Dementia And Young Onset Parkinson’s
In this 1-hour webinar movement disorders specialist, Rodolfo Savica, MD, explains that YOPD is not the same disorder as older-onset PD.; Generally speaking, people with YOPD have the same life expectancy and develop the same types of dementia at the same ages as the general population.; He offered tips for coping with YOPD, like taking higher doses of dopamine medications during vigorous exercise or stressful times of day.
Possible Risk Reduction Factors
While age, genetics, and being a man make it more likely you’ll develop Parkinson’s disease, some factors make it less likely. It is generally believed that;Asian-Americans and African-Americans seem to have a lower risk of developing Parkinson’s as compared to Caucasians. Drinking coffee may lower risk, as a 30-year study of Japanese-American men found the greater amount of coffee they drank, the lower their risk of Parkinson’s disease became.;
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
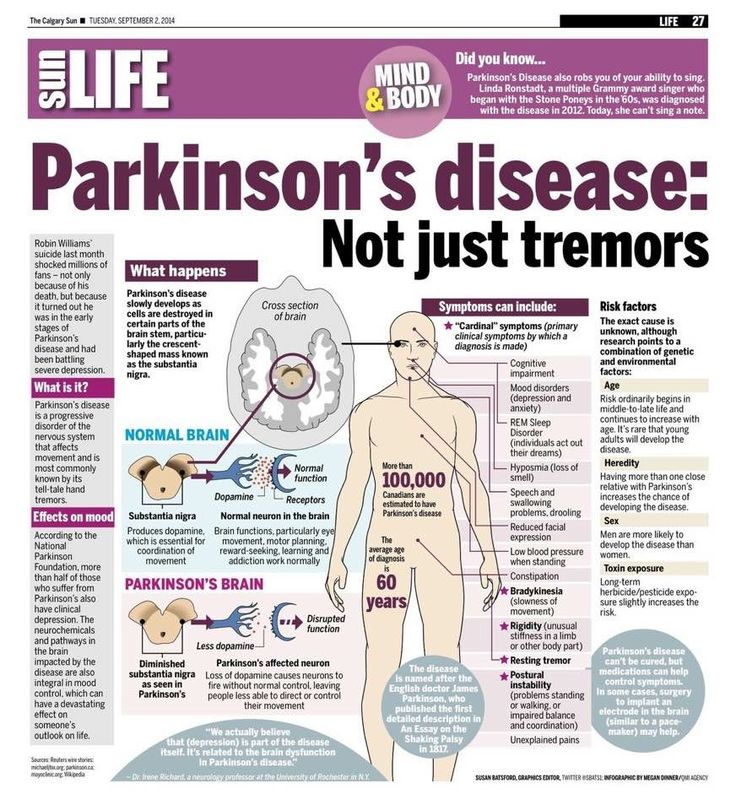
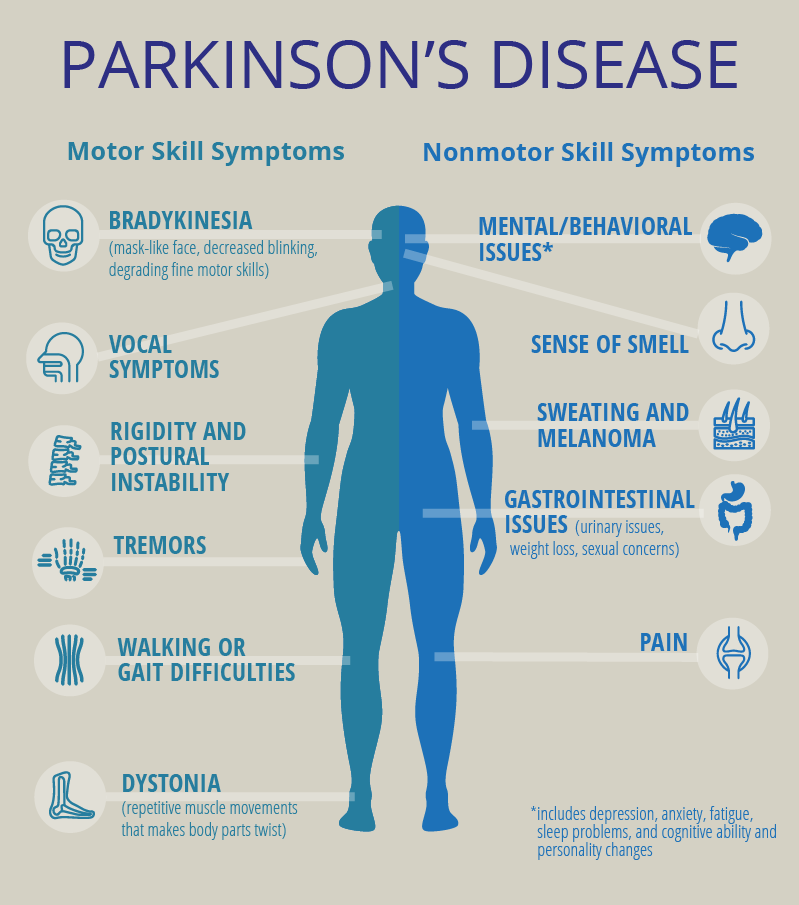
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder and the most common movement disorder. Characteristics of Parkinsons disease are progressive loss of muscle control, which leads to trembling of the limbs and head while at rest, stiffness, slowness, and impaired balance. As symptoms worsen, it may become difficult to walk, talk, and complete simple tasks.
The progression of Parkinson’s disease and the degree of impairment vary from person to person. Many people with Parkinson’s disease live long productive lives, whereas others become disabled much more quickly. Complications of Parkinsons such as falling-related injuries or pneumonia. However, studies of patent populations with and without Parkinsons Disease suggest the life expectancy for people with the disease is about the same as the general population.
Most people who develop Parkinson’s disease are 60 years of age or older. Since overall life expectancy is rising, the number of individuals with Parkinson’s disease will increase in the future. Adult-onset Parkinson’s disease is most common, but early-onset Parkinson’s disease , and juvenile-onset Parkinson’s disease can occur.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Ribbon Color
