Chemical Properties And Distribution
PQ is a member of a chemical class known as bipyridyl derivatives, which includes diquat and cyperquat that has the same structure as the MPTP metabolite MPP+ . One-electron reduction of PQ, , , probably underlies its toxic effects in the lung after accidental ingestion. Reduced PQ is then rapidly re-oxidized to its cation form by molecular oxygen with the formation of superoxide radicals in a classical redox-cycling reaction.
Because PQ is highly polar, it is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Over 50% of a single dose administered to rats localizes to the gut at some 32h after administration and only approximately 5 to 10% of an ingested dose is absorbed, although the presence of emulsifiers and/or co-solvents may enhance absorption. Excretion occurs in urine and faeces with approximately 45% of a single dose being excreted after 48h in rats. Because of these properties and some early evidence that PQ is largely excluded from the brain, it has been assumed that PQ would not cross the blood-brain barrier to a significant extent. After a single administration, most of the PQ that reaches the brain is apparently associated with structures outside the BBB or with three areas of the brain: the anterior portion of the olfactory bulb, the hypothalamus and the area postrema, which do not have a tight BBB.
Pesticides Deplete Neurons Of Energy
It was found that the neurons that had been exposed to the chemicals had faulty mitochondria.
Mitochondria, also known as the powerhouses of the cell, are the organelles inside a cell that turn sugar, fats, and proteins into the energy our body needs to survive and function.
But this study demonstrated that the mitochondria inside the dopamine neurons affected by pesticides could not move freely as they normally would. This sucked the energy out of the neurons.
Importantly, the levels of chemicals used to impair these neurons were below the ones deemed lowest observed adverse effect level by the United States Environmental Protection Agency .
Prof. Ryan says that this means we should re-evaluate EPAs guidelines for these two pesticides.
This study shows that everyone is not equal, and these safety standards need to be updated in order to protect those who are more susceptible and may not even know it, he adds.
People with a predisposition for Parkinsons disease are more affected by these low-level exposures to agrochemicals and therefore more likely to develop the disease.
Prof. Scott Ryan
This is one of the reasons, he concludes, why some people living near agricultural areas are at a higher risk.
Modelling Pd In Rodents And Simple Organisms
Impaired mitochondrial function is a predominant feature in cases of Parkinson’s disease due to genetic or environmental modifications, which result in mitochondrial stress. This may directly compromise the neuron or cause alterations in neurotransmitter release, resulting in post-synaptic damage. A pro-inflammatory component is increasingly considered to be important in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative conditions including PD, and pro-inflammatory activation of glial cells may be pivotal in disease onset.,
Although many of the genes involved in PD have been identified, their interactions are still unclear. Mutations of -synuclein or duplications of -synuclein are linked to familial PD and -synuclein is a component of Lewy bodies. -synuclein tends to form intracellular fibrils and aggregates, particularly after oxidative stress. Loss of an ubiquitin ligase, Parkin, is responsible for autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Finally, mutations in genes coding for UCH-L1 and Pink-1 are linked to autosomal recessive PD, whereas mutations in LRRK2 are linked with autosomal dominant PD. Recent work has shown that mutations in the mitochondrial protease HtrA2 are also linked to PD downstream of the kinase, Pink 1. Mutations in Parkin are recognized as the most common cause of familial parkinsonism and may be involved in sporadic PD. Parkin seems to work as a broad-spectrum neuroprotectant, the efficacy of which decreases with ageing.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
One Of The First Studies To Look At Human Cells
The researchers used stem cells from patients with Parkinsons disease who had a mutation in the gene responsible for encoding the -synuclein protein.
At least 30 alterations in this gene have been associated with Parkinsons, and -synuclein protein clumps are a well-documented, albeit poorly understood, hallmark of the disease.
For the new research, the scientists also worked with normal embryonic cells that they modified using genetic editing to replicate the -synuclein genetic mutation.
Prof. Ryan explains why using human cells makes this study particularly valuable. Until now, he says, the link between pesticides and Parkinsons disease was based primarily on animal studies as well as epidemiological research that demonstrated an increased risk among farmers and others exposed to agricultural chemicals.
