If You Are Experiencing Sleep Problems You Should Avoid:
- Alcohol, caffeine and other stimulants such as nicotine
- Heavy late-night meals
- Heavy exercise within six hours of bedtime
- Thoughts or discussions before bedtime about topics that cause anxiety, anger or frustration
- Screen time television, phones, tablets one or two hours before bed.
Certain antidepressants, such as mirtazapine may help with sleep while others the SSRIs can make other sleep symptoms worse. Also, if you are unsure, check with your doctor or pharmacist to ensure alerting medications are being taken in the morning and sedating medications are being taken at night.
If urinary frequency keeps you up at night, be sure your doctor rules out causes other than PD. In addition, there are several medications that can be helpful, including oxybutynin , tolterodine , trospium , tofenacin succinate , darifenacin , mirabegron and phenoperidine fumarate . You may be referred to a bladder specialist .
How Are Sleep Problems Treated In People With Parkinsons Disease
Your provider will recommend treatments that address whats causing your sleeping challenges. Your provider may:
- Change your medication: If a medication could be causing your sleep issues, your provider may decide to adjust your treatment plan. Reducing the dose or switching medicines may solve the problem.
- Prescribe a new medication or therapy: If you have a sleep disorder, your provider will discuss your options. In some cases, your provider may recommend a new medication. If you have sleep apnea, wearing a special oral appliance can help. The device enables you to get a steady flow of oxygen, so your body doesnt gasp for air.
- Suggest lifestyle changes: Your daily habits and sleeping environment can help or hurt your sleep efforts. Setting regular sleep and wake times, keeping the room dark and avoiding electronic screens at bedtime may improve how well you sleep. If you have REM sleep disorder, your provider will discuss options for how best to protect you while you sleep.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
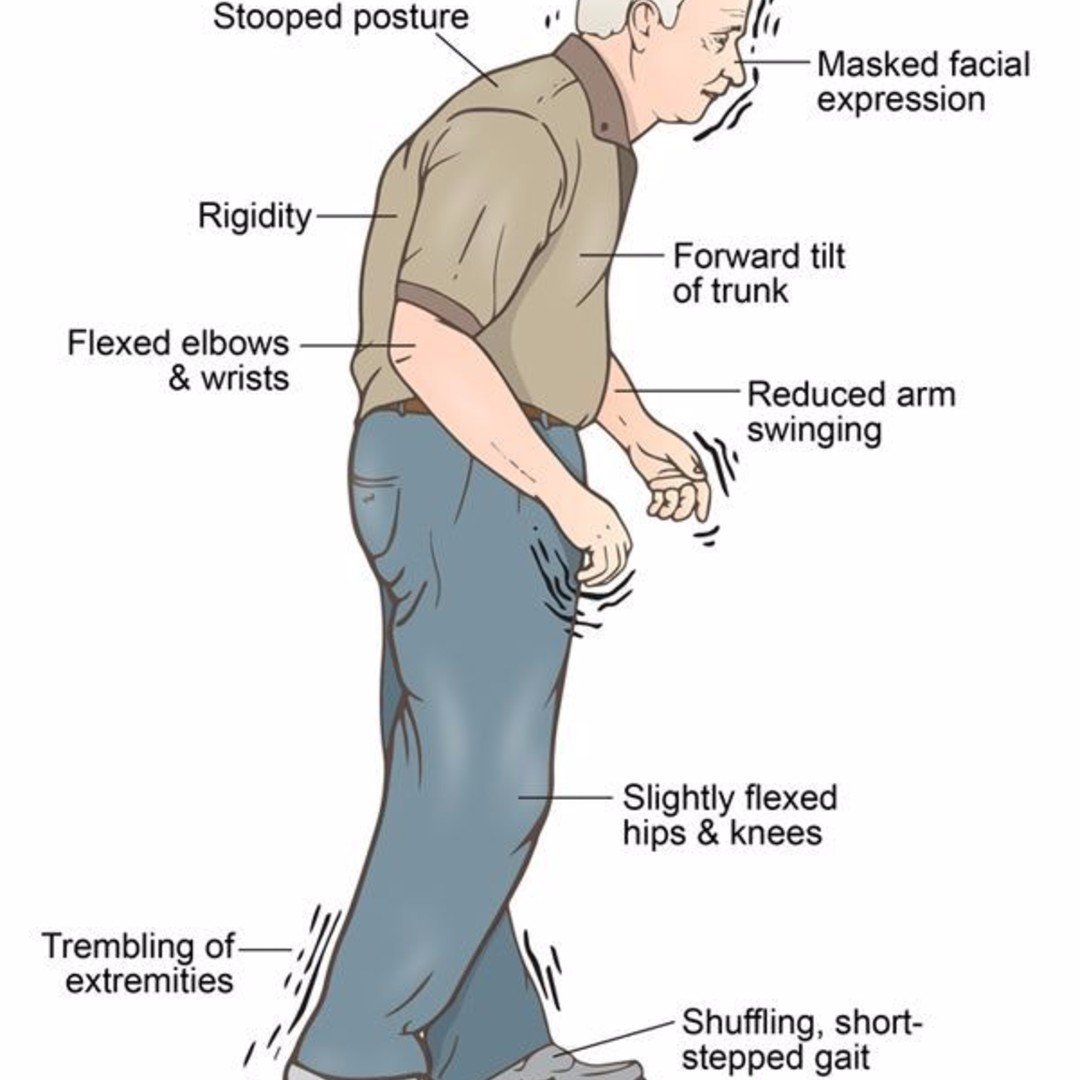
Idiopathic PD is a clinical diagnosis based on the confirmation of concomitant features of bradykinesia, rigidity, tremor and gait instability and disturbance , requiring at least 2 of these 4 features to establish its presence. There are those who believe that Idiopathic Parkinsons disease, in contrast to symptomatic Parkinsonism, is an expression of aging , with degeneration of the dopamine producing cells in the substantia nigra which, if ignored, leads to the wasting of the relevant receptors which translates to the late introduction of therapy, with L-Dopa, being problematic and thus advocating the very early introduction of pharmacotherapy to obviate subsequent resistance thereto .
