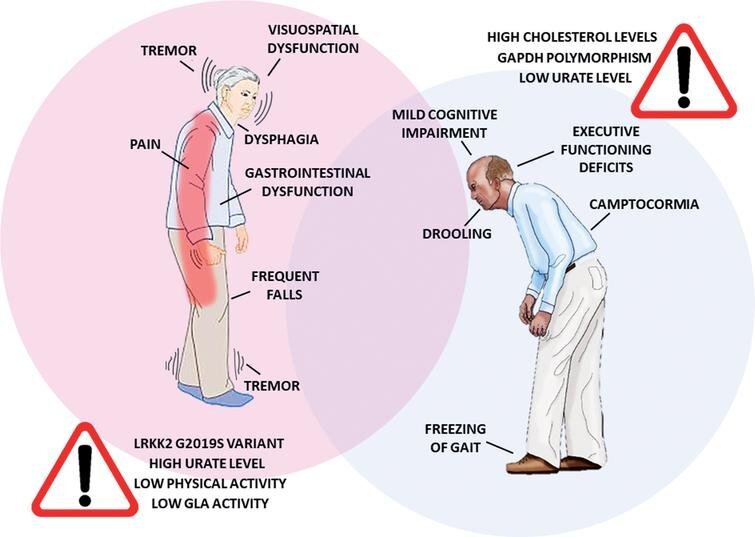
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Propensity Score Matching Results
After propensity score matching, the baseline characteristics between the PD and control groups became equivalent . The distribution of the propensity score after matching was well-balanced and assessed by standardized differences of baseline characteristics . In line with our main results, the risk of AF was significantly higher in the PD group than in the control group . Subgroup analyses were performed using the propensity score-matched population . Significant interaction was consistently observed in the subgroup of patients with hypertension after propensity score matching. The subgroup with diabetes showed significant interaction after matching. However, subgroups with previous stroke and one or more cardiovascular risk factors did not show significant interaction after propensity score matching.
Researchers Trace Parkinson’s Damage In The Heart
- Date:
- University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Summary:
- A new way to examine stress and inflammation in the heart will help Parkinson’s researchers test new therapies and explore an unappreciated way the disease puts people at risk of falls and hospitalization.
A new way to examine stress and inflammation in the heart will help Parkinson’s researchers test new therapies and explore an unappreciated way the disease puts people at risk of falls and hospitalization.
“This neural degeneration in the heart means patients’ bodies are less prepared to respond to stress and to simple changes like standing up,” says Marina Emborg, a University of Wisconsin-Madison professor of medical physics and Parkinson’s researcher at the Wisconsin National Primate Research Center. “They have increased risk for fatigue, fainting and falling that can cause injury and complicate other symptoms of the disease.”
Emborg, graduate student Jeanette Metzger, and colleagues including UW-Madison specialists in cardiology and medical imaging developed a method for tracking the mechanisms that cause the damage to heart nerve cells. They tested the method in the human-like nervous system and heart of monkeys, and published their results today in the journal npj Parkinson’s Disease.
The scans were accurate enough to allow the researchers to focus on changes over time in specific areas of the heart’s left ventricle.
Story Source:
Journal Reference:
Cite This Page:
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
Does Parkinsons Run In Families
Genetics cause about 10% to 15% of all Parkinsons cases. Studies reveal that the appearance of Parkinsons disease is a mix of genetics and environmental factors that induce the development of the disease.
In some families, changes in specific genes are passed down from generation to generation. Yes, Parkinsons disease can run in families, but it is rare. Despite that, if someone is positive for gene mutations directly correlated to Parkinsons disease, that does not mean that the patient will surely develop Parkinsons.
It is possible for people who inherit these genes not to develop the disease if there is no environmental factor that triggers it and a healthy lifestyle.
There are ongoing clinical trials testing therapies to treat people with Parkinsons that carry specific gene mutations. For doctors, it is essential to know which gene mutation does the patient carries.
What The Researchers Did
The research team studied 2909 people recently diagnosed with Parkinson’s and found that:
- More than 60% had a high or medium risk of developing cardiovascular disease over the next 10 years.
- These people tended to be older, and had worse walking and memory compared to those with lower risk.
- Only 27% of these people were taking statins to reduce their risk of experiencing a vascular event, such as a stroke or heart attack.
Also Check: Can U Die From Parkinson’s Disease
I’m Concerned About My Cardiovascular Health What Should I Do
The first thing to do is make an appointment with your GP or practice nurse.
They can carry out an assessment using special computer software that can calculate your risk based on factors including things like age, blood pressure and family history of vascular disease.
If you are at medium or high vascular risk they will be able to discuss the best ways to reduce your risk. These include lifestyle changes to diet and exercise, and possibly medications like statins.
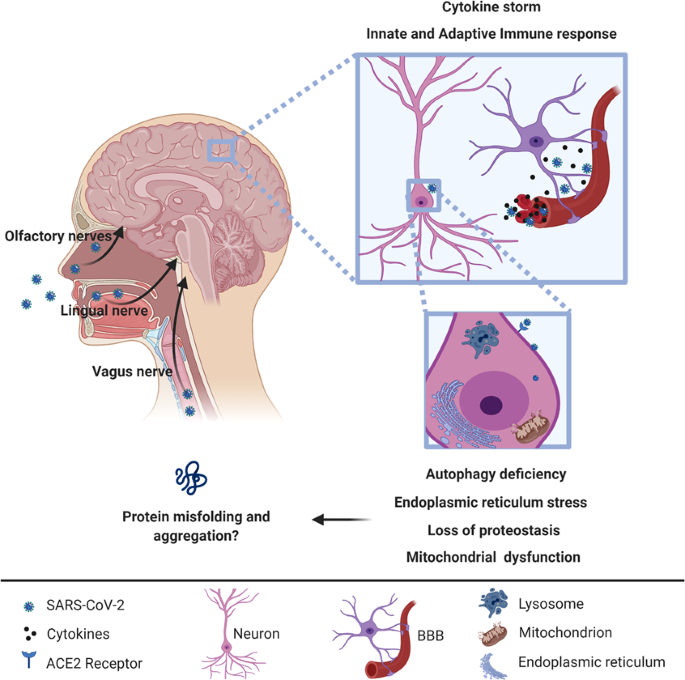
The Spread Of Parkinsons
Researchers have found that areas of the brain stem below the substantia nigra show cell loss in Parkinsons. And cells in these areas have been found to contain clumps of alpha-synuclein protein, which may form before those in the substantia nigra.
These findings have led some researchers to suggest that . Indeed, there is evidence that, for some, Parkinsons may start in the gut and travel up the vagus nerve, which connects the gut and the brain, to the substantia nigra.
The theory that Parkinsons may spread up the brain stem and progress throughout the brain is the basis of the Braak staging of Parkinsons.
The 6 stages in Braaks theory aim to describe the spread of Parkinsons through the brain:
While there is still some debate over the origin of Parkinsons, and even competing and more complex theories about the spread of Parkinsons, attempts to understand how and why different areas of the brain are involved in the motor and non-motor symptoms are helping in the development of better treatments.
You May Like: Average Lifespan With Parkinson’s
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
The Gastrointestinal Effects Of Parkinson’s Disease
Surveys show that between 20% and 40% of people with Parkinson’s disease suffer from serious constipation . Larger numbers of people with PD have related gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, a feeling of fullness and nausea. As the disease progresses, all of these GI problems become more common. In rare cases, serious complicationssuch as megacolon and perforation or tearing of the colonmay arise from these GI problems.
The connection between the two may seem odd on the surface, but research shines some light on these unpleasant consequences of the disease.
A large survey of healthy people who were followed over several years revealed that men who reported having less than one bowel movement daily had a 2 to 7 times higher risk of developing PD than that of men who had daily bowel movements their risk was four times higher than that of men who had two or more bowel movements a day.
Also Check: Levodopa Induced Dyskinesias
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Parkinsons Doesnt Always Cause Dementia
While cognitive decline is common in both Alzheimers and Parkinsons, it is less likely to occur in Parkinsons patients. According to studies, only half of those with Parkinsons develop cognitive difficulties. This can range from mild forgetfulness to full-blown dementia.
When dementia does manifest itself with Parkinson, it occurs in the subcortical area of the brain. Alzheimers dementia occurs in the cortical area of the brain. As a result of this, the clinical symptoms of these two dementias can be somewhat different.
Recommended Reading: Does John Flannery Have Parkinson’s
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Who Develops Parkinson’s Disease
PD mainly develops in people over the age of 50. It becomes more common with increasing age. About 5 in 1,000 people in their 60s and about 40 in 1,000 people in their 80s have PD. It affects men and women but is a little more common in men. Rarely, it develops in people under the age of 50.
PD is not usually inherited and it can affect anyone. However, one type of PD, which appears in the small number of people who develop it before the age of 50, may be linked to inherited factors. Several family members may be affected.
Read Also: Essential Tremor Prognosis
Other Medicines Used For Pd
- Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors are relatively new medicines. They include tolcapone, entacapone and opicapone. These help to stop the breakdown of levodopa by the body, so more of each dose of levodopa can get into the brain to work. A COMT inhibitor is sometimes advised in addition to levodopa when symptoms are not well controlled by levodopa alone.
- Other medicines are sometimes used to help relieve symptoms. They have various effects which try to correct the chemical imbalance in the brain. They include beta-blockers, amantadine and anticholinergic medicines. One of these may be tried when symptoms are mild. However, you are likely to need levodopa or a dopamine agonist at some point.
Various things may influence which medicine is advised. For example, your age, severity of symptoms, how well your symptoms respond to treatment, if side-effects develop, other medicines that you may take, etc. Your specialist will advise on the best medicine for you to take. Whatever medicine or medicines you are prescribed, read the leaflet in the medicine packet for a full list of possible side-effects. Mention to your doctor if you develop a troublesome side-effect. A modification of the dose, dose schedule, or the type of medication, may be possible to help keep side-effects to a minimum.
Bowel Issues In Parkinson’s
Recently, I was doing an interview about Parkinsons troublesome issues and I had to admit that by far my most troublesome and annoying problem is related to the effects of my gut. This is true for the majority of us living with this disease. Whether it be a direct or indirect consequence of our illness is irrelevant in my opinion when the effect is the same. Plus to be honest I am not sure anyone of us can tell the difference most of the time.
As I have re-discovered the agony of suffering from one of these ailments over the last several months when I had several bouts of ileus. In my opinion, there is nothing worse than having stomach pain, bloating, nausea, indigestion, and gas to make life miserable.
Below are all the plausible GI symptoms all of us can experience throughout our journey with PD.1 The most common symptoms are those related to poor motility or dysmotility and can be compounded by the effect of the medication.
You May Like: Does Senator Susan Collins Have Parkinson’s
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Research Is Underway To Further Understand The Cardiac Effects Of Parkinsons
It is possible to image the sympathetic nervous system of the human heart by injecting a radioactive tracer, meta-iodo-benzyl-guanidine, . Development of this technique, known as MIBG cardiac imaging, holds much promise as a test to confirm the diagnosis of PD , to identify those who are at risk of developing PD in the future, and to distinguish PD from related disorders. MIBG cardiac imaging is still considered an experimental procedure for detection of PD and is not yet in use as a clinical tool for this purpose.
A recent research study was conducted in monkeys in which the destruction of the sympathetic nerves of the heart was chemically induced to mimic the changes that are seen in PD. The cardiac system was then imaged using a number of new-generation radioactive tracers, which bind to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. This model system may help to shed light on the molecular changes that accompany the loss of the sympathetic nerves of the heart and can also be used to track the response of the cardiac system to therapeutic agents.
Recommended Reading: Does Dr Phil Mcgraw Have Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
How Quickly Does Parkinsons Progress
Parkinsons disease is slowly progressive, and each case may be different. People may have symptoms for a year or two before a doctor makes a diagnosis.
The longer the symptoms are present, the easier it is to predict how a person with Parkinsons disease will do. In those with tremors and symptoms on one side of the body, the disease typically advances more slowly than in those without tremors who have symptoms that affect both sides of the body.
While the life expectancy of these patients reduces, people with Parkinsons disease usually function quite well for many years. However, these patients are at risk of suffering dementia, or from developing instability that could lead to falls.
This condition is by far the most treatable of all neurodegenerative disorders. A doctor may indicate treatment to help control symptoms.
For example, there are cases where people can function better in their daily lives five years later after they start medication.
The treatment includes exercise and changes in lifestyle. As well as medication with carbidopa-levodopa or dopamine agonists to improve body functionality.
There are surgical options as well, like deep brain stimulation, surgeons implant electrodes in the brain, and they receive electrical pulses, which reduces symptoms.
However, symptoms and responses to treatment vary from person to person, so it is not possible to accurately predict how Parkinsons disease will progress.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal

