Complications Of Pd: Akinetic Crisis
An akinetic crisis or acute akinesia is a life-threatening complication of PD that can be caused by a variety of issues including infections, medication errors, or failed surgery. A patient with AC becomes completely immobile, can no longer speak and no longer swallow. Accompanying symptoms include sweating and fast pulse. Such a crisis is dangerous and must be treated immediately. Without the ability to swallow, saliva can enter the lungs and cause pneumonia.
Are We Close To A Solution
Stem cell treatment for Parkinsons disease is in its infancy. There are certain cancer drugs that can raise dopamine levels in Parkinsons sufferers and may help ameliorate the symptoms until researchers can find more permanent ways of addressing the disease. These drugs, as well as the stem cell therapies described above, are undergoing clinical investigation and will reach a wider audience if they are proven effective and given regulatory approval.
To learn more about the use of stem cells for neurological conditions and other disesases, watch the video below:
If you found this blog valuable, subscribe to BioInformants stem cell industry updates.
How will stem cell therapy help in treating other brain-related diseases? Tell us what you think in the comments below.
Clinical Trials Using Stem Cells For Parkinsons Disease
In 2019, the International Stem Cell Corporation completed enrolment for a stem-cell based clinical trial for the treatment of moderate to severe Parkinsons disease. These stem cells are injected directly into specific areas of the brain which are directly affected in Parkinsons disease.
Initial results from the clinical trial taken from a six-month analysis have revealed that the therapy was safe with no serious adverse events.
Other preclinical studies have also shown that neural stem cells were safe to use and improved motor symptoms, increased dopamine levels and number of neurons in animal models.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson Disease Life Span
New Advanced Stem Cell Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
Nowadays, new advanced stem cell treatment such as Stem Cell Therapy Plus is giving new hope to Parkinsons Disease patients.
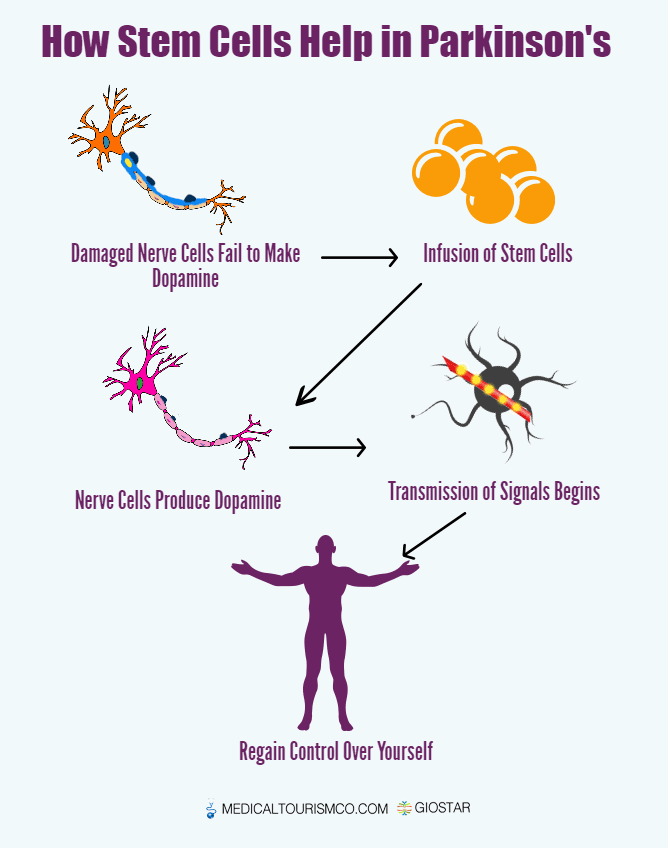
Stem cells are those cells that can easily become the cells of different organs where their need arises. This means that stem cells can evolve into cells of the brain, nervous system and other organ & tissues and so to treat degenerative diseases such as Parkinsons Disease. Stem Cell Therapy is at the heart of a new field of science and medicine called regenerative medicine.
Since stem cells have the unique ability to renew themselves and give birth to generations of cells with different degrees of differentiation, the use of stem cell therapy becomes very encouraging and promising for those who suffer with debilitating diseases. The stem cells can also replace damaged cells in different body parts without any risk of being rejected and without causing any side effects.
