standard treatment today for cognitive DLB and PDD symptoms. Early diagnosis is important, as DLB patients may respond differently than Alzheimerâs disease patients to certain drug, behavioral, and dementia care treatments.
This challenging, multi-system disorder involving movement, cognition, behavior, sleep, and autonomic function requires a comprehensive treatment approach to maximize the quality of life for both the care recipient and their caregiver. It is very important to pay attention to symptoms of dementia and to search for an expert clinician who can diagnose the condition accurately.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Diagnose Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, it’s called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. It’s also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesn’t go away and continues to get worse over time.
Locating The Basal Ganglia
|
The basal ganglia are collections of nerve cells located deep within the brain. They include the following:
The basal ganglia help initiate and smooth out muscle movements, suppress involuntary movements, and coordinate changes in posture. |
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
Structural Changes In The Cerebellum
With the deformation-based morphometry method, revealed significant contraction in the left cerebellum in patients with early-stage Parkinsons disease compared with control subjects. Using the voxel-based morphometry method, found that in patients with mild-to-moderate Parkinsons disease with and without resting tremor, grey matter volume is decreased in the right quadrangular lobe and declive of the cerebellum in Parkinsons disease with tremor compared with those without. Other studies also found cognitive- or olfactory-related structural changes in the cerebellum in patients with Parkinsons disease. Therefore, there are specific Parkinsons diseaserelated morphological changes in the cerebellum.
Brain Sculptures By Leading Artists To Be Auctioned For Parkinsons Uk
Works by Tracey Emin, David Bailey and others, reflecting on what their brain means to them, set to sell for thousands
Brain sculptures created by leading artists including Tracey Emin and David Bailey are expected to raise thousands of pounds for research into Parkinsons disease when they are auctioned on Wednesday.
Fifteen works have been created for the charity auction, Me, My Brain and I, by artists including Gavin Turk, who were asked to reflect what their brain means to them. Some of the artists have been affected by Parkinsons.
The sculptures are estimated to sell for between £2,000 and £20,000 each at the online auction at Christies in London, which is supported by the Auction Collective.
Alex Echo, an American-born abstract artist who has raised more than $1.2m for charity by selling his works, was diagnosed with Parkinsons in 2020 after experiencing symptoms for seven years.
He said he hoped Tremor, his multicoloured brain sculpture created with spray paint, would be a visual representation of what its like to live with Parkinsons. Its been difficult, but when Im doing art, time disappears. Parkinsons disappears. Worries disappear. Art saves my life every day and has for 42 years.
In an article for the Parkinsons UK magazine, Echo said his diagnosis came as a shock and led him to be full of self-pity.
But it had been wonderful to be introduced to the huge community of people who are battling something really quite debilitating.
Read Also: Tardive Dyskinesia Vs Parkinson’s
The Symptoms That Dbs Treats
Deep brain stimulation is used primarily to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but this can vary somewhat between the different placement sites. Symptoms treated include:
- Abnormal movements : Dyskinesias are often a side effect of medications for Parkinsons disease and include involuntary movements such as twisting, head bobbing, squirming, and more.
DBS is not usually helpful with walking problems or balance, though improvements in the symptoms above can indirectly affect walking. It also does not provide significant benefits for non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as cognitive changes, mood changes , or problems with sleeping.
The benefits of DBS can be estimated by looking at how a person responds to levodopa. Symptoms that respond to levodopa will often respond to DBS . But symptoms that are not changed with levodopa are unlikely to be improved by DBS.
DBS often allows for a reduction in the dosage of levodopa, which in turn can result in fewer involuntary movements and a reduction in off time. The result is often improved quality of life.
G2019s Mutation Alters Striatal
In behaviorally naive young adult male wildtype and G2019S mice, the mutation alone, in the absence of any particular prior experience, is generally insufficient for altering motor coordination, anxiety, exploratory activity, self-care and anhedonia-like behaviors . Additionally, behaviorally naive G2019S mice exhibit social interaction behavior that is indistinguishable from wildtype mice . When multiple, independent cohorts of young adult male G2019S and wildtype mice were subjected to 10-day-SDS followed by a social interaction test, wildtype cohorts yielded expected ratios of socially interactive and socially avoidant subpopulations, while in contrast, G2019S mice were essentially all highly socially interactive despite 10-days of defeat experience . Additionally, such resilient G2019S mice exhibited less anhedonia-like behaviors compared to defeated wildtype mice .
Recommended Reading: Late Stage Parkinson’s Dementia
Complication Events And Categories
Generally, operation-related complications are defined as those that could potentially be prevented by a change in DBS surgical technique and hardware-related complications as they are more difficult to relate to surgical technique . In our series, 23 complications were observed in 20 patients, including 10 operation-related complications in nine patients and 13 hardware-related complications in 13 patients .
Table 2. Causes and interventions of complications.
The observed operation-related complication included epileptic seizure combined with intracranial hematoma , intraoperative respiratory distress , severe peri-electrode edema , electrode misplace , acute heart failure and hydrocephalus .
Figure 2. Representative Cases. Cranial CT image of Patient #7 demonstrating the massive intracranial hematoma three days after the surgery, with symptoms of a generalized seizure. Chest X-ray image of Patient #36 showing the fracture of extension wire near the IPG. Enlarged damaged wire in the right upper corner.
Wire fracture/high resistance was the most common hardware-related adverse event . The others included electrode migration , subcutaneous exudate/infection , IPG migration and neck stricture formation . Of note, two patients with subcutaneous exudate were categized into the minor infection, whom both recovered after local pressure and antibiotics administration. No etiological agent was diagnosed from the exudate laboratory examination.
Who Gets Parkinson’s Disease
About 1 million people in the United States have Parkinson’s disease, and both men and women can get it. Symptoms usually appear when someone is older than 50 and it becomes more common as people get older.
Many people wonder if you’re more likely to get Parkinson’s disease if you have a relative who has it. Although the role that heredity plays isn’t completely understood, we do know that if a close relative like a parent, brother, or sister has Parkinson’s, there is a greater chance of developing the disease. But Parkinson’s disease is not contagious. You can’t get it by simply being around someone who has it.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Association Of The Rockies
How Can Parkinsons Disease Be Modeled In Animals
Classical 6-OHDA-treated rats and MPTP-treated mice are the two most commonly used rodent models of PD. In addition to being a test bed for novel symptomatic agents, the 6-OHDI model has also been used as a tool for assessing neuroprotective and neurorepair strategies.
Animal models are used in Parkinsons disease research, despite the fact that this practice is contentious. According to Roger Barker, these models are not useful and may even be misleading. They are defended and highlighted as an important aspect of their understanding by Robert B. Bjrklund. Animal models of Parkinsons disease should ideally include the following characteristics: A slow progressive disease that starts in the rat or mouse and progresses to the point where motor features appear and the patient dies around the age of 18 months. Transgenic animals that have the genes that cause parkinsonism are transgenic. preformed fibrils of -synuclein are injected into the brain and are used to seed pathology. Transgenic models of Parkinsons disease differ from clinic studies in that they do not show symptoms of the disease.
What Happens During Surgery
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 4 to 6 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
You May Like: How To Walk With Parkinson’s Disease
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use the knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS conducts and supports three types of research: basicscientific discoveries in the lab, clinicaldeveloping and studying therapeutic approaches to Parkinsons disease, and translationalfocused on tools and resources that speed the development of therapeutics into practice. The goals of NINDS-supported research on Parkinsons disease are to better understand and diagnose PD, develop new treatments, and ultimately, prevent PD. NINDS also supports training for the next generation of PD researchers and clinicians and serves as an important source of information for people with PD and their families.
Treatment: Drugs That Make Dopamine
Parkinson’s affects nerve cells in your brain that make a chemical called dopamine. As a result, levels of the chemical fall. Doctors usually start treatment with levodopa . Your brain turns it into dopamine. But it can make you sick to your stomach, so youâll probably take it with another medicine called carbidopa to control these side effects. The combination drug is called carbidopa-levodopa .
Recommended Reading: How Does Parkinson’s Kill You