How Is Parkinsons Disease Tested And Diagnosed
At Banner Health, our neurologists have years of experience in testing and diagnosing Parkinson’s disease. Our team of compassionate experts knows that each patient is different, so we work with you to quickly find the right diagnosis to begin building your treatment plan.
Parkinsons is not simple to diagnose. No test exists to diagnose Parkinsons disease. Doctors test and diagnose Parkinsons based on your medical history, symptoms and neurological and physical exams.;
Many times a primary care provider is the first to suspect a Parkinsons diagnosis. If youre experiencing symptoms such as tremors, shaking, slow movement, stiffness and/or trouble with balance, talk to your doctor or seek the opinion of a neurologist. Banner Health neurologists are movement disorder specialists, who have experience and specific training to assess and treat Parkinsons.
What Is Essential Tremor And How Is It Different To A Parkinsons Tremor
A tremor is a rhythmical, involuntary movement that affects a part of the body, such as the hand.
Essential tremor is the most common type of tremor. Its most noticeable when your hands are doing something and it usually affects both the right and left sides of the body equally. Essential tremors often lessen when your body is resting.;
Unlike an essential tremor, a Parkinsons tremor is most obvious when the affected body part is resting and tends to be less noticeable with movement. It usually starts on one side of the body and may progress to the other side as Parkinsons develops.
The time it takes to get a diagnosis can vary from person to person. Some people may receive a diagnosis of Parkinsons quite quickly, but for others it may be a long process. This can be due to a number of things, including your medical history, your age and what symptoms you have.
Your specialist may wish to rule out other causes of your symptoms first and see how you respond to treatment. This may take some time, and, as already mentioned, there is currently no definitive test;for Parkinsons.
How you respond to treatment may help your specialist make a diagnosis. Keeping a diary or record of your symptoms will give the specialist more information to guide their decision.
Because the symptoms of Parkinsons are sometimes similar to other forms of parkinsonism, people can sometimes be misdiagnosed.;
What Are My Next Steps
If your doctor doesnt diagnose Parkinsons, they can help you find out what the best next step is depending on what condition they suspect. In some cases, treatment may be as simple as changing the dosage of a medication that may be leading to Parkinsons-like symptoms.
Receiving a Parkinsons diagnosis can be overwhelming. If your diagnosis is confirmed, contact a movement disorder specialist as soon as possible. A specialist can help you develop a strategy to delay the onset of more severe disease and manage symptoms youre already experiencing.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Autoimmune
Ological Limitations Of The Diagnostic Studies
When interpreting the literature about diagnosis, the following methodological issues should be considered:
- lack of long-term prospective clinical and pathological as a reference standard
- lack of operational definitions such as defining specialists or clinical diagnostic criteria
- unclear whether investigators were blinded to initial diagnosis
- sample sizes necessarily limited by the number of cases available with neuropathological outcomes
- trial age groups are often young as studies were performed by neurologists who see a younger population of people with PD
- most studies included people with established disease lasting some years
- varying geographical locations
- some studies are in specialised units and may not reflect the diagnostic accuracy of other units in the UK
- exclusion of some studies using magnetic resonance volumetry and magnetic resonance spectroscopy as they lacked appropriate population, intervention and outcome criteria
- lack of statistical details of diagnostic accuracy such as sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive values
- lack of economic evaluations of SPECT.
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease

Parkinsons occurs when neurons in the part of the brain that control body movement become impaired or die. These neurons are responsible for creating dopamine, an important brain chemical that is vital for normal body function.
With fewer of these neurons in the brain, insufficient dopamine is created. Scientists are still not sure what exactly causes these neurons to become impaired or die.
People with Parkinsons also lose nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system that controls heart rate and blood pressure. This could be why fatigue and a decrease in blood pressure regularly occur with people who have Parkinsons.
While there have been cases of the disease that appear to be hereditary and can be traced to specific genetic mutations, there isnt enough evidence yet to conclusively prove it is passed down from parents to their children.
Most cases of Parkinsons occur randomly, and researchers believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors are responsible.
Also Check: How Is The Family Of A Person With Parkinson’s Affected
Imaging And Lab Tests
Your doctor may order some imaging tests and laboratory tests. Imaging tests can include computed tomography scans and magnetic resonance imaging scans. Laboratory tests can include blood tests and urine tests.;
While these tests and scans will not help diagnose Parkinsons disease, they can help rule out other conditions that have similar symptoms.;
Your doctor may also suggest that you get a dopamine transporter scan . This scan requires a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner. It involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug so that your doctor can study the dopamine systems in your brain .;
While a DaTscan cannot conclusively prove that you have Parkinsons, it can help confirm your doctors diagnosis and eliminate other conditions.;
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that progresses over time. It harms the neurons, or nerve cells, in your brain, causing them to slowly die off. The area of the brain that PD mainly affects helps control and coordinate your bodys movements, from running to walking to climbing stairs, or even writing a letter. As PD gets worse, muscle movement, control, and coordination become more and more difficult.
Much of this damage is caused by dopamine loss, the feel-good chemical in the brain that serves many important functions in your body. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps the brain send signals to your central nervous system and, from there, to the muscles in your body. The messages that dopamine carries tell the body when and how to move. But as PD progresses, brain cells keep dying. The result: less and less dopamine gets produced and daily activities become harder to perform. It’s this decline in function, including difficulty moving or walking, that often sends people to their doctors, seeking a diagnosis and eventual treatment.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when;brain cells that make dopamine, a chemical that coordinates movement, stop working or die. Because PD can cause tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems, it is called a movement disorder. But constipation, depression, memory problems and other non-movement symptoms also can be part of Parkinsons. PD is a lifelong and progressive disease, which means that symptoms slowly worsen over time.
The experience of living with Parkinson’s over the course of a lifetime is;unique to each person. As symptoms and progression vary from person to person, neither you nor your doctor can predict which symptoms you will get, when you will get them or how severe they will be. Even though broad paths of similarity are observed among individuals with PD as the disease progresses, there is no guarantee you will experience what you see in others.
Parkinsons affects;nearly 1 million people in the United States;and;more than 6 million people worldwide.
For an in-depth guide to navigating Parkinsons disease and living well as the disease progresses, check out our;Parkinsons 360 toolkit.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Dr. Rachel Dolhun, a movement disorder specialist and vice president of medical communications at The Michael J. Fox Foundation, breaks down the basics of Parkinson’s.
What Is The Prognosis For Parkinsons Disease
The rate at which Parkinsons progresses varies from patient to patient. Some patients experience its changes over 20 years or more. While others find the disease advances quicker.
Parkinsons is not a fatal disease. However, secondary complications from symptoms may increase falls, blood clots or pneumonia, which can be life-threatening. These are more common in later stages of Parkinsons.
In general, the average life expectancy of Parkinson’s patients is similar to people without the disease.;
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
The Problem Of Missed Diagnosis Or Misdiagnosis
If widely circulated, this skin test could potentially cause a spike in the number of successful diagnoses made every year.;
Parkinsons disease is not straightforward to diagnose because diagnosis is based on clinical evaluation, meaning the patient history and physical exam, Miocinovic says. So one has to suspect Parkinsons disease in order to ask the right questions and test for specific disease signs. And early on, symptoms may not clearly point to Parkinsons disease.
Many early symptoms of Parkinsons are dismissed as byproducts of the aging process. In some cases, they are even attributed to another epidemiological cause entirely.;Some of these symptoms include:
- Constipation
- Restless leg syndrome
- Reduced sense of smell
Sometimes other disorders early on can mimic Parkinson’s, with a couple of the disorders that commonly are mistaken for Parkinson’s being progressive supranuclear palsy, or PSP, or multiple system atrophy, or MSA, because sometimes early in the course, they can look very similar to Parkinson’s, Simon says. Even movement disorder specialists who think it’s Parkinson’s early in the course aren’t right as often as we’d like to think we are.;
This wide margin of error has immense ramifications for the work of the neuroscientists who study the disease in the hope of developing successful treatments.;
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
If youre concerned that you or a loved one may have Parkinsons disease, be sure to consult a neurologist who specializes in movement disorders like PD.
Theres no blood test or other specific test that will tell your doctor that you have the disease, however you will likely still undergo blood and other laboratory tests, possibly including brain scans, to rule out other causes of your symptoms. After that, your doctor must make whats called a clinical diagnosis, reviewing your current health and symptoms in order to determine if you have PD.
Because the disease moves slowly and symptoms develop gradually, its not uncommon for doctors to first test someone with Parkinsons after theyve had the disease for one to three years, and sometimes longer, according to a neurologist on our pro panel.
Read Also: What Causes Dyskinesia In Parkinson’s
Why Genetic Testing For Parkinsons Disease Is Complex:
- There are many genes that are associated with the development of PD. This list continues to grow as more genes are discovered. Testing of only some of these genes is available in commercial labs.
- The majority of people with PD, even those with a family history of PD, do not harbor one of these identified abnormal genes. The genetic contribution to PD in these people is yet to be discovered.
- For a particular gene there may be a number of different mutations associated with disease, some of which are more common than others. Commercial testing may identify only the most common of the mutations, and therefore not capture everyone who carries a disease-causing mutation.
- Conversely, only particular mutations in a gene may be associated with disease. Commercial testing may identify changes in a gene that may not have clinical consequences. This can be confusing for patients who even after genetic testing may not know whether they harbor a disease-causing mutation.
- Different mutations can be enriched in different ethnic populations. For example, Ashkenazi Jews and North African Berbers have an increased risk of carrying Leucine rich repeat kinase 2 mutations. Glucocerebrosidase mutation frequency also varies greatly with ethnicity and is also increased among Ashkenazi Jews.
In addition to the above, it is important to realize that not all genes associated with PD contribute to disease in the same way:
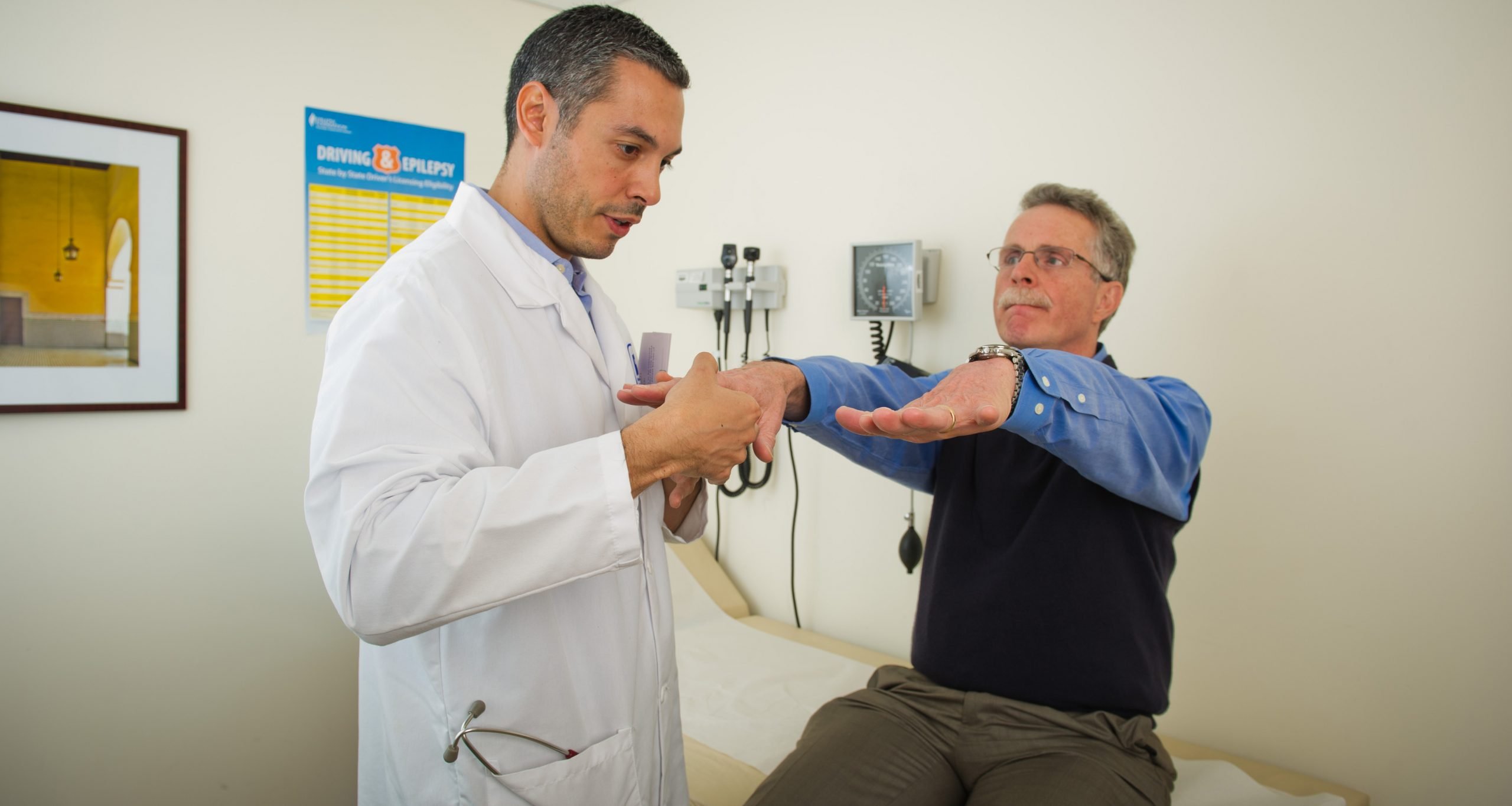
Physical And Neurological Examination
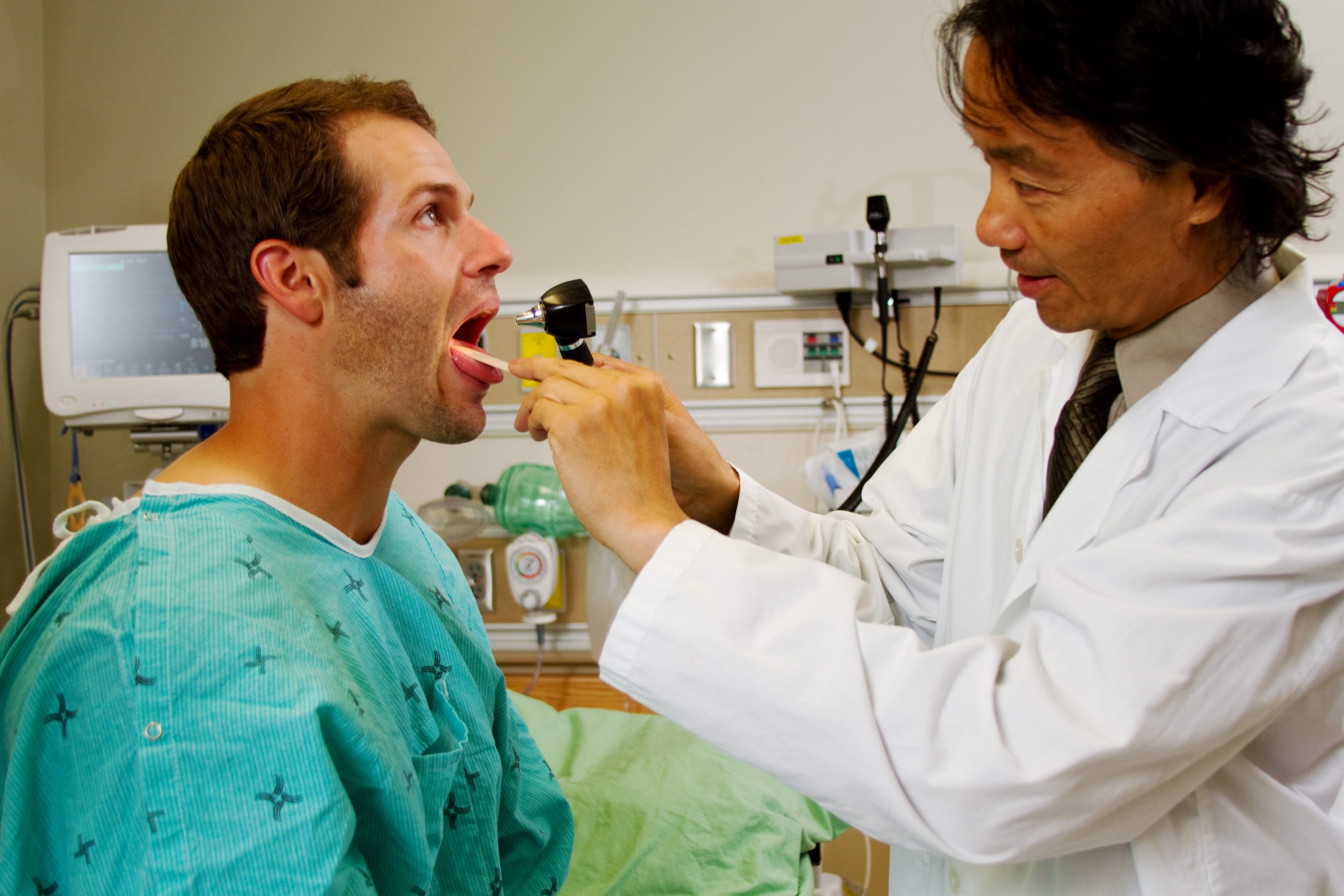
Your doctor will conduct a physical and neurological examination. This can involve observing your behavior, movements, and mental state and conducting tests or asking you to perform certain exercises.;
These are some of the symptoms of Parkinsons your doctor can determine visually:
- Fewer spontaneous movements or hand gestures
- Reduced frequency of blinking
- Tremors in your hands while they are at rest, often only in one hand
- Hunched posture or forward lean while walking
- Stiff movements
These are some of the exercises your doctor may ask you to do to evaluate your movements, balance, and coordination:
- Opening and closing your fist
- Tapping your fingers, toes, and heels
- Holding your arms out in front of you
- Moving your finger from one point to another
- Rotating your wrists or ankles
- Standing from a chair
Also Check: Essential Oils And Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Managed
Your doctors will tailor your treatment based on your individual circumstances. You will manage your condition best if you have the support of a team, which may include a general practitioner, neurologist, physiotherapist, occupational therapist, psychologist, specialist nurse and dietitian.