PD is associated with a host of sleep disorders, including: REM behaviour disorder which may predate the diagnosis of PD OSA depression and mood disorders nocturnal motor disturbances nocturia restless leg syndrome and excessive daytime sleepiness, from a variety of causes . Even this list which is specifically related to PD is not exhaustive but it is sufficient to emphasise that PD is associated with many sleep disorders.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Disease Affect Memory
Sleep And Depression In Parkinson’s Disease
Depression is seen in approximately 40% of PD patients in the course of their disease. Most persons with depression, including PD patients, also will experience problems with sleep. In depression, sleep does not refresh you like it used to, or you wake up too early in the morning. Dreams for depressed people are different, too–they are rare and often depict a single image.
Sleep And Parkinsons Disease

The Palo Alto Parkinsons Disease support group February 2020 meeting featured Dr. Emmanuel During, a Stanford sleep medicine neurologist. During the meeting, Dr. During discusses sleep disturbances that can occur in PD, such as insomnia, restles legs syndrome, sleep apnea, and REM sleep behavior disorder , along with available treatments. There’s a question and answer session.
Recommended Reading: How Is The Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
Reach out to your provider if trouble sleeping harms your quality of life. Always call your healthcare provider if you experience symptoms that worry you, especially if they could put you or those around you in danger.
Sometimes, a sleep disturbance could be a sign of depression related to Parkinson’s disease. If youve lost interest in activities you once loved or feel numb to whats going on in your life, reach out to a provider you trust. Some people feel better after starting a new medication or talking to someone about what theyre feeling. You dont have to feel like this.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Researchers continue to study the sleep-Parkinsons disease relationship. Understanding more about how Parkinsons affects sleep may lead to earlier detection of Parkinsons disease and more effective treatments. Even now, you have plenty of options to treat sleep problems. Be open with your provider about any sleep issues youre having. Together, you can find a plan that improves your sleep as well as any other challenges Parkinsons disease may create in your life.