Anecdotal evidence shows the stem cells from Stem Cell Therapy Plus can help create dopamine-producing cells which enhance normal communication between neurons and provide a vastly improved quality of life.
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease signs and symptoms can be different for everyone. Early signs may be mild and go unnoticed. Symptoms often begin on one side of your body and usually remain worse on that side, even after symptoms begin to affect both sides.
Parkinsons signs and symptoms may include:
- Tremor. A tremor, or shaking, usually begins in a limb, often your hand or fingers. You may a rub your thumb and forefinger back-and-forth, known as a pill-rolling tremor. Your hand may tremor when its at rest.
- Slowed movement . Over time, Parkinsons disease may slow your movement, making simple tasks difficult and time-consuming. Your steps may become shorter when you walk. It may be difficult to get out of a chair. You may drag your feet as you try to walk.
- Rigid muscles. Muscle stiffness may occur in any part of your body. The stiff muscles can be painful and limit your range of motion.
- Impaired posture and balance. Your posture may become stooped, or you may have balance problems as a result of Parkinsons disease.
- Loss of automatic movements. You may have a decreased ability to perform unconscious movements, including blinking, smiling or swinging your arms when you walk.
- Speech changes. You may speak softly, quickly, slur or hesitate before talking. Your speech may be more of a monotone rather than with the usual inflections./li>
- Writing changes. It may become hard to write, and your writing may appear small.
Recommended Reading: Epidemiology Of Parkinson?s Disease
Signs & Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
A diagnosis of PD is given when a patient develops a rapid accumulation of the alpha-synuclein proteins into the Lewy bodies due to the inadequate activity of neurons and dopamine. Dementia with Lewy bodies is reported as the 3rd leading cause after Alzheimers and Vascular Dementia. The four main symptoms of Parkinsons disease are bradykinesia, rigors, tremors, and postural instability.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s DIsease can include a variety of symptoms that vary in severity and type amongst the affected population. Early signs of the condition can sometimes go unnoticed but as the disease progresses one can expect these symptoms:
- Difficulty speaking
- Difficulty writing
- Loss of automatic movements
- Slowed overall movement
- Muscle stiffness
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Hereditary
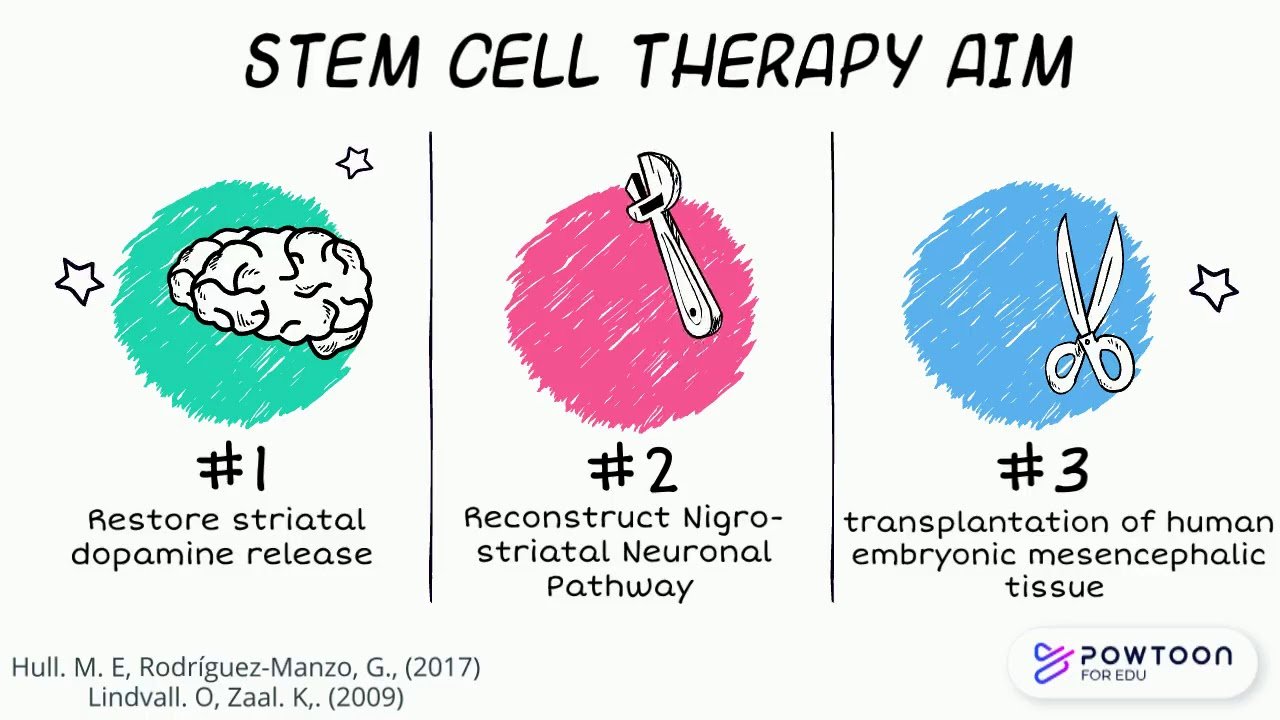
Cell Replacement Therapy For Parkinsons Disease Hurdles And Solutions
A successful cell transplantation has to be safe, well-tolerated by the recipient, and efficacious in reversing the symptoms of disease. It has been extremely well-established that loss of dopamine in the striatum is responsible for PD. Levodopa, which is a dopamine precursor, has been used to treat PD patients since that replaces the dopamine that is lost . Moreover, numerous animal studies have shown that transplanting dopaminergic neurons improves motor symptoms in PD animals . Even though there was sufficient evidence supporting that dopaminergic cells are clinically relevant for cell therapy in PD, there were aspects relating to their safety and reproducibility. Below, we list some of the hurdles that were eventually overcome so that stem cell derivatives can be used in the clinic.
Hurdle 1 deriving the right neural cell type for transplantation
Hurdle 2 eliminating the risk of tumorigenesis
Hurdle 3 transplanting floorplate progenitor cells, fully differentiated SNpc dopaminergic neurons or an intermediate?
Hurdle 4 source of stem cells: autologous or allogeneic? Fetal, ESC or iPSC-derived?
Hurdle 5 how many cells to transplant? Where to transplant?
Current Status Of Clinical Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
PD is the second most common chronic neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimers disease. Currently, the main clinical treatments include drug therapy, surgical treatment, gene therapy, and rehabilitation training. Since the pathogenesis and causative factors of the disease are still unclear, all treatments can only improve the quality of life and work of the patient, but cannot prevent the development of the disease. The outcome is that the patient loses the ability to live. Therefore, continuing to find effective treatments is of great significance to PD.
Read Also: Essential Oils For Parkinsons
Stem Cells For Parkinsons: Therapy And Tools For A Neurological Disorder
This is a guest post from The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinsons Research . MJFF is committed to the pursuit of a Parkinsons cure and better quality of life for those living with the disease today. Stem cells are valuable tools in that work, helping develop new therapies and learn more about the disease. Find out more about the work they do at www.michaeljfox.org.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that affects one in 100 people over age 60. The disease causes a variety of symptoms including motor problems such as tremors, muscle rigidity and slowed movement, and non-motor symptoms of cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and autonomic dysfunction. It is estimated that nearly 1 million people in the United States and more than 6 million worldwide have Parkinsons disease. Current treatments can ease some symptoms, but no available therapies stop or slow the progression of the disease.
Scientists are using stem cells to better understand and treat Parkinsons disease.
Stem Cell TreatmentsIn Parkinsons disease , cells that make the chemical messenger dopamine degenerate and die. Introducing new dopamine cells into the brain may help replace what is lost in PD and reduce its symptoms. Such a treatment also could reduce medication side effects. Long-term use of the most commonly prescribed PD medication and progressing disease can lead to dyskinesia or uncontrolled, involuntary movements.
What Are Stem Cells
The human body is a complex structure, with many complex cells within it. The vast majority of these cells are highly specialized. For instance, it uses muscle fibers to lengthen and contract muscles, creating movement. Brain cells are composed of long axons that transmit messages from nerve to nerve. Heart cells are a specialized form of muscle cell that keeps the ticker ticking away through the long decades.
Of course, these cells have to come from somewhere. Otherwise, a single egg and sperm could never create the entirety of a human body in all its miraculous function. Thats where stem cells come in. They are the bodys master cells, able to differentiate into more specific cells where needed. While many people associate stem cells with embryos, they actually exist in the adult body in many places, including:
- bone marrow
- teeth
- heart and liver cells
These multipotent stem cells are capable of turning into multiple types of cell. While they are not as powerful as pluripotent stem cells those used by fetuses to become every cell in the human body they do have significant potential. Researchers can take these cells and force them backward into a less differentiated state, so they become induced pluripotent stem cells free of controversy, often coming from the patient themselves and able to become any cell needed, including nerves.
Recommended Reading: Cardinal Features Of Parkinson’s
Stem Cells Have Been Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
In 2010, this group published a study with follow-up at the three year point for some of their patients. Now, you must pay attention to how they implanted the cells here, because they did it right. This group used the same brain surgery approach I described earlier for those spaghetti noodle implants, but instead of those implants, these guys placed MSCs from the patients bone marrow in the target area.
very important note:
Every time someone uses stem cells, or a drug, or anything to treat anything in the human body. In order for it to work, they must first figure out how to get it where it needs to go.
So when someone says they want to treat Parkinsons Disease, they need to figure out how to get their treatment into the specific area of the brain where we know the cells are dying.
And thats a challenge. Because the blood-brain barrier is legit. It lets very few things pass. Imagine it as Gandalf just constantly yelling YOU SHALL NOT PASS at almost everything. Including stem cells. Stem cells CANNOT pass the blood-brain barrier. Theyre too big.
So when you read about someone using stem cells to treat Parkinsons Disease, you should be looking for an actual brain surgery to get those cells where they need to be.
end very important note
I know this research sounds cool, and Im hopeful that well see some of the MSC based therapies in the regular world within the next ten years. The results thus far are definitely promising.
Ethics Questions Swirl Around Historic Parkinsons Experiment
They pulled into Cornells driveway two hours late. Kim grabbed the cooler and handed it to a waiting Cornell official, who carried it up to the cell facility. There, a technician loaded syringes with the brain cells. Then Kim saw the cells: They had formed very un-therapeutic-looking clumps. If this had been the day of the actual surgery, it would have been ruinous.
This, Kim thought, is why we do practice runs.
A month later, when the cells journeying from Boston to New York were to actually be transplanted, it seemed that Kims nearly decade-long project was cursed: He learned that Hanscom would be closed on Sept. 5, the day of the surgery. They had to leave from the much busier Logan Airport.
But the air ambulance was wheels up at 5 a.m. and arrived at Weill Cornell at 6:30. Technicians carefully sucked the cells into special syringes, which Song speed-walked to the surgical suite where the neurosurgeon and the patient awaited.
In late 2018, news reports said surgeons in Japan had, that October, performed an experimental procedure that had been on neurologists wish list for more than a decade: transplanting into the brain of a Parkinsons patient replacement cells created from the patients own skin cells using a Nobel-winning protocol. It was, claimed the reports, a first.
It wasnt.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Pathophysiology Of The Disease
Basal ganglia motor circuitry: Parkinson’s disease is predominantly a disorder of the basal ganglia, which are a group of nuclei situated at the base of the forebrain . The striatum, composed of the caudate and putamen, is the largest nuclear complex of the basal ganglia. The striatum receives excitatory input from several areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as inhibitory and excitatory input from the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra pars compacta . These cortical and nigral inputs are received by the spiny projection neurons, which are of 2 types: those that project directly to the internal segment of the globus pallidus , the major output site of the basal ganglia and those that project to the external segment of the globus pallidus , establishing an indirect pathway to the GPi via the subthalamic nucleus . The actions of the direct and indirect pathways regulate the neuronal output from the GPi, which provides tonic inhibitory input to the thalamic nuclei that project to the primary and supplementary motor areas .
Figure 2: Anatomy of basal ganglia. View Figure 2
Two pathways exist within the basal ganglia circuit, the direct and indirect pathways , as follows:
Figure 3: Basal ganglia circuitry in Parkinson’s disease. View Figure 3
â¢In the direct pathway, outflow from the striatum directly inhibits the GPi and SNr striatal neurons containing D1 receptors constitute the direct pathway and project to the GPi/SNr
Common symptoms:
b.Terminates with movement
Patient Services At Anova Institute For Regenerative Medicine
- Located in the center of Germany, quick access by car or train from anywhere in Europe
- Simple access worldwide, less than 20 minutes from Frankfurt Airport
- Individualized therapy with state-of-the-art stem cell products
- Individually planned diagnostic work-up which include world-class MRI and CT scans
- German high quality standard on safety and quality assurance
- Personal service with friendly, dedicated Patient Care Managers
- Scientific collaborations with academic institutions to assure you the latest regenerative medical programs
Strahlenbergerstr. 110
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
How Does Our Stem Therapy Treatment For Parkinsons Disease Process Work
All our stem cell treatments in Mexico are reviewed and administered by subject manner specialist in the area trained in US and Mexico, not just general doctors or physicians, to ensure the highest level of precision, understanding of the condition and quality of treatment for our patients. We are 100% clear and honest with our patients, not everyone is a candidate for our stem cell treatments, we turn-down many patients where the our specialist evaluates the current health condition and medical history and deems not a good fit for the treatment, to avoid false promises or expectations when the risks outweigh the benefits. For this reason and to ensure patient safety in all our treatments, all our patients get evaluated by the specialist before being able to schedule their treatment.
Step 1. Specialist Evaluation For Parkinsons Disease patients, our specialist will need to know the patients age and previous medical treatments. In addition, will need to review specific tests you will be asked to bring.
Step 2. Specialist Phone Consultation Once the specialist has reviewed the medical records and approved your case, we will present options and pricing, at which point we will also offer a free phone consultation to discuss questions and concerns.
Step 5. Treatment Follow-up Our follow up specialist will check in with you according to our follow up calendar for your specific treatment to ensure you have all the tools at your disposal for maximum benefits.
Genetic Testing For Parkinsons
Hereditary neurodegenerative diseases occur when genetic mutations are passed from the parents to their children. A genetic disease, however, can be due to environmental causes or hereditary. Random mutations can cause some genetic conditions in the DNA due to environmental factors or exposure to toxins. Familial PD accounts for less than 15% of all confirmed cases. Inherited parkinsonism is either an X-linked dominant pattern or autosomal recessive pattern. Each parent carries one copy of the mutated gene, but often do not show any signs or symptoms of the condition. For this reason, autosomal recessive PD can often be misdiagnosed dementia with Lewy bodies, multiple system atrophy or ALS/MND. The most common genetic markers used for screening hereditary Parkinsons include LRRK2, Glucocerebrosidase , RIC3, PARK2, PARK6, PARK7, SYNJ1, PTRHD1, TMEM230, UCHL1, DNAJC6, CYP2D6, VPS13C, PODXL, DNAJC13, CHCHD2, and RAB39B. Recent research also suggests that abnormalities in tau proteins are also a potential cause of familial parkinsonism and frontotemporal dementia.
The Regeneration center offers gene sequencing tests for 18 of the most common genes causes associated with Parkinsons disease and monogenic parkinsonism related conditions. The genes we can test for include: SLC6A3, LRRK2, DNAJC6, FBXO7, GCH1, PARK7, VPS35, PINK1, PRKRA, PRKN, SNCA, SPR, TH, CHCHD2, MAPT, ATP13A2, ATP7B & DCTN1
TREATMENT PRECAUTIONS & RISKS
Recommended Reading: Is Sugar Bad For Parkinson’s Disease
Can Stem Cell Therapy Cure Parkinsons Disease
Benefits from stem cell treatment for Parkinsons Disease can vary from patient to patient depending on many factors including current health condition, medical history, level of damage and other factors. It is important to understand that although the use of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell injections for damaged neurons and autonomic function has shown some of the highest efficacy for treating this condition, patients undergoing this treatment should not create the false expectation of a guaranteed cure.
- Paseo de los Héroes 10999 – 309, Zona Urbana Rio Tijuana, 22010 Tijuana, B.C.
- +1-800-646-0290