Treating Early Onset Parkinsons Disease
Although no cure exists, identifying symptoms and determining a proper course of treatment helps many Parkinsons patients;to remain active and lead fulfilling lives. Carbidopa/levodopa is usually prescribed for Parkinsons disease. However,;early onset Parkinsons patients;are;more likely to develop side effects from this treatment, such as or involuntary movements at the medicines peak effect, and cramping as the effect wears off.
For this reason, physicians often treat movement symptoms in people newly diagnosed with early onset Parkinsons disease with other types of drugs, such as anticholinergics, monoamine oxidase B inhibitors, and dopamine agonists.
Parkinsons News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
In Silico Prediction Analysis

To predict the potential pathogenicity of genetic variants, in silico prediction analysis was performed according to the American college of medical genetics and genomics guideline . Multiple sequence alignment of PLA2G6 protein sequences from different species was performed by ClustalX program to test the gene evolutionary conservation. Three in silico algorithms, including Mutation Taster , PolyPhen-2 , and Mutation assessor , were used to predict the effect of mutations on PLA2G6 function. Possible changes of the splice sites were predicted using NNSplice program encoded in Mutation Taster program. 3-D protein structures of both wild and variant type PLA2G6 protein were predicted using an ab initio modeling server, I-TASSER program , which were then viewed and edited by the molecular visualization system PyMOL . The missense variant was classified as Benign , Likely benign , Uncertain significance , Likely pathogenic , and Pathogenic using the automated pathogenicity tool, InterVar software , which can generate the preliminary interpretation according to the ACMG guideline. The splice site variant was evaluated manually based on the ACMG guideline.
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s
Young Onset Parkinson’s: A Conversation Of Our Unique Needs
In this one-hour video, a panel of people with Young Onset Parkinson’s Disease discuss the challenges faced by those with YOPD. The panel features Larry Gifford, famous for his podcast “When Life Gives You Parkinson’s,” Dr. Soania Mathur, a member of Parkinson Canada’s Medical Advosory Council, Tim Hague, who won the first Amazing Race in Canada after being diagnosed, and Omotola Thomas, founder of ParkinStand.
Yopd Council Webinar Series
Offered the third Thursday of every month from 12p-1p PT, this series of moderated panel discussions with members of the YOPD Council focuses on topics related to issues unique to people living with YOPD.; The panel shares experiences and resources, and answers questions from attendees.; Recent topics include Sex, Love, and Dating & PD, Work, Money, Meaning & PD, Disability, Insurance & PD, and more.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How Can Someone With Parkinsons Benefit From Exercise
The number one benefit of exercise for someone with a Parkinsons diagnosis is;symptom management. Studies have shown that rather than being sedentary, engaging in any level of physical activity can be beneficial. Certain activities can address specific Parkinsons disease symptoms, like performing walking exercises to help with gait. It has also been shown that increased mobility can lead to improvements in cognition and memory and reduce the risk of falls. Symptoms that lead to a Parkinsons diagnosis typically appear when the dopamine-producing neurons in the brain begin to deteriorate.;
Seven Signs Of Early Onset Parkinsons
There are a series of symptoms that can alert us to the early onset of Parkinsons disease. There are more signs, but were going to focus on these seven:
- Sleep disorders. The most common disorders are insomnia , restless legs syndrome, and REM sleep behavior disorder.
- Depression. This is one of the first symptoms to appear and is in fact considered an early indicator of the disease.
- Other mood changes. In addition to depressive symptoms, anxiety and apathy are very common. These symptoms can negatively influence the desire to seek help and resolution.
- Cognitive changes. Many people with early onset Parkinsons usually find it difficult to do more than one thing at once. Poor task execution, slower thinking speed, attention and concentration problems, memory problems, and dementia are all symptoms of early onset Parkinsons.
- Tremors. Although they usually start in the hands, they start in the jaw or on the feet in other patients. The most characteristic thing about these tremors is that they occur at rest.
- Bradykinesia. This is a gradual loss of spontaneous movement. General movement simply slows down. This is one of the most disabling and frustrating symptoms for those affected.
- Fatigue.;With early onset Parkinsons, the patient feels tired all the time without having exerted themselves at all.
Recommended Reading: Average Life Expectancy With Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
Whats Different About Young
The age of diagnosis matters for a variety of reasons, from probable causes of early cases to symptoms and treatment:
- Genetics.;As with any case of Parkinsons disease, the exact cause is usually unknown. That said, The young-onset cases of Parkinsons disease are, on average, a bit more likely to be familial or genetic, says Gregory Pontone, M.D., director of the Johns Hopkins Movement Disorders Psychiatry Clinic.
- Symptoms.;In many patients with YOPD, dystonia is an early symptom. People with YOPD also report more dyskinesia . They also tend to exhibit cognitive problems, such as dementia and memory issues, less frequently.
- Progression.;Patients with young-onset Parkinsons appear to have a slower progression of the disease over time, says Pontone. They tend to have a milder course, staying functional and cognitively intact for much longer.
- Treatment.;Most patients with Parkinsons take the medication levodopa. However, other drugs, such as MAO-B inhibitors, anticholinergics, amantadine, and dopamine receptor agonists, may be used before levodopa.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
Chapter And Author Info
- Laboratory of Neurobiology, Department of Neurology, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poland
Wojciech Kozubski
Jolanta Dorszewska*
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.80400
Dopamine And Pathogenesis Of Parkinsons Disease
Dopamine is the organic chemical of the catecholamine family and precursor for noradrenaline. It is synthesized in presynaptic neuron from tyrosine to L-dihydroxyphenylalanine via tyrosine hydroxylase. Subsequently, aromatic amino acid decarboxylase removes a carboxyl group, form neurotransmitter, which is packed into synaptic vesicles. DA is released into the synapse during stimulation, actives dopaminergic receptors, and evokes a response in the postsynaptic cell . It plays a pivotal role in the generation of normal movements by transmission information from SN to the striatum, where movements are initiated and controlled facility and balance .
The pathomechanism of PD is progressive and subsequent degeneration of neurons in SN, which results in the decreased level of DA in the dopaminergic neurons. Further, there is also the presence of Lewy bodies , intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusion bodies, in others neurons in SN. The literature indicates that loss of 6070% of dopamine neurons in SN is presented as PD motor symptoms . Pathogenesis of PD involves both environmental and genetic factors. It is thought that the pathways involved in PD are impairment of cellular clearance pathways, protein aggregation, oxidative stress, mitochondria dysfunction, and neuroinflammation .
Figure 1.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Who Gets Early Onset Parkinsons Disease
About 10%-20% of those diagnosed with Parkinsons disease are under age 50, and about half of those are diagnosed before age 40. Approximately 60,000 new cases of Parkinsons are diagnosed each year in the United States, meaning somewhere around 6,000 12,000 are young onset patients.
Is it genetic or hereditary?
The cause of Parkinsons disease is not yet known. However, Parkinsons disease has appeared across several generations of some families, which could indicate that certain forms of the disease are hereditary or genetic. Many researchers think that Parkinsons disease may be caused by genetic factors combined with other external factors. The field of genetics is playing an ever greater role in Parkinsons disease research, and scientists are continually working towards determining the cause or causes of PD.
Genetic Risk Factors For Early
The etiology of EOPD is not completely explained. It seems that genetic factors, environmental factors, or both of them may play an important role in the pathogenesis of this disease. There have been identified several genes and their mutations associated with EOPD, but new loci are still being identified. Most of these genes are inherited autosomal recessive, for example, PRKN, PINK1, or DJ1, but some of them are associated with the autosomal dominant pattern, for example, SNCA
You May Like: How To Help Someone With Parkinson’s
Researchers Say They Have Clue To Early
Patients with early-onset Parkinson disease may have been born with disordered brain cells that mishandled dopamine for decades, according to a study released Monday.
A study published Monday, focusing on patients with Parkinson disease who developed the nervous system disorder before the age of 50, says these individuals may have been born with disordered brain cells that went undetected for decades.
To perform the study, researchers at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and UCLA generated special stem cells, known as induced pluripotent stem cells , from cells of 3 patients with young-onset Parkinson disease; the patients were aged 30-39 and had no known familial history of PD or PD mutations.
The process involved taking adult blood cells back to a primitive embryonic state. These iPSCs can then produce any cell type of the human body, all genetically identical to the patient’s own cells. The team used the iPSCs to produce dopamine neurons from each patient and then cultured them in a dish and analyzed the neurons’ functions.
The researchers detected 2 key abnormalities in the dopamine neurons:
- Accumulation of alpha-synuclein, a protein that occurs in most forms of Parkinson disease
- Malfunctioning lysosomes, cell structures that help the cell to break down and dispose of proteins; in this case, the malfunction could cause alpha-synuclein to build up.
Reference
Treatments For Early Onset Parkinson’s Disease
The treatments for any case of Parkinsons disease are the same. Here are the treatments:
1.;;;;;; Levodopa- Carbidopa
Levodopa is one of the first lines of treatments for Parkinsons disease. The levodopa goes into the brain where it is changed into dopamine. The carbidopa which is combined with Levodopa prevents the levodopa from being changed too soon outside the brain. Carbidopa also helps with some of the side-effects including nausea, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Levodopa effects may wear off with long-term use and cause other side-effects like involuntary movements. This drug is available for oral use and by infusion.
2.;;;;;; Dopamine Agonist Medications
Dopamine agonists act like dopamine inside your brain. They tend to be less effective but the effects last longer. They are often given with levodopa to make it work better. Side-effects includeincreased sexuality, addictive behavior, hallucinations, and lethargy.
3.;;;;;; MAO-B Inhibitors
These stop your brain from breaking down dopamine. They inhibit a chemical in the brain called monoamine oxidase B that reduces the amount of dopamine you have available. Side-effects include inability to sleep and nausea. This medication should not be used with carbidopa-levodopa as this combination can cause hallucinations. They also cannot be taken with anti-depressant medications.
4.;;;;;; Catechol-O-methyltransferase Inhibitors
5.;;;;;; Anticholinergics
6.;;;;;; Amantadine
7.;;;;;; Deep Brain Stimulation
Recommended Reading: Dementia And Parkinsons Disease
Stooping Or Hunching Over
Are you not standing up as straight as you used to? If you or your family or friends notice that you seem to be stooping, leaning or slouching when you stand, it could be a sign of Parkinson’s disease .
What is normal?If you have pain from an injury or if you are sick, it might cause you to stand crookedly. Also, a problem with your bones can make you hunch over.
Trouble Moving Or Walking
Do you feel stiff in your body, arms or legs? Have others noticed that your arms dont swing like they used to when you walk? Sometimes stiffness goes away as you move. If it does not, it can be a sign of Parkinson’s disease. An early sign might be stiffness or pain in your shoulder or hips. People sometimes say their feet seem stuck to the floor.
What is normal?If you have injured your arm or shoulder, you may not be able to use it as well until it is healed, or another illness like arthritis might cause the same symptom.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Hereditary
Parkinsons Disease Has Many Stages
There are five stages of Parkinsons disease:
- Stage 1: At this stage, you will have only mild symptoms and can go about your day-to-day life relatively easily.
- Stage 2: Symptoms such as tremors and stiffness begin to worsen and affect both sides of the body. You may develop poor posture or have trouble walking.
- Stage 3: In this stage, your movement will begin to slow down and you lose balance. Symptoms can hinder your ability to perform daily tasks such as getting dressed or cooking.
- Stage 4: Symptoms are severe and cause significant issues with day-to-day living. At this point, you are unable to live alone because you cannot complete daily tasks on your own.
- Stage 5: Walking or standing could be impossible at this point. Typically, people at this stage are confined to a wheelchair or bed and require a nurse to take care of them at home.
A Life Changing Diagnosis
About 10 to 20 percent of those diagnosedwith PD are under age 50, and about half of those are diagnosed before age 40.Approximately 60,000 new cases of Parkinsons are diagnosed each year in theUnited States, meaning somewhere around 6,000 to 12,000 of those diagnosed areyoung onset patients.
Whatsets young onset Parkinsons apart from a diagnosis at an older age? Becausethe majority of people who get PD are over the age of 60,;the;diseaseis often overlooked in younger people, causing many to go undiagnosed ormisdiagnosed for extended periods of time. However, once it has beendiagnosed,;the rate of the diseases progression is usually much slower inyounger than older people, due in part to the fact that younger people havefewer general health problems and are more capable during physical therapytreatment.
Another difference is that people in this younger age bracket are often parenting younger children, in the midst of their careers, perhaps single and dating. Aside from their physical symptoms, their lifestyle priorities and demands are typically different from someone who is diagnosed in their 60s or 70s. For this reason, there are support groups geared towards people with young onset PD so they can focus on the concerns that are particular to their age group.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Heritability
Medications For The Disease Are Toxic
There are several medications available for Parkinsons disease, but the most commonly used is Sinemet . It is designed to restore levels of dopamine in the brain. The medication works well, but a myth that it was toxic began circulating and is still somehow commonly accepted. The truth is as long as the medicine is being used properly and the dose is where it should be, it is completely safe and can benefit people with Parkinson’s disease.