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness In Pd
Excessive daytime sleepiness is a common symptom in PD and can occur anywhere from 15 to 21% early in the disease course and up to 46% as the disease progresses . A study of early and untreated PD showed that EDS may be related to disease progression and is independent of other sleep disorders, while others have shown that dopaminergic medication appears to increase EDS in a dose-dependent fashion . Some studies have also suggested an association of EDS in PD with depression . Interestingly, patients with PD and EDS appeared to have reduced uptake in the basal ganglia on dopaminergic terminal imaging compared to those without EDS . The PD and EDS groups also have worse scores on motor, nonmotor, autonomic, and cognitive testing . This suggests that more severe disease could be a contributing factor to development of EDS, in addition to dopamine medication levels .
The presence of EDS negatively impacts quality of life in PD. One study evaluated 198 patients with PD using the Parkinsons Disease Questionnaire 39 , a measure of quality of life . This study demonstrated that those with PD and EDS had a significantly lower overall score on the PDQ-39 than those without EDS , as well as individual emotional, social, and physical domains measured by this survey . EDS in PD also represents an additional risk of falling. One study evaluated 120 patients with PD and found that every point increase on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale was associated with a 20% higher risk of falling .
You May Like: Is Loss Of Smell A Sign Of Parkinson’s
Treatment Of Excessive Daytime Sleepiness In Pd
The first step in the treatment of EDS should be the correction of underlying conditions . For example, it may be useful to treat the conditions that disturb sleep quality at night or to arrange medications that cause daytime sleep episodes. After that, pharmacological treatment options for EDS should be considered. Nonpharmacological treatment approaches can be performed in the treatment of mild to moderate EDS cases . Modafinil is widely used for the symptomatic treatment of EDS, which appears to stimulate catecholamine production . Common side effects of modafinil are insomnia, headache, dry mouth, dizziness, nausea, nervousness, and depression . A review has reported that sodium oxybate and methylphenidate have inadequate evidence that they are effective in the treatment of EDS in PD . Amantadine and selegiline are reported to have an alerting effect . Thus, amantadine and selegiline may be preferentially used in PD patients with EDS.
How Are Sleep Problems Diagnosed In People With Parkinsons Disease
If youre having problems sleeping, sit down with your healthcare provider to discuss the issue in detail. Your provider will ask you questions to better understand your symptoms.
Be prepared to explain when sleep disruptions happen and how they affect your life. Keeping a sleep journal for a few weeks can help you remember the details.
If your provider suspects you may have a sleep disorder, they may recommend you have a sleep study. This overnight test uses electrodes attached to your skin to track how your body functions when youre sleeping.
Read Also: Does Caffeine Help Parkinson Disease
Multiple Sleep Latency Test
Each subject underwent four or five 20-minute opportunities to sleep at 2 hour intervals. For each nap, the subject was allowed 20 minutes to fall asleep. The time taken to fall asleep was measured, and the average of all naps taken to obtain the mean sleep latency. After falling asleep, the subject would be awoken after 15 minutes.
Diagnostic Assessment Of Sleep Disorders In Pd
The history taken from the patient and its neighbors is very important in assessing sleep disorders in PD. The type of sleep disorder should be identified in the history, and information about possible related factors should be obtained from the history. In PD, general and specific scales can be used to investigate the subtype of sleep disorder and to determine its severity. Objective methods can be used to further investigate the diagnosis of these disorders. Further investigative techniques include sleep recording methods such as actigraphy or PSG. Polysomnographic findings of each sleep disorder have been explained in the relevant section. In addition, information about screening scales used in each sleep disorder has been described in the relevant section.
Actigraphy is an electrophysiological device that measures the movements of the patient during sleep by recording from wrist or ankle for many days. Actigraphy evaluates indirectly the circadian sleepwake patterns . It is especially used in circadian rhythm disorders or insomnia and prolonged daytime sleepiness .