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, symptoms can be treated with a combination of the following.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
Don’t Miss: Does Diet Soda Cause Parkinson’s
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
As Parkinsons disease progresses, deep brain stimulation surgery may become an option. Our team is one of the most experienced in the United States. Under the direction of Dr. Delaram Safarpour, Dr. Kim Burchiel, an OHSU neurosurgeon, pioneered asleep DBS so you dont have to be awake during surgery.
For this procedure, our team places tiny electrodes in your brain. The electrodes are connected to a small pacemaker-like device placed under the skin of your chest. The device sends mild electrical pulses to regulate movement and control Parkinsons symptoms such as:
- Tremors
- Slowness
- Imbalance
In some parts of the state, you can have follow-up care at a doctors office in your community.
Colin Halstead had deep brain stimulation surgery at OHSU to treat his Parkinsons. It gave me my life back, he says.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Also Check: What Color Is The Ribbon For Parkinson’s
Tests To Rule Out Other Conditions
Blood tests can help rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
An MRI or CT scan can check for signs of a stroke or brain tumor, which may cause similar symptoms.
Hydrocephalus due to atrophy can occur with some types of dementia and would be visible with one of these imaging tests. If the person has neurologic symptoms but a normal scan result, Parkinsons disease may be present.
The doctor a lumbar puncture to rule out inflammation or a brain infection.
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Also Check: What Is Life Expectancy Of Parkinson’s Patients
