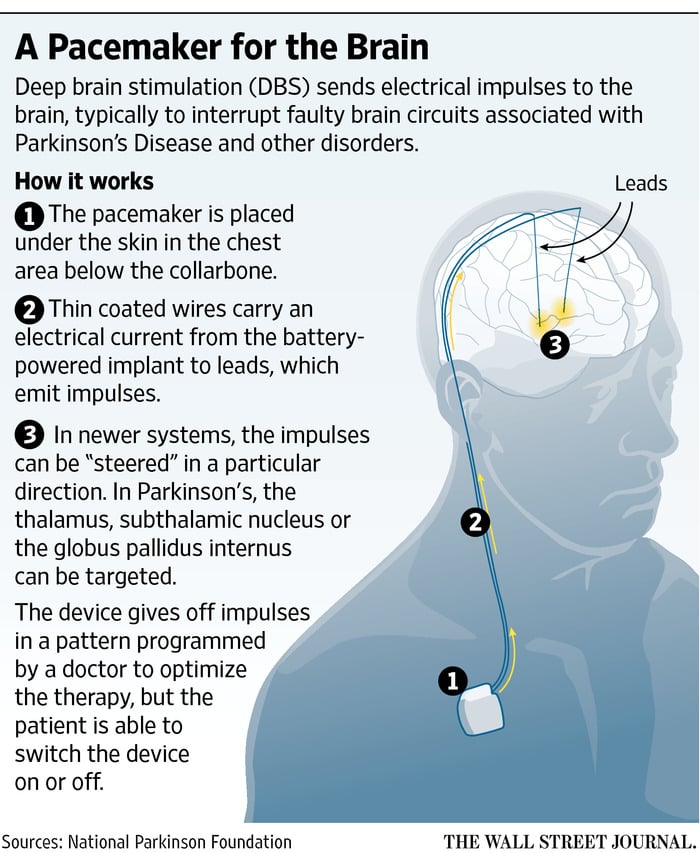
What Happens After Surgery
After surgery, you may take your regular dose of Parkinsons medication immediately. You are kept overnight for monitoring and observation. Most patients are discharged home the next day.
During the recovery time after implanting the electrodes, you may feel better than normal. Brain swelling around the electrode tip causes a lesion effect that lasts a couple days to weeks. This temporary effect is a good predictor of your outcome once the stimulator is implanted and programmed.
About a week later, you will return to the hospital for outpatient surgery to implant the stimulator in the chest/abdomen. This surgery is performed under general anesthesia and takes about an hour. Patients go home the same day.
Step 7: implant the stimulator You will be taken to the OR and put to sleep with general anesthesia. A portion of the scalp incision is reopened to access the leads. A small incision is made near the collarbone and the neurostimulator is implanted under the skin. The lead is attached to an extension wire that is passed under the skin of the scalp, down the neck, to the stimulator/battery in the chest or abdomen. The device will be visible as a small bulge under the skin, but it is usually not seen under clothes.
You should avoid arm movements over your shoulder and excessive stretching of your neck while the incisions heal. Pain at the incision sites can be managed with medication.
Read Also: What Age Parkinsons Disease
Who Is A Candidate For Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS is more than just a surgical procedure. It involves a series of evaluations, procedures, and consultations before and after the actual operation, so people interested in being treated with DBS should be prepared to commit time to the process.
For example, those who do not live close to a medical center that offers DBS surgery may need to spend significant time traveling back and forth to appointments.
The procedure, as well as the pre-operative evaluation and post-operative follow-up, can be expensive depending on the persons insurance coverage. DBS surgery is an FDA-approved treatment for Parkinsons disease, and Medicare and most private insurers cover the procedure, but the extent of coverage will depend on each persons individual policy.
Prospective patients should have realistic expectations about DBS results. Although DBS can improve movement symptoms of Parkinsons disease and greatly improve quality of life in properly selected patients, it is not likely to return anyone to perfect health.
Dont Miss: What Can You Do To Prevent Parkinsons Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Still Effective After 15 Years In People With Parkinson Disease Study Shows
Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus was shown to remain effective in treating motor complications of people with Parkinson disease 15 years after initial surgery.
Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus may prove effective after more than 15 years in patients with Parkinson disease , according to study findings published last week in Neurology.
Associated with several positive outcomes in patients with PD, including of disease progression, researchers say that STN-DBS has been shown to maintain efficacy in patients up to 11 years after surgery. However, conflicting reports have indicated DBS may lose efficacy over time.
Initial post-operative quality of life improvement has been described to fall to preoperative levels after 5-year stimulation, likely due to the escalation of both levodopa- and stimulation-resistant motor and nonmotor features of PD, such as impairments of gait, balance, speech and cognition, said the study authors.
With a growing rate of PD diagnoses and number of STN-DBS procedures conducted, researchers note that large data examining efficacy after the second and third decades post-procedure is lacking, with small populations having been the focus of previous studies examining motor response from STN-DBS after more than 10 years.
A mean follow-up time of 17.06 ± 2.18 years was reported among the study cohort.
Reference
Also Check: Should Someone With Parkinson’s Drive
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
In just 27-minutes we follow Andy McDowell, a 48-year-old marketing consultant, husband and father to two young girls with early onset Parkinsons disease, in the lead-up to his first Deep Brain Stimulation surgery. When switched on, wires deeply embedded in his brain help him regain some control of his body.
Effects Of Et And Pd On Gait And Balance:
In order to understand the effects of DBS on gait and balance it is important to first appreciate the complexity of normal functioning, as well as the effects that ET and PD have on these activities. Walking is an activity that requires adequate strength, vision, proprioception and motor planning. Similarly, balance control depends upon the proper functioning of the inner ear , vision, proprioception, cerebellar function, cognitive function and motor strength.
Proper functioning of multiple neurotransmitter systems is part of this equation.
Unfortunately, balance generally declines with aging, even in the absence of a neurodegenerative disorder. In addition, PD and ET are associated with deterioration of gait and balance over time. ET has been associated with changes in gait and balance which might only be recognized through specific testing in the clinic or in an instrumented gait laboratory. ET related gait and balance problems include impaired tandem gait , wide based gait , reduced gait speed, an increased number of near falls and other subtle abnormalities. These gait and balance impairments are thought to be related to dysfunction in cerebellar pathways. Interestingly, the severity of the tremor does not clearly predict the severity of the balance problem.
You May Like: How Can I Test Myself For Parkinson’s
Multivariable Linear Regression Analysis
At baseline, a higher UPDRS part III score during the off phase , a higher part IV score , and a higher BIS11 score were significantly associated with higher PDQ-39 SI. At 3 months after DBS, a higher UPDRS part I score and a higher BIS/BAS score were significantly associated with higher PDQ-39 SI. At 1 year after DBS, although no parameters were associated with PDQ-39 SI, a higher BIS11 score tended to be associated with higher PDQ-39 SI. At 3 years after DBS, a higher UPDRS part I score was associated with higher PDQ-39 SI.
The cognitive functions as evaluated by the MMSE, FAB, and MoCA did not significantly contribute to pre- and postoperative QOL .
Table 2. Standardized beta values of the factors determining quality of life at each follow-up point.
Complications And Adverse Effects
A total of 30 patients had complications within 30days after surgery. One patient suffered from hemorrhage during surgery. Two patients had pneumocephalus. The patient who suffered from hemorrhage and 1 of the patients who suffered from pneumocephalus had persisting hemiparesis after surgery .A3).A total of 14 patients experienced complications attributed to battery replacements. At the first replacement 4%, at the second 12%, and from the third replacement 25% of patients suffered complications .
One patient committed suicide 1.2years after surgery. The patient started antidepressant medication 3 months after surgery. He was regularly followed, and no hallucinations or psychoses were reported.
None of the adverse effects attributed to DBS became significantly more frequent over time .
Recommended Reading: Icd 10 Code Parkinson’s Disease
Determining Dbs Lead Orientation
DBS lead locations in the GPi were estimated based on information obtained during intraoperative electrophysiological mapping as well as co-registered preoperative MRI and postoperative CT scans . The orientation of the DBS lead and relative direction of individual segments for each patient were derived from the fiducial marker on the lead, in combination with the unique artifact characteristics of the segments, using a modified version of the DiODe algorithm. The original DiODe algorithm was designed and validated for the Boston Scientific Cartesia electrodes since most of our patients were implanted with the Abbott Infinity electrodes, the MATLAB code was modified to be compatible with the new electrode characteristics in collaboration with Dr. Dembek, the lead author of the DiODe algorithm . Additional details can be found in ref. .
What Are The Risks
No surgery is without risks. General complications of any surgery include bleeding, infection, blood clots, and reactions to anesthesia. Complications related to placement of the DBS lead include seizures, infection, and a 1% chance of bleeding in the brain.
Reasons for which you might need additional surgery include breakage of the extension wire in the neck parts may wear through the skin and removal of the device due to infection or mechanical failure. If you have a non-rechargeable DBS system, the battery will need to be replaced every 3 to 5 years. Rechargeable DBS systems have a battery that lasts 10 to 15 years.
DBS may also cause worsening of some symptoms such as speech and balance impairments. In some patients with Parkinson’s, DBS may cause or worsen depression. If you develop any side effects from a stimulation adjustment, you need to return to the office for further programming.
Recommended Reading: A Typical Parkinson’s Progression
Questions Youve Always Wanted To Ask About Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical therapy used to treat certain aspects of Parkinsons disease . Mel Mitchell, age 74, was diagnosed with Parkinsons disease in 2013. Mel underwent DBS surgery in 2020 with the goal of improving his PD symptoms. We asked the most frequently asked questions for someone who has undergone this brain surgery.
Why did you decide to undergo DBS surgery?
I was diagnosed with Parkinsons nine years ago. I had been taking the medication Sinemet since my diagnosis, but Parkinsons medications only have so much impact when it comes to improving motor symptoms. About two and a half years ago, it seemed that DBS would be the next logical step in my Parkinsons journey. When I spoke with my neurologist and a neurosurgeon, they agreed I would be the perfect candidate for DBS.
Did you have any fears going into surgery?
My biggest fear was that the surgery wouldnt work. There is a lot of preparation that goes along with getting ready for DBS surgery, so I didnt want it to be for nothing. I also have a blood clotting disease which creates a bigger chance of blood clots, so I need to manage that whenever I go into surgery.
One thing that helped ease my fears was meeting with a representative from the company I used for my DBS instrument. She talked to me and my wife about DBS and she attended my surgery and my fine tune sessions. She was extremely helpful in sharing real life examples and answering our questions.
What was it like getting brain surgery?
Testing Before Deep Brain Stimulation
For patients with Parkinsons disease, the doctor must confirm that the PD is levodopa-responsive and determine which symptoms are most likely to respond to DBS and discuss these with the patient.
To accomplish these two objectives, the movement disorders neurologist will examine the patient in the absence of his or her PD medications, then again after having taken them. Seeing the effect of PD medications on the movement and non-motor symptoms helps the physician and patient identify good target symptoms for DBS.
A cognitive assessment can help determine a persons ability to participate in the procedure, which involves providing feedback to the doctor during surgery and throughout the neurostimulator adjustment process. This assessment also informs the team of the risk of having worsened confusion or cognitive problems following the procedure.
Some hospitals also perform an occupational therapy review or speech, language and swallowing assessment. A psychiatrist may examine the person to determine if a condition such as depression or anxiety requires treatment before the DBS procedure.
Also Check: What Do Parkinson’s Patients Usually Die From
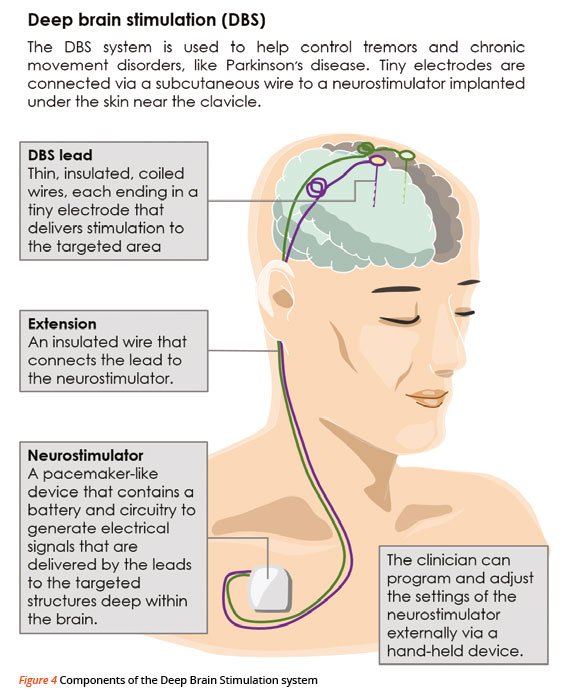
Surgery To Implant The Deep Brain Stimulation Device
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical implantation of an electrical device into the brain. A neurosurgeon uses imaging scans to pinpoint the right spot in the brain for implanting the electrode.
When surgeons have determined the correct location, they create a small opening in the skull and insert a thin, insulated wire, through which they insert the electrode. Surgery to implant the electrode takes about four hours and requires general anesthesia. You may then stay overnight in the hospital for observation.
The next day, doctors perform the second part of the surgery, which involves connecting the insulated wire to a battery-operated pulse generator that is implanted under the skin near the collarbone. Most people can return home after this procedure.