We are one of the first to investigate what is happening inside human cells, explains Prof. Ryan.
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that go on to individualize into specific types of cells. Prof. Ryan and his colleagues used the two types of stem cells to derive dopamine-producing nerve cells from them.
Then, they exposed these dopaminergic neurons which are known to be affected the most by Parkinsons disease to the two pesticides.
Disabilities Secondary To Parkinsons Disease
While most people tend to think of Parkinsons disorder as a neurological movement disorder, and it most certainly is, many people do not realize that other systems in the body can also be severely affected by Parkinsons. Often, the same chemical exposure can also cause other disorders, such as ischemic heart disease. However, often it is the Parkinsons itself, or the medication used to treat it that is the causal factor in the development of a new disorder. Whether a veterans Parkinsons was caused by exposure to the TCDD in agent orange, pesticides, trichloroethylene, or its origins are unknown, Parkinsons cause many secondary health effects and disabilities.
Cardiovascular Complications
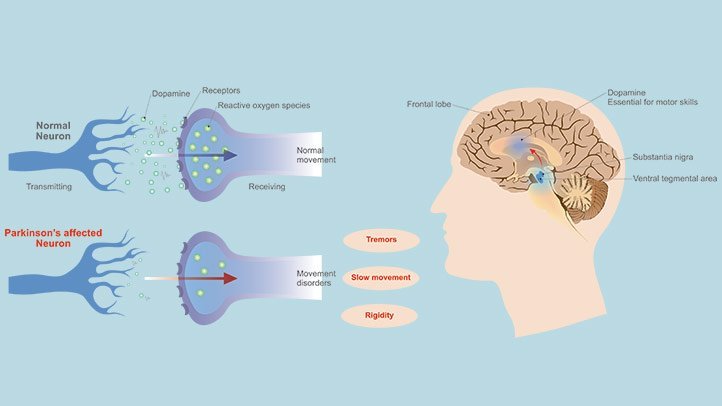
Parkinsons is known as a neurodegenerative disorder that is, it causes neurons to degenerate or decay. The most famous area for PD degeneration is in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra, where Parkinsons causes the death of neurons that generate dopamine, a neurotransmitter which is involved with movement. However, more recent studies have also shown that Parkinsons also attacks nerves in the heart which produce another neurotransmitter, noradrenaline. This typically takes place in the left ventricle and can have many complications.
Orthopedic Problems
Psychiatric Problems
Other Problems
Recommended Reading: When Was Muhammad Ali Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
Many Different Dopamine Receptors
Dopamine signalling is a little more complex there are at least 5 varieties of dopamine receptor that can respond to this messenger. The receptors are classified in two families:
- D1 and D5 are in the D1-like family
- D2, D3 and D4 are in the D2-like family
The reason for so many different receptors is so the brain can use the dopamine signal to activate different responses in different parts of the brain. For instance, in the D1-like family, the D5 receptor can be found in brain regions that play a role in emotion and behaviour, long-term memory and smell. In the D2-like family, the D2 receptor is most abundant in the basal ganglia where it has a role in motor control and learning while D3 receptors are found in various regions of the brain and are involved in encouraging rewarding behaviour.
Why is this important? Well it helps explain the main difference between the dopamine the brain produces and dopamine agonist. Natural dopamine will activate any of the dopamine receptors in the region of the brain where it is released, whereas dopamine agonists are unable to target specific locations but are able to be more selective and activate specific dopamine receptors.
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinson’s disease. People with Parkinson’s-like symptoms that result from other causes are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinson’s, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to distinguish them from Parkinson’s. Since many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, it is important to make an exact diagnosis as soon as possible.
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose nongenetic cases of Parkinson’s disease. Diagnosis is based on a person’s medical history and a neurological examination. Improvement after initiating medication is another important hallmark of Parkinson’s disease.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Exercise Recommendations
What To Do If Youre Affected
If you or a loved one have used Roundup or were exposed to Roundups dangerous ingredient, glyphosate, and later developed Parkinsons disease, you may be eligible for compensation. Contact a personal injury attorney in your area who has experience in chemical exposure or herbicide cases. They can help review your situation and advise to whether you could win back some damages.
How Is A Diagnosis Made
Because other conditions and medications mimic the symptoms of PD, getting an accurate diagnosis from a physician is important. No single test can confirm a diagnosis of PD, because the symptoms vary from person to person. A thorough history and physical exam should be enough for a diagnosis to be made. Other conditions that have Parkinsons-like symptoms include Parkinsons plus, essential tremor, progressive supranuclear palsy, multi-system atrophy, dystonia, and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Also Check: Parkinson\’s Stage 5 Life Expectancy
Roundup Causing Parkinsons: A Brief Guide
Roundup is a popular chemical herbicide used on lawns, farms, and in gardens across the world. However, following recent studies that link Roundup to Parkinsons and other diseases, the herbicide is being more heavily regulated. Though there are regulations and Roundup has been banned in many counties, there are still areas of the United States where it goes unregulated. While Roundup may be an effective herbicide, its been shown to be extremely dangerous, and one of its key ingredients, glyphosate, is linked to Parkinsons disease.
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
Disability Ratings For Parkinsons Disease
Once you are awarded service connection for Parkinsons, the fight may not be over. This is mostly because of the rating system the VA uses for Parkinsons. The minimum rating you can be awarded by the VA for Parkinsons disease is 30 percent, but if you fail to appeal that rating, you are potentially leaving thousands of dollars of benefits on the table.
The 30 percent rating is given to veterans who have the diagnosis of Parkinsons, and is basically acknowledging that they have the condition. What many veterans do not realize is that once you are service connected for Parkinsons Disease, you are entitled to service connection for all the other problems that the condition causes: talking, swallowing, walking, balance problems, using your hands, memory, concentration, depression, and many more. If you have Parkinsons, you are entitled to a separate rating for any condition that it causes. As you may guess, this can be a long list, especially as the disease progresses.
Don’t Miss: Parkinsons Facial Expression
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Sadly, no.
It is not possible to prevent Parkinsons disease, but some believe that lifelong healthy habits may reduce ones risk of developing the condition. Some medications may also relieve some of its symptoms.
In some PD patients, particularly those who are at the late stage of the disease, surgery may be an option to help improve symptoms.
Some experts also advise doing rpeventive measures such as wearing gloves and other protectvie equipment when applying pesticides as it may help protect you against the disease.
The Genetics Of Parkinsons
A 2020 study including 1,676 people with Parkinsons in mainland China suggested that genes play a role in the development of the condition. An estimated 10 to 15 percent of people with Parkinsons have a family history of the condition.
In fact, a number of specific genes have been linked to the development of Parkinsons.
How do genetics factor into Parkinsons in some families? According to Genetics Home Reference, one possible way is through the mutation of genes responsible for producing dopamine and certain proteins essential for brain function.
Read Also: X Linked Dystonia Parkinsonism
Do Chemicals Cause Parkinsons Disease
Short answer: The best available scientific evidence suggests that a few chemicals, including some pesticides, increase risk of Parkinsons disease, but only a small fraction of cases are believed to be caused by any sort of environmental exposure.
Longer answer: The first chemical demonstrated to cause Parkinsons disease is MPTP, as discussed here and in the fascinating book, The Case of the Frozen Addicts. MPTP, or more precisely its metabolite MPP+, is an exceptionally potent toxin that selectively kills dopaminergic neurons by poisoning their mitochondria. This is not a case of slightly increased risk it quickly and irreversibly causes symptoms essentially indistinguishable from idiopathic Parkinsons disease.
MPTP
MPP+
It is highly unlikely that you will come in contact with these molecules at the present time. Rather alarmingly, however, in the 1970s, MPP+ was apparently developed, and field tested, as a herbicide under the name Cyperquat, by Gulf Oil Chemicals Company .
Of much greater concern are widely used pesticides, which have been demonstrated to increase risk of Parkinsons disease with varying strengths of evidence. Some of the strongest evidence is for rotenone, thousands of tons of which have been used to kill unwanted fish and various agricultural pests it has even been used to kill head lice on humans.
Rotenone
Another pesticide worth highlighting is paraquat, due to its chemical similarity to MPP+.
Paraquat
Agent Orange & Parkinsons Disease
Agent Orange was used in chemical warfare during the Vietnam War. Since then, Vietnam veterans have developed a variety of symptoms related to Agent Orange exposureincluding Parkinsons Disease.
There is research that is starting to show exposure to certain chemicals do cause Parkinsons Disease, and some of those chemicals such as TCE and PCE have been found in the water of Camp Lejeune. There is also evidence that Agent Orange herbicide exposure causes Parkinsons, which the VA has now conceded. Parkinsons Disease is one of the presumptive conditions related to Agent Orange that the VA recognizes.
According to the Parkinsons Foundation, the main chemical in Agent Orange, called dioxin, is the main culprit in causing disease.
Agent Orange has also been linked to respiratory cancer, multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, lymphoma, soft tissue sarcoma, and chronic b-cell leukemias. This service connection is particularly prevalent for Vietnam War veterans.
Also Check: How Much Does Carbidopa Levodopa Cost
Benefits Of Dopamine Agonists
There is one final twist in the story about dopamine agonists. In the early 2000s, there was another feature of dopamine agonists under investigation the possibility that they could help to protect brain cells. Unfortunately early suggestions of a protective effect of these drugs, which were highlighted in brain imaging studies, have yet to be substantiated. To date there are no treatments that have conclusively been demonstrated to slow the progression of Parkinsons.
So, where do we stand with dopamine agonists? Dopamine agonists are currently used in clinical practice, sometimes alone, sometimes alongside other treatments. While these medications cause side effects such as dyskinesia less frequently than levodopa, even the newer dopamine agonists still cause a number side effects these can include nausea and hallucinations and they have been linked to sudden sleep attacks and increased risk of impulsive and compulsive behaviours. In fact, this latter side effect recently made the news as new research suggests that around half of people taking dopamine agonists may experience impulsive behaviours. You can read more about this in our blog post:
When it comes to starting Parkinsons medications
Metal Elements And Pesticides As Risk Factors For Parkinson’s Disease
Common miRNA association between Parkinson’s Disease and pesticides exist.
-
Pesticide-deregulated miRNAs affect PD-related molecules, e.g. -synuclein.
-
There exist an association between essential, non-essential metals and PD.
-
UPS and mitochondrial impairment, oxidative stress, gene mutation and -Syn aggregation are prime mechanisms involved in essential, non-essential metals neurotoxicity in PD.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s
Neurotoxicity Of Pq Mptp And Other Dopamine Congeners
Several studies suggest that systemic administration of PQ can cause neuronal damage and a parkinsonian-like syndrome in experimental animals . The linking mechanism between PQ exposure and Parkinson’s disease is suggested by the alleged chemical similarity between this compound and others known to cause a parkinsonian syndrome, particularly MPTP. MPTP can reproduce most of the biochemical, neuropathological and clinical characteristics of human parkinsonism in both human and non-human primates, with the notable exception of Lewy body formation. MPTP toxicity has been studied in cell systems in mice and in non-human primates. In rats, dopaminergic neurodegeneration is observed at high doses, whereas mice have become the most commonly used species for MPTP studies as they develop a dopaminergic degeneration that may be related to human parkinsonism.
Figure 1
Mechanisms of PQ and MPTP toxicity. PQ can cause an oxidative stress either intracellularly by redox cycling or by activation at cell surfaces by the NADPH oxidase . Mitochondria can be affected indirectly or directly by PQ. In neurons the effects of PQ are believed to be primarily cytosolic. MPTP is converted to its toxic metabolite MPP+ and then sequestered through the dopamine transporter in dopaminergic neurons in which it primarily affects complex I, promoting oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage
It is apparent from this analysis that the initial targets and toxicity mechanisms of PQ and MPP+ differ .

