Whats The Difference Between Dystonia And Dyskinesia
Both dystonia and dyskinesia affect your muscles and joints; however, there are distinct differences between them that require unique treatments. Dystonia is a movement disorder that can occur with or without a Parkinsons diagnosis, while dyskinesia is often a side effect people experience as a result of taking Parkinsons medications. Though both involve similar abnormal movements of the arms, legs, neck, and face, dystonia is characterized by more sustained muscle contractions and pain.
What Do Researchers Know About Dystonia
Researchers believe that dystonia results from an abnormality in or damage to the basal ganglia or other brain regions that control movement. There may be abnormalities in the brains ability to process a group of chemicals called neurotransmitters that help cells in the brain communicate with each other. There also may be abnormalities in the way the brain processes information and generates commands to move.;In most cases, no abnormalities are visible using magnetic resonance imaging or other diagnostic imaging.;
The dystonias can be divided into three groups:; idiopathic, genetic, and acquired.
Idiopathic dystonia;refers to dystonia that does not have a clear cause.; Many instances of dystonia are idiopathic.;
There are several;genetic;causes of dystonia. ;Symptoms may vary widely in type and severity even among members of the same family. In some instances, people who inherit the defective gene may not develop dystonia.;Having one mutated gene appears to be sufficient to cause the chemical imbalances that may lead to dystonia, but other genetic or even environmental factors may play a role.;Forms of dystonia for which the genetic cause is known include:
Recently, researchers have identified other genetic causes of dystonia, including one resulting from mutations in the DYT6 gene.;Dystonia caused by DYT6 mutations often presents as cranial dystonia, cervical dystonia, or arm dystonia. Rarely, a leg is affected at the onset.;
Dystonia Or Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps and dystonia occur when one of your muscles, or a group of muscles, tightens or shortens involuntarily.
Muscle cramps and dystonia can be confusing as they can feel very similar. You may not always be able to tell the difference between them, but they are caused by separate problems and are therefore treated differently.
Muscle cramps in Parkinsons are generally caused by muscular rigidity and reduced movement rather than by muscles contracting. But, like dystonia, cramps can also be painful and very distressing.
Normal painkillers do not usually relieve them, but cramps often respond well to massage and the use of a hot water bottle or heated pad. Movement and exercise may also help to release cramps and reduce stiffness. If these do not help, then your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
What Are The Symptoms
Dystonia can affect many different parts of the body and the symptoms are different depending upon the form of dystonia. Symptoms may include:
- a foot cramp or a tendency for one foot to turn or drageither sporadically or after running or walking some distance
- a worsening in handwriting after writing several lines
- the neck may turn or pull involuntarily, especially when the person is tired or under stress
- both eyes might blink rapidly and uncontrollably; other times, spasms will cause the eyes to close
- tremor
- difficulty speaking
The initial symptoms can be very mild and may be noticeable only after prolonged exertion, stress, or fatigue.;Over time, the symptoms may become more noticeable or widespread; sometimes, however, there is little or no progression.
In some cases, dystonia can affect only one specific action, while allowing others to occur unimpeded. For example, a musician may have dystonia when using a hand to play an instrument, but not when using the same hand to type. ;
Dystonia may cause pain due to muscle contractions but typically is not associated with problems thinking or understanding. Depression and anxiety may occur.
Prolonged Ssrt In Pd Patients
In our study we observed that both RT and ocSSRT were significantly prolonged in PD compared to healthy volunteers. Interestingly, in healthy controls RT and ocSSRT showed a trend towards positive correlation, whereas these measures were uncorrelated in PD. In agreement with our findings, Gauggel et al. compared the stop signal task in 32 patients with PD and 31 orthopaedic controls. The extent of bradykinesia was unrelated to SSRT in PD, but in the orthopaedic controls initiation speed could explain some of the variance in time taken to inhibit action. It is likely that some common processes influence both response speed and stopping, and that these vary across healthy individuals to generate a weak correlation. However, the pathological processes which lead to slowing in RT and SSRT appear separable.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
What Dystonia Looks Like In Pd
The involuntary muscle movements of dystonia can be subtle or very noticeable. They may manifest as:
-
Blepharospasm , squinting or repeated blinking
-
Grimacing or repeated jaw clenching
-
Thin, hoarse or shaky voice
-
Twisting of the neck into an abnormal posture
-
Twitching and cramping of the hands, fingers, feet or toes
If you experience symptoms of cervical dystonia, you should notify your doctor right away. Keeping a log of your dystonia symptoms can be helpful in finding the right treatment.
S Of The Body Affected By Dystonia
- Arms, hands, legs and feet: Involuntary movements, spasms or twisting and “curling”
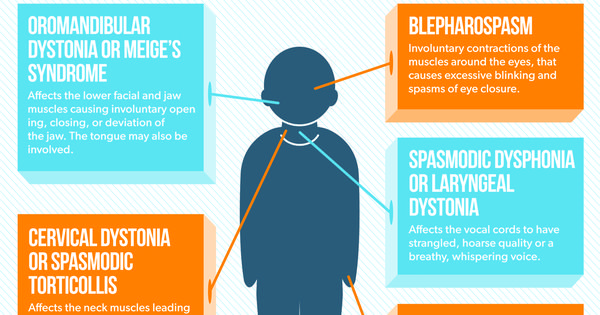
- Neck: May twist uncomfortably, causing the head to be pulled down or to the side. This is called cervical dystonia or spasmodic torticollis
- Muscles around the eyes: May squeeze involuntarily, leading to a person to blink too much or to have difficulty opening the eyes. This is also called blepharospasm
- Vocal chords and swallowing muscles: May cause a person’s voice to sound softened, hoarse or breathy
- Jaw: May open or close forcefully or there may be grimacing of the face
- Abdominal wall: May cause sustained contractions and involuntary, writhing movements of the abdominal wall
Read Also: Parkinson’s How Long To Live
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
When Can Dystonia Occur
Each persons experience with Parkinsons and dystonia is unique. Dystonia can occur unexpectedly or during repetitive actions, such as writing or golfing. It can be brief or prolonged. It can occur as a response to your levodopa therapy, even if your medication is working optimally. And, it can occur at different times throughout the day or can be cyclical.;
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Parkinson’s Disease To Progress
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Population And Study Procedure
The study was conducted in the movement disorders laboratory of a tertiary care referral centre in Eastern India. Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Institute of Neurosciences, Kolkata; written informed consent was taken from all participants. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulation of the ethical approval.
The study was conducted in three parts.
Experiment 1: We measured optimal combination SSRT and average SSRT in 20 healthy subjects. Thereafter, the reliability of these measures was estimated by a repeat measurement in 14 subjects after a one-month interval; the remaining 6 healthy subjects were not available for retest. All healthy participants had no apparent neurological disease, were free from any uncontrolled systemic disease, and were not taking any neurotropic medications. None were colour blind by self-report and all had normal visual acuity . There was no history of substance abuse disorder or head injury.
Recommended Reading: What To Buy Someone With Parkinson’s
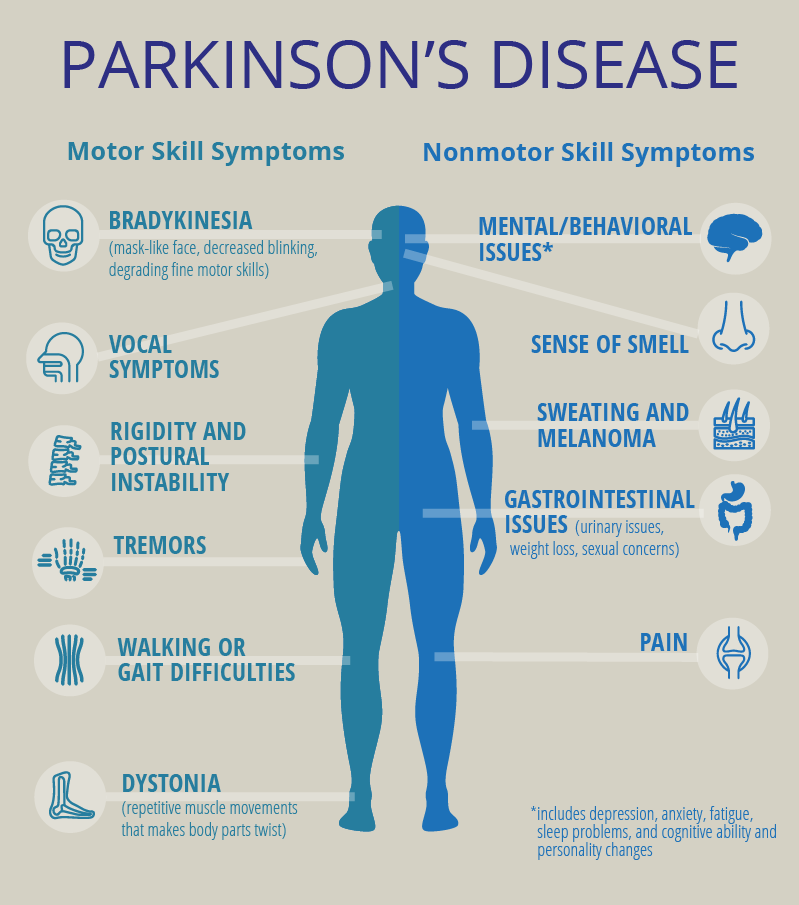
Dystonia In Parkinsons Disease
Dystonia refers to a condition in which the muscles repeatedly contract or twist involuntarily, leading to movement and postural abnormalities. Dystonia can affect a single muscle, a group of muscles, or the whole body. These symptoms can occur on their own or as a symptom of another disorder, such as Parkinsons disease. Dystonia does not always indicate a person has PD, and not every person with Parkinsons will experience dystonia.
When dystonia does occur in PD, it frequently affects the feet and toes. A significant portion of people with Parkinsons disease awake with painful cramping in one or both feet. Dystonic Parkinsons disease also can cause a rare condition called cervical dystonia . Cervical dystonia causes involuntary in the neck that cause painful misalignment of the spine. Fortunately, the vast majority of people with PD will not develop this type of dystonia.
Other Causes Of Dyskinesia And Dystonia
There are many types of dystonia unrelated to Parkinsons disease. Many forms of dystonia occur with no known cause. Some causes of dystonia are hereditary, while brain injury can also cause dystonia.
Huntingtons disease is a rare, genetic condition in which nerve cells in the brain degenerate over time. This disease causes movement disorders similar to Parkinsons, including chorea and dystonia.
Multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy are other rare, degenerative disorders that affect muscle movements. Dyskinesia can occur when people with MSA or PSP are treated with levodopa, and untreated MSA or PSP can lead to the development of dystonia.
Also Check: Does Lack Of Sleep Cause Parkinson’s
How Might Dystonia Be Experienced
- Feet: people with Parkinsons mainly experience dystonia in their feet. Typically the toes curl up into a claw-like position, the foot turns inwards at the ankle, and occasionally the big toe sticks up. This position, caused by spasms in the calf muscles, can be very uncomfortable and makes it hard to fit feet into tight shoes.
- Hands: writers cramp in the hands only occurs during handwriting.
- Neck: cervical dystonia affects the neck muscles, which causes the head to twist to one side, forwards or occasionally backwards.
- Eyelids: the eyelid muscles may contract and make the eye close involuntarily . This is often experienced as excessive blinking, intolerance to light, a burning feeling in the eye or irritation.
- Vocal cords: dystonia affecting the vocal cords or speech muscles makes speaking difficult or strained.
- Jaw area and side of the face:oromandibular dystonia affects the jaw area, tongue, mouth or one side of the face. The jaw may be pulled either open or shut, and speech and swallowing can be difficult.
Prolonged Ssrt In Focal Dystonia Patients
We also observed prolonged SSRT in CD and WC patients compared to healthy participants. The result in WC is in agreement with previous work, which demonstrated a lower rate of response inhibition in patients with task specific focal hand dystonia. It is intriguing that we additionally found elevated SSRT in CD, as our task involved releasing a button with the hand as a response; the hand was not affected by the dystonia in these individuals. The size of the increase in SSRT was actually larger in CD than in WC , emphasising that congruence between the muscles used to respond in the task and those involved in the dystonia was not an important factor. Even in WC, our results were surprising as the response movement required by the task did not induce dystonia, which was specific to writing. It seems likely that these patients have a more general underlying pathology in networks for response inhibition, which is unrelated to the nature of the focal presentation of the dystonia itself.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Parkinson’s Disease To Progress?
How To Manage Dystonia
Dystonia can be treated in many of the same ways as dyskinesia, such as with dopaminergic medications and DBS. However, there are other ways to manage this condition, including Botox , physical therapy to work the dystonic muscles, or anticholinergic medications.
Botox is most well known for its cosmetic uses, such as for decreasing wrinkles. However, it can also be used to manage dystonia. This toxin comes from the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, which interferes with the chemical acetylcholine, used by nerve endings in muscles to send messages. When this communication is interrupted, the muscles are weakened, which can alleviate certain symptoms of Parkinsons.
Similar to botulinum toxin, anticholinergic medications can be used to interfere with acetylcholine signaling between the nerves and muscles. These include Artane , Parsitan , and Cogentin .
Exercise Stretch And Strengthen
- Even if you dont feel like it, exercising every day can increase flexibility in your muscles and joints, reduce pain and discomfort, and improve circulation. Exercise can increase the secretion of your happy hormones, improve your mood, and decrease anxiety and depression.
- If you have discomfort in your calves, ankles, feet, or toes, and;try the eight exercises physical therapist Sarah King recommends.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Different Forms Of Dystonia
There are many different forms of dystonia. Within Axis I, some are grouped by the regions of the body which they affect:
- Generalized dystonia affects most or all of the body.
- Focal dystonia is localized to a specific part of the body.
- Multifocal dystonia involves two or more unrelated body parts.
- Segmental dystonia affects two or more adjacent parts of the body.
- Hemidystonia involves the arm and leg on the same side of the body.
Some of the more common focal forms are:
Cervical dystonia,;also called;spasmodic torticollis;or;torticollis, is the most common of the focal dystonias. The muscles in the neck that control the position of the head are affected, causing the head to turn to one side or to be pulled forward or backward. Sometimes the shoulder is pulled up.;Cervical dystonia can occur at any age, although most individuals first experience symptoms in midlife. It often begins slowly and usually reaches a plateau over a few months or years. About 10 percent of those with torticollis may experience a spontaneous remission, but unfortunately the remission may not be lasting.
Blepharospasm,;the second most common focal dystonia, is the involuntary, forcible contraction of the muscles controlling eye blinks. The first symptoms may be increased blinking, and usually both eyes are affected. Spasms may cause the eyelids to close completely, causing functional blindness even though the eyes are healthy and vision is normal.
Is Dystonia A Form Of Parkinson’s
Dystonia can be one of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease . PD is a long-term neurological movement disorder with various symptoms ranging from slowness of movement , rigidity of muscles, tremor, loss of balance, memory impairment, personality changes and others. In young-onset PD, foot dystonia may be the first feature. Later, other symptoms such as personality changes and memory impairment become noticeable.;
Dystonia may sometimes develop as an isolated symptom in individuals who do not have PD. It may be seen in people who suffer from Huntingtons chorea, birth injury, stroke, brain infections, etc. Sometimes, a person with Parkinsons may develop dystonia due to the drug Leva Dopa that is given as a part of PD treatment.
Dystonia is a neurological disorder that purely affects movement and is characterized by involuntary contractions of the muscles causing repetitive or twisting movements or abnormal postures. Dystonia can occur in isolation or as a symptom of PD. It, however, does not affect everyone with PD.
Both PD and dystonia seem to occur due to the involvement of a part of the brain called the basal ganglia. Thus, the symptoms of both can occur in the same person.
Read Also: Average Life Expectancy Of Parkinson’s Patients
When Do Symptoms Occur
Dystonia can occur at any age, but genetic and idiopathic dystonia are often divided as either early, or childhood onset, versus adult onset.;
- Early onset dystonia often begins with symptoms in the limbs and may progress to involve other regions. Some symptoms tend to occur after periods of exertion and/or fluctuate over the course of the day.
- Adult onset dystonia usually is located in one or adjacent parts of the body, most often involving the neck and/or facial muscles.;Acquired dystonia can affect other regions of the body.;
Dystonia often progresses through various stages. Initially, dystonic movements may be intermittent and appear only during voluntary movements or stress. Later, individuals may show dystonic postures and movements while walking and ultimately even while they are relaxed. Dystonia can be associated with fixed postures and shortening of tendons.
What Causes Dystonia In Parkinson’s Disease

The exact disease processes that cause dystonia remain unknown, but it likely is caused by dysfunction in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that is also affected in Parkinsons. The basal ganglia are a group of neurons located deep in the brain that process information on movement and play an important role in planning actions to achieve specific goals, such as using hands to catch a ball or write with a pen. The basal ganglia work in cooperation with the cortex to signal and activate muscles.2,3
Dystonia may be classified as primary, secondary, or dystonia-plus. In primary dystonia, the dystonia is the only neurological disorder the individual has. Secondary dystonia results from a specific external factor, such as trauma, infections, stroke, or as a side effect from some medications. Dystonia-plus includes dystonia experienced by people with PD, as well as dystonia that results from other neurological disorders.1
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
