Be Your Own Health Advocate
Every drug carries risks.The Save Institute recommends avoiding prescriptions drugs except in matters of life and death. The dire, life-altering consequences of DIP are a striking example of why this recommendation is so important for maintaining your health.
Do your own research about the potential side effects of any drug, and always seek a natural remedy instead of a synthetic drug. In the case of osteoporosis and osteopenia, reversal is possible through a combination of diet, exercise and bone-healthy lifestyle choices.
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing vascular Parkinsonism starts with a thorough review of your current symptoms and medical history, including your family medical history. A physical examination and a review of your current medications are also necessary.
To make sure your doctor gets an accurate diagnosis, brain imaging is critical. A 2019 scholarly review article suggests that an MRI of the brain can help determine whether your symptoms are caused by vascular Parkinsonism or PD. An accurate diagnosis is an important step in getting the most effective treatment.
Other brain imaging, such as a CT scan, can also be helpful for detecting signs of small strokes in the regions of the brain responsible for movement and muscle control.
Frequency Of Asymmetry In Parkinsonism
Symmetry of parkinsonism was evaluated for all measurements of parkinsonism in the upper and/or lower limb , as shown in Table 3. The mean symmetry index was 0.13 , which was the highest for the bradykinesia items: 0.16 . Asymmetric parkinsonism was present in 84 of the measurements.
Table 3. Symmetry of UPDRS motor scores in the measurements with parkinsonism in the upper and/or lower limba .
Also Check: How Long Do Parkinson’s Patients Live
How Is Drug Induced Parkinsonism Different From Parkinsons Disease
Is it possible to distinguish drug induced parkinsonism from Parkinsons Disease on clinical grounds?
Drugs are one of the most common causes of parkinsonism in the general population.
Drugs that block postsynaptic dopamine receptors and/or deplete presynaptic dopamine may cause parkinsonism.
Clinical studies indicate that drug-induced parkinsonism is indistinguishable from Parkinsons Disease.
Discontinuation of the offending drug promotes remission of the syndrome in most cases, although sometimes the parkinsonism persists.
Such patients may have subclinical Parkinsons Disease and require dopaminergic therapy. DaTSCAN is a useful tool to differentiate between Parkinsons Disease and drug-induced parkinsonism.
Biological Basis Of Iatrogenic Movement Disorders

The biological basis of the movement disorders is complex. However, those listed above as secondary to medication are characterised by the action of drugs on central nuclei and in particular pathways and nuclei associated with the basal ganglia, a functional unit located at the base of the forebrain.
The basal ganglia have principal connections to the cortices and thalamus. Although involved in multiple functions including cognition and emotional function, it is their role in the control of involuntary movements that is relevant to this chapter. The other functions, though, are clinically important and discussed elsewhere in this book. At rest, the structures of the basal ganglia can be considered to provide a tonic inhibition of motor activity. This inhibition is released through conscious activity via an increased release of dopamine from the substantia nigra, thereby allowing voluntary control of motor activity in the necessary area.
However, cholinergic pathways elsewhere are involved in cognition, vigilance and emotional modulation and degenerate in Parkinsons disease while anticholinergic medication may therefore be associated with an improvement in movements, it is at the expense of deterioration in cognition in this disease, as well as in patients with psychosis, where anticholinergic medication may additionally mediate confusion and psychotic symptoms.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Tremors Caused By Medications
In addition to drug-induced parkinsonism, which includes rest tremor and is caused by medications that block the dopamine receptor, there are also a wide variety of medications that do not block the dopamine receptor, but can cause other types of tremors, such as postural and action tremors. So if you have these types of tremors, but without the slowness, stiffness and other PD-like symptoms, you could have drug-induced tremor .
A postural tremor occurs when a body part is held against gravity. Postural tremors occur for example, when the arms are extended, such as when holding a tray. An action tremor occurs when a body part is moving. Action tremors occur for example, when the arm is moving toward the mouth to eat.
Drug-induced tremors typically are symmetric or equal on both sides of the body. The medications that can cause tremor include, but are not limited to, lithium, valproic acid, amiodarone, beta-adrenergic agonists, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors . Be attentive to whether a tremor starts after any new medication is started. If it does, discuss this with your doctor.
Dip Can Easily Be Misdiagnosed As Pd
Both DIP and PD have identical symptoms, which makes certain cases extremely hard to differentiate and can lead to DIP being misdiagnosed by PD. These symptoms can include some or all of the following: tremor, resting tremor, muscle stiffness, impaired speech, slow gait and movements, and problems with posture and balance. Collectively, these symptoms are known as parkinsonism. In some cases, these symptoms have also been called atypical Parkinsons disease, secondary parkinsonism, or Parkinsons plus. Of course parkinsonism can be caused by PD, but it can also occur as a result of DIP. The main difference between parkinsonism associated with DIP and PD is that parkinsonism associated with DIP generally comes on rapidly, while parkinsonism associated with PD tends to develop gradually.
Read Also: What Causes Dyskinesia In Parkinson’s
Correlation Analysis Between Rsfmri Values And Dat Uptake In Pd Patients
To define whether altered functional activities common to both PD and DIP patients compared to the control group were associated with dopaminergic depletion, we performed a correlation analysis between the rsfMRI values in the overlapping ROIs and SNBR in the striatal ROIs. We included only 59 PD patients who underwent DAT scans and MR scanning at an interval of 2 months or less in this analysis as DIP patients have normal DAT uptake in the striatum and as such, correlation results would not adequately reflect dopaminergic depletion in the brains of these patients.
Common Symptoms Of Drug
The motor features of PD are often very easy to see via a neurologic exam in a doctors office. Rest tremor for example, is seen in virtually no other illness and can therefore be very important in diagnosing PD. But there is one other common condition that induces the symptoms of PD, including a rest tremor, which must be considered every time PD is being considered as a diagnosis, and that is drug-induced parkinsonism.
Parkinsonism is not technically a diagnosis, but rather a set of symptoms including slowness, stiffness, rest tremor, and problems with walking and balance. This set of symptoms can be caused by PD, but also can occur as a side effect of certain prescription medications .
A number of medications can cause parkinsonism because they block the dopamine receptor and thereby mimic the symptoms of PD that are caused by loss of dopamine neurons in the brain. Reviewing a patients medications is therefore a critical step for a neurologist when seeing someone with parkinsonism. Anti-psychotics and anti-nausea treatments make up the bulk of the problematic medications, although there are other medications that can also cause parkinsonism. The primary treatment for this type of parkinsonism is weaning off of the offending medication, if possible.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Tremor
How Often Do Drugs Induce Parkinsons Disease
Before I begin I wish to state clearly: this is not aimed at blaming patients with Parkinsons disease for becoming ill. The aim of this blog post is to explore and review the extent to which drugs, both illegal and legal, induce Parkinsons disease. Officially this type of Parkinsons is known as drug-induced Parkinsons and the symptoms termed Parkinsonism instead of Parkinsons symptoms. The terminology is not the only variation between drug-induced and organic forms of Parkinsons disease. Drug-induced Parkinsonism is occasionally reversible with the aggressive treatment. In addition drug-induced Parkinsonism features symmetrical symptom manifestation. If both arms shake symmetrically and simultaneously drug-induced Parkinsons is the culprit. These two key differences set drug-induced Parkinsonism apart from organic Parkinsons disease.
Overall the chemicals and prescription drugs associated with Parkinsonism have diverse applications with the only common factor being dopamine. Most is known concerning the ability for anti-psychotic medications to cause Parkinsonism. While eliciting opposite behavioral effects, amphetamine and anti-psychotics both disrupt use of dopamine by the brain with enough potency to cause Parkinsonism. MPTP acts as a toxin that selectively destroys the dopamine system leaving the user with Parkinsonism.
Clinical Features Of Drug
- Course of Neurology, Department of Health Sciences, Tsukuba University of Technology, Japan.
- Akira TamaokaDeparment of Neurology, Graduate School of Comprehensive Human Science, University of Tsukuba, Japan.
- Norio OhkoshiCourse of Neurology, Department of Health Sciences, Tsukuba University of Technology, Japan.
Don’t Miss: Stage 5 Parkinson Disease Life Expectancy
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
DLB is second only to Alzheimers as the most common cause of dementia in the elderly. It causes progressive intellectual and functional deterioration. In addition to the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease, people with DLB tend to have frequent changes in thinking ability, level of attention or alertness and visual hallucinations. They usually do not have a tremor or have only a slight tremor. The parkinsonian symptoms may or may not respond to levodopa.
Treatments And Outcomes Of Dip

DIP is generally treated by cessation of the offending drugs. Patients who cannot stop taking antipsychotic drugs because of their psychiatric diseases, such as those with schizophrenia or major depressive disorders, may be switched to atypical antipsychotics that have a lower risk of EPS. People who are prescribed dopamine antagonists due to simple GI disturbance, headache, dizziness, or insomnia should stop taking the offending drugs as soon as possible. Anticholinergics including trihexyphenidyl, benztropine, amantadine, and levodopa have been empirically tested for their ability to relieve symptoms of DIP, but this has produced no clear evidence of their effects in DIP patients.,,,,
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How To Differentiate