Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Studies that satisfy one or more of the following criteria and used machine learning methods were included:
Classification of PD from healthy controls ,
Classification of PD from Parkinsonism and multiple system atrophy ), and
Classification of PD from other movement disorders ).
Studies falling into one or more of the following categories were excluded:
Studies related to Parkinsonism or/and diseases other than PD that did not involve classification or detection of PD ,
Studies not related to the diagnosis of PD ,
Studies related to the diagnosis of PD, but performed analysis and assessed model performance at sample level ,
Classification of PD from non-Parkinsonism ,
Study did not use metrics that measure classification performance,
Study used organisms other than human ,
Study did not provide sufficient or accurate descriptions of machine learning methods, datasets or subjects used used),
Not original journal article or conference proceedings papers , and
In languages other than English.
What Should I Expect During The Mri
As the MRI scan begins, you will hear the equipment making a variety of banging, clanging and muffled thumping sound that will last for several minutes. None of them are anything other than annoying. Other than the sound, you should experience no unusual sensations during the scanning.
Certain MRI exams require an injection of a contrast material. This helps identify certain anatomic structures on the scan images.
Please feel free to ask questions. Tell the technologist or the doctor if you have any concerns.
Comparing Studies With Different Objectives
In the 132 studies that proposed or tested novel machine learning methods , a majority used data from publicly available databases . Data collected from human participants were used in 41 studies and the two remaining studies used commercially sourced data or data from both existing public databases and local participants specifically recruited for the study. Out of the 77 studies that used machine learning models in clinical settings , 52 collected data from human participants, 22 used data from public databases. Two studies obtained data from a database and a local cohort, and 1 study collected data postmortem.
Data Modality
In methodology studies, the most commonly used data modalities were voice recordings , movement , and MRI data . For studies on clinical applications, MRI data , movement , and SPECT imaging data were of high relevance. All studies using CSF features focused on validation of existing machine learning models in a clinical setting .
Number of Subjects
The average sample size was 137.1 for the 132 methodology studies . For 41 out of the 132 studies that used data from recruited human participants, the average sample size was 81.7 . In the 77 studies on clinical applications, the average sample size was 266.2 . For 52 out of the 77 clinical studies that collected data from recruited participants, the average sample size was 145.9 .
You May Like: Do Dogs Get Parkinson’s
Early Signs Of Parkinson’s
Early physical signs include the common motor symptoms: tremor, muscle rigidity and slowness. They may also include the following:
- Symptoms starting on one side of the body
- Change in facial expression
- Failure to swing one arm when walking
- Stooped posture
- Loss of sense of smell
- Depression or anxiety
Some of these symptoms are quite common and by no means exclusive to Parkinsons, so if you have some of them, it does not mean you have Parkinsons.
What Are The Stages Of Parkinsons
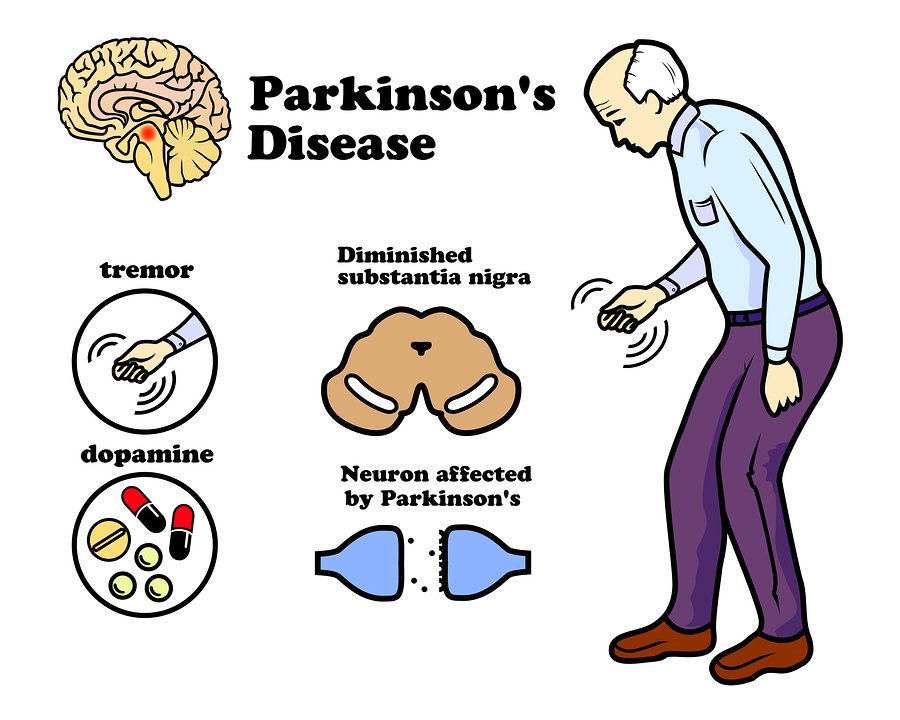
Neurologists often use a system of stages, called the Hoehn and Yahr scale, to describe the progression of symptoms. These stages are:
- Stage 1 Symptoms are seen on one side of the body only.
- Stage 2 Symptoms are seen on both sides of the body. There’s no impairment of balance.
- Stage 3 Balance impairment has begun. In this mild to moderate stage of the disease, the person is still physically independent.
- Stage 4 This stage is marked by severe disability, but the person is still able to walk or stand unassisted.
- Stage 5 The person is wheelchair-bound or bedridden unless assisted.
You May Like: When Was Parkinson’s Disease Discovered
The Evolution Of Treatments
The history of Parkinson’s disease is tightly linked to therapeutic interventions, ranging from serendipitous observations to controlled clinical trials of specifically designed agents.
Parkinson devoted a chapter of his monograph to considerations respecting the means of cure . In humility and perhaps with a vision toward current concepts of neuroprotection, he hoped for the identification of a treatment by which the progress of the disease may be stopped . To this end, he advocated very early therapeutic intervention when signs were largely confined to the arms without balance and gait impairments. Reflecting therapeutic approaches of the early nineteenth century, Parkinson recommended venesection, specifically advocating bloodletting from the neck, followed by vesicatories to induce blistering and inflammation of the skin. Small pieces of cork were purposefully inserted into the blisters to cause a sufficient quantity of purulent discharge . All these efforts were designed to divert blood and inflammatory pressure away from the brain and spinal cord, and in this way, decompress the medulla that Parkinson considered the seat of neurological dysfunction.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
We do not know what causes Parkinsons disease. There is some evidence to suggest that there is a genetic factor which increases the risk of Parkinsons disease within some families. Also, there might be an increased risk if people have come into contact with a particular toxin or toxins found in the environment via pesticides and other chemicals used in agriculture. The specific toxin or toxins have not yet been identified but there is ongoing research into this possible cause.
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
S For Detecting Parkinsons Disease:
1) Import Libraries
Firstly we will import all the required libraries which have been shared in the prerequisites section.
Code:
#load all modules for Parkinson's Disease Detection Projectimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_errorimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn import treefrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
2) Preprocessing
Read the parkinsons.csv file in dataframe using the pandas library
Code:
#read csv file of parkinson's datasetdf=pd.read_csv
dataset file :
Fetch the features and targets from the dataframe. Features will be all columns except name and status. Therefore we will drop these two columns. And our target will be status column which contains 0s and 1s
Code:
#extract features but we don't want 'name' and 'status' columns#so we will drop these two columns and store remainings#axis 1 is for columnsfeatures = df.drop#our target data will be 'status'target = df.loc
3) Normalization
We will scale our feature data in the range of -1 and 1. Scaling is important because variables at different scales do not contribute equal fitting to the model which may end up creating bias. For that we will be using MinMaxScaler to fit and then transform the feature data.
Code:
4) Training and Testing
Code:
5) Building the classifier model
Random forest example:
Code:
Mri Brain Scans Detect People With Early Parkinson’s
Oxford University researchers have developed a simple and quick MRI technique that offers promise for early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.
The new MRI approach can detect people who have early-stage Parkinson’s disease with 85% accuracy, according to research published in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
‘At the moment we have no way to predict who is at risk of Parkinson’s disease in the vast majority of cases,’ says Dr Clare Mackay of the Department of Psychiatry at Oxford University, one of the joint lead researchers. ‘We are excited that this MRI technique might prove to be a good marker for the earliest signs of Parkinson’s. The results are very promising.’
Claire Bale, research communications manager at Parkinson’s UK, which funded the work, explains: ‘This new research takes us one step closer to diagnosing Parkinson’s at a much earlier stage one of the biggest challenges facing research into the condition. By using a new, simple scanning technique the team at Oxford University have been able to study levels of activity in the brain which may suggest that Parkinson’s is present. One person every hour is diagnosed with Parkinson’s in the UK, and we hope that the researchers are able to continue to refine their test so that it can one day be part of clinical practice.’
We think that our MRI test will be relevant for diagnosis of Parkinson’s
Dr Michele Hu
Don’t Miss: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Brain Mri Advances For Parkinsons Disease
In Parkinsons disease, the damage to brain cells begins long before any symptoms develop. Therefore, at-risk patients can benefit from early diagnosis, and efforts to slow the progression of the disease can start early.
Researchers are working on newer MRI approaches to precisely detect Parkinsons disease-related structural and metabolic activity in the brain and correlate it to the function of the organ. For example, scientists from Oxford University used a technique called the resting-state functional MRI to assess the strength of nerve cells in the a region of the brain called the basal ganglia to send and receive information. Because the physical signs of brain cell damage in Parkinsons disease are not recognizable by conventional MRI, this approach may help visualize the impact of the damage on the activity of brain cells and aid in early diagnosis.
Similarly, MRI is used to identify Parkinsons disease-specific biomarkers. Tracking the biomarkers using high-field and ultra-high field MRI can identify Parkinsons disease patients and help follow the progression of the condition.
Although many of these advancements are yet to be implemented in the clinical setting, such adaptations may help better understand the disease and develop new treatments.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy For Someone With Parkinson Disease
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
How Is Parkinson’s Diagnosed
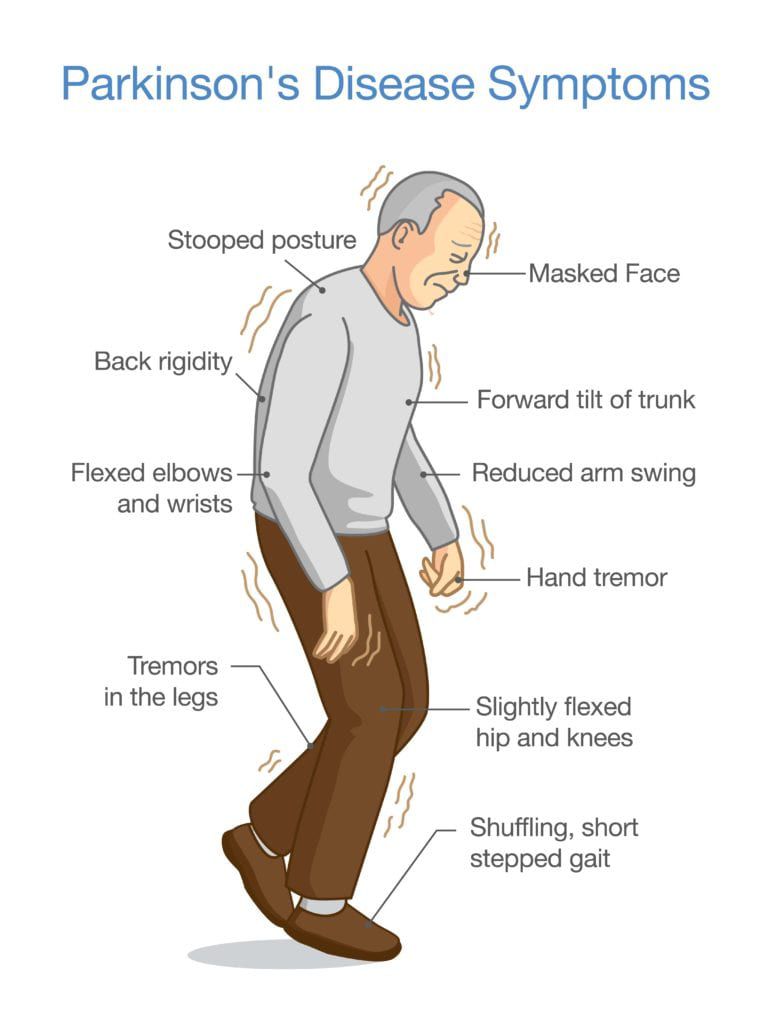
Current evidence suggests that Parkinsons tends to develop gradually. It may be many months, even years, before the symptoms become obvious enough for someone to go to the doctor.
This information looks at what parkinsonism is, how Parkinsons and other similar conditions may be diagnosed, and explains some of the tests that may be involved in the process.
Parkinsonism is a term used to describe symptoms or signs that are found in Parkinsons, but which can also be found in other conditions that cause slowness of movement, stiffness and tremor.
Most people with a form of parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinsons disease, also known as Parkinsons. Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
Other less common forms of parkinsonism include multiple system atrophy , progressive supranuclear palsy , drug-induced parkinsonism and vascular Parkinsons.
If youre concerned about symptoms youve been experiencing, you should visit your GP. If your GP suspects you have Parkinsons, clinical guidelines recommend they should refer you quickly to a specialist with experience in diagnosing the condition .
Its not always easy to diagnose the condition. So its important that you see a Parkinsons specialist to get an accurate diagnosis and to consider the best treatment options.
Diagnosing Parkinsons can take some time as there are other conditions, such as essential tremor , with similar symptoms. There is also currently no definitive test for diagnosing Parkinsons.
Don’t Miss: Yopd Life Expectancy
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when brain cells that make dopamine, a chemical that coordinates movement, stop working or die. Because PD can cause tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems, it is called a movement disorder. But constipation, depression, memory problems and other non-movement symptoms also can be part of Parkinsons. PD is a lifelong and progressive disease, which means that symptoms slowly worsen over time.
The experience of living with Parkinson’s over the course of a lifetime is unique to each person. As symptoms and progression vary from person to person, neither you nor your doctor can predict which symptoms you will get, when you will get them or how severe they will be. Even though broad paths of similarity are observed among individuals with PD as the disease progresses, there is no guarantee you will experience what you see in others.
Parkinsons affects nearly 1 million people in the United States and more than 6 million people worldwide.
For an in-depth guide to navigating Parkinsons disease and living well as the disease progresses, check out our Parkinsons 360 toolkit.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Dr. Rachel Dolhun, a movement disorder specialist and vice president of medical communications at The Michael J. Fox Foundation, breaks down the basics of Parkinson’s.
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.
You May Like: How To Take Mannitol For Parkinson’s
Data Source And Sample Size
In 93 out of 209 studies , original data were collected from human participants. In 108 studies , data used were from public repositories and databases, including University of California at Irvine Machine Learning Repository , Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative , PhysioNet , HandPD dataset , mPower database , and 6 other databases .
Table 2. Source of data of the included studies.
In 3 studies, data from public repositories were combined with data from local databases or participants . In the remaining studies, data were sourced from another study , collected at another institution , obtained from the authors’ institutional database , collected postmortem , or commercially sourced .
The 209 studies had an average sample size of 184.6 , with a smallest sample size of 10 , and a largest sample size of 2,289 . For studies that recruited human participants , data from an average of 118.0 participants were collected . For other studies , an average sample size of 238.1 was reported . For a description of average accuracy reported in these studies in relation to sample size, see Figure 2C.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Change Your Personality
Looking For Signs Of Parkinsons
Your specialist will examine you to look for common signs of Parkinsons. You may be asked to:
- write or draw to see if your writing is small or gradually fades
- walk to see whether theres a reduction in the natural swing of your arm or in your stride length and speed
- speak to see if your voice is soft or lacks volume
The specialist will also look at and ask you about your:
- face to see if there is a masked look or if you have difficulty with facial expressions
- limbs to see if you have a tremor, any stiffness or slowness of movement
As well as examining you for any of the typical signs of Parkinsons, the specialist will also look for signs that may suggest a different diagnosis.
It may be helpful to take someone with you for support when seeing a specialist. Taking a list of questions you want to ask can also be useful so you dont forget to mention something you want to know about. If a healthcare professional says something you dont understand, dont be afraid to ask them to explain what they mean.