Several days after the surgery, you meet with your neurologist, who programs the pulse generator. Pushing a button on an external remote control sends electrical impulses from the pulse generator to the electrode in the brain.
People who use deep brain stimulation work closely with their neurologist to find the combination of settings that best controls their symptoms. After several visits, they are able to control the strength of the electrical impulses on their own. Following this adjustment period, most people require only occasional maintenance visits.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinsons Cause Sleepiness
Effect On Motor Symptoms
Before surgery, the motor symptoms were significantly reduced by 52% by medication . STNDBS significantly reduced UPDRS III by 61% when comparing the OFF/off and the ON/off conditions 1 year after surgery and significantly by 39% at the longterm followup 8 to 15years after surgery .
Medicine significantly reduced motor symptoms further when added to the DBS treatment. The effect of both STNDBS and medicine was a reduction of motor symptoms by 69% 1 year after surgery , and by 51% at the longterm followup compared with the OFF/off condition .
Also Check: Will There Be A Cure For Parkinson’s
Stereotactic Dbs Vs Interventional Image
Stereotactic DBS surgery requires the patient to be off their medication. During the procedure, a frame stabilizes the head and provides coordinates to help the surgeons guide the lead to the correct location in the brain. The patient gets local anesthesia to keep them comfortable throughout each step along with a mild sedative to help them relax.
During image-guided DBS surgery, such as with interventional MRI or CT scan, the patient is often asleep under general anesthesia while the surgeon uses images of the brain to guide the lead to its target.
Some advanced centers offer both the stereotactic and iMRI-guided options for DBS surgery. In this case, the doctor and patient will discuss which procedure is better based on a number of factors.
For instance, the doctor may recommend an image-guided procedure for children, patients who have extreme symptoms, those who are especially anxious or fearful or those whose leads are going into certain parts of the brain.
Generally, DBS surgery follows this process:
What Conditions And Symptoms Can Dbs Treat
DBS can treat several conditions that affect your brain, including movement disorders, mental health conditions and epilepsy.
DBS has approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat the following conditions:
It’s important to keep in mind that while the above conditions might benefit from DBS, experts still don’t know if this is the case. It usually takes years of research and clinical trials to determine if a medical procedure like DBS is helpful for conditions like these. While researchers are looking into them, DBS surgery to treat these conditions is not common.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease A Motor Neuron Disease
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
What Are The Results
Successful DBS is related to 1) appropriate patient selection, 2) appropriate selection of the brain area for stimulation, 3) precise positioning of the electrode during surgery, and 4) experienced programming and medication management.
For Parkinsons disease, DBS of the subthalamic nucleus improves the symptoms of slowness, tremor, and rigidity in about 70% of patients . Most people are able to reduce their medications and lessen their side effects, including dyskinesias. It has also been shown to be superior in long term management of symptoms than medications .
For essential tremor, DBS of the thalamus may significantly reduce hand tremor in 60 to 90% of patients and may improve head and voice tremor.
DBS of the globus pallidus is most useful in treatment of dyskinesias , dystonias, as well as other tremors. For dystonia, DBS of the GPi may be the only effective treatment for debilitating symptoms. Though recent studies show little difference between GPi-DBS and STN-DBS.
Patients report other benefits of DBS. For example, better sleep, more involvement in physical activity, and improved quality of life .
Research suggests that DBS may protect or slow the Parkinsons disease process .
Also Check: What Are The Motor Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Benefits Does The Procedure Offer
DBS is not a cure for Parkinsons, but it may help control motor symptoms while allowing a reduction in levodopa dose. This can help reduce dyskinesias and reduce off time. DBS does not usually increase the peak benefits derived from a dose of levodopa the best levodopa response before DBS is a good indicator of the best response after DBS. But it can help extend the amount of on time without dyskinesias, which may significantly increase quality of life.
DBS does not provide most patients benefit for their non-motor symptoms, such as depression, sleep disturbance, or anxiety. DBS also does not usually improve postural instability or walking problems. If a symptom you have does not respond to levodopa, it is not likely to respond to DBS.
Preoperative Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder And Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation Outcome In Parkinson Disease 1 Year After Surgerylearning Objectives:
Upon completion of the article by Besse-Pinot et al, the participant should be able to:
- State differences in characteristics between preoperative patients with REM sleep behavior disorder and those without REM sleep behavior disorder in this study
- Discuss differences between RBD+ and RBD patients in quality of life outcomes after surgery found in this study
- Compare the motor outcome for RBD+ and RBD patients after surgery in this study
Also Check: Parkinsons And Memory Loss
Don’t Miss: When To Take Parkinson’s Medication