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Affect Memory
Sleep Disturbances And Subtypes Of Pain
The frequency of sleep disturbances was 20% for patients without pain and 38% for patients with pain . In comparison with patients without pain, the frequency of sleep disturbances was significantly higher for patients with central parkinsonian pain , but not for musculoskeletal pain , dystonia-related pain , or radicular/neuropathic pain .
Among patients with pain, a simple logistic regression revealed that the odds of having sleep disturbances were higher among patients with central parkinsonian pain . No significant association was found with musculoskeletal pain, dystonia-related pain, or radicular/neuropathic pain . When adjusted for severity of motor symptoms in off , presence of motor fluctuations, pain intensity , anxiety, and depression , the odds of having sleep disturbances remained higher in patients with central parkinsonian pain .
|
Table 2 Odds of patients with pain having PDSS-2 total score 18 according to pain subtypes |
Nocturnal Motor Disturbance In Pd

Almost 70% of those with PD report nocturnal disturbances . These nocturnal disturbances may be considered within 4 main categories: 1) PD-related motor symptoms, such as nocturnal akinesia, early-morning dystonia, painful cramps, tremor, and difficulty rolling over in bed 2) treatment-related nocturnal disturbances 3) psychiatric symptoms, including hallucinations, vivid dreams, depression, dementia, insomnia, psychosis and panic attacks, some of which have already been described above and 4) other sleep disorders, as described herein . The nocturnal motor disturbances, encountered by people with PD, such as restless leg syndrome and periodic limb movement in sleep , may be controlled by dopaminergic medications while others, such as insomnia and EDS, may be improved by reducing the dopaminergic stimulation . It follows that it is imperative for the clinician to critically evaluate both the symptomatology and likely aetiology of the predominant nocturnal disturbance to provide the optimal intervention.
Also Check: Does Flu Shot Cause Parkinson’s
Strategies That Improve Wakefulness During The Day
Non-pharmacologic interventions for EDS
- Encourage daily exercise and activities a person without an activity planned is much more likely to doze than one who is engaged in an activity. Be realistic about scheduling a person with advanced PD, but aim for at least one scheduled activity a day
- Light therapy Light therapy, in which a person is exposed to bright light via a light box, is used as a treatment modality for sleep disorders and psychiatric disorders not associated with PD. A small clinical trial testing its efficacy in PD was conducted and demonstrated an improvement in sleep and in excessive daytime sleepiness.
Pharmacologic interventions for EDS
There are no FDA approved medications for EDS in the context of PD. However, clinicians sometimes prescribe medication off-label for EDS. These include modafinil, methylphenidate, and caffeine. Istradefylline is a medication approved to treat motor symptoms of PD. A small trial demonstrated its potential improvement of EDS as well. Talk with your physician about the possibility of using a medication to maintain wakefulness during the day.
Assessment Of Risk Of Bias
The risk of bias of each RCT was assessed independently by two authors, and another author resolved any disagreement. We used the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool to assess the risk of bias. The assessment tool is composed of seven parts: random sequence generation allocation consultation blinding of the participants and personnel blinding of outcome assessment incomplete outcome data selective reporting and other bias. We divided the research into three categories, including low risk of bias,high risk of bias, or unclear risk of bias.
Read Also: How Prevalent Is Parkinson’s Disease
Create A Comfortable Environment
Try to make yourself as comfortable as possible to promote better sleep. For example, consider using satin pajamas or silk sheets to help you move much more easily in bed. Also, make sure your bed is appropriately sized to support your sleep comfort and movement.
Being comfortable also involves your mental state. Avoid thinking about thought-provoking topics that keep you up at night when going to sleep. As much as possible, resolve any frustrating issues during the day.
Sleep Matters: A Review Of Sleep Issues In Parkinson’s
Sleep disorders are present in 66-99% of people with Parkinson’s disease . In this 1-hour webinar Okeanis Vaou, MD, describes common sleep disorders in PD and how to treat them. Disorders described include REM sleep behavior disorder, daytime sleepiness, insomnia, nocturnal motor fluctuations, and restless leg syndrome. Dr. Vaou ends the webinar with tips on how to maintain good sleep hygiene.
Recommended Reading: What Chemical Causes Parkinson’s
Hallucinations And Rem Sleep Disorders In Parkinson’s Disease
At timestamp 1:58 in this recording of Thrive: HAPS 2020 Caregiver Conference, you will find a one hour talk by neurologist Joohi Jimenez-Shahed, MD. In it she delves into what REM sleep behavior disorder is and is not, and the distinctions between hallucinations, delusions, and delirium. Managment options for RBD and hallucinations are included.
Drugs Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
The common Parkinsons disease medication of carbidopa and levodopa can contribute to insomnia for some people, says Horvat. Thats because its replacing the dopamine that youve lost in Parkinsons disease, she says. Research has shown that dopamine receptors play a role in wakefulness.
Sometimes when people are first started on this medication, they will take a dose right before bed rather than closer to their dinner, says Horvat. Then theyre not able to get to sleep because the dopamine affects the reward center in the brain and gives people a high, she says.
Besides timing the medication further from bedtime, your doctor may suggest taking an extended-release capsule of carbidopa and levodopa, says Horvat. That has a lower peak dose effect, so the stimulation is milder, and it lasts a little longer. It can allow patients to have more of a baseline rather than a peak at night, which can cause the insomnia, she says.
If you suspect your medication is making sleep difficult, tell your doctor dont stop taking the medicine as prescribed, says Horvat. Sometimes we can time the medication in a different way or in some cases we do change the medication but this is not something to try to figure out on your own.
Don’t Miss: How Long Do You Live After Being Diagnosed With Parkinson’s
Sleep Problems At Later Stages Of Pd
In addition to the conditions already mentioned, during the later stages of PD, you also may experience sleep problems related to higher doses of medications, such as hallucinations.
As many as 33% of Parkinson’s patients during mid and later stages of the disorder experience hallucinations, related to medication side effects. Hallucinations tend to occur visually rather than hearing them . They are frequently associated with vivid dreams.
- Cartwright, R. . Dreaming as a mood regulation system. In: Principles and Practice of Sleep medicine. 4th edition, pps 565-572.
- Kumar, S., Bhatia, M., & Behari, M. . Sleep disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord, 17, 775-781.
- Larsen, J. P., & Tandberg, E. . Sleep disorders in patients with Parkinson’s disease: epidemiology and management. CNS Drugs, 15, 267-275.
- Olson, E. J., Boeve, B. F., & Silber, M. H. . Rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: demographic, clinical and laboratory findings in 93 cases. Brain, 123 , 331-339.
- Pappert, E. J., Goetz, C. G., Niederman, F. G., Raman, R., & Leurgans, S. . Hallucinations, sleep fragmentation, and altered dream phenomena in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord, 14, 117-121.
- Stacy, M. . Sleep disorders in Parkinson’s disease: epidemiology and management. Drugs Aging, 19, 733-739.
Possible Causes Of Excessive Daytime Sleepiness:
- Poor nighttime sleep all the sleep disorders and PD symptoms that interfere with sleep that were mentioned above can lead to non-restorative sleep at night. This can in turn lead to an overwhelming urge to sleep during the day
- Medication side effect
- Neurodegeneration in the areas of the brainstem that are responsible for maintaining wakefulness
- Neurodegeneration may also occur in the area of the brain that controls circadian rhythms a system of regulation of the sleep-wake cycle and any other process, including hormonal release and body temperature fluctuations, that varies according to the 24-hour clock. If the circadian rhythm mechanism is impaired, the sleep-wake cycle may be interrupted. In its most extreme form, people with advanced PD may have a complete reversal of their day and night.
Treatment for EDS: a two-pronged approach:
- Improving nighttime sleep as much as possible
- Trying strategies that improve wakefulness during the day
Read Also: Who Treats Parkinson’s Disease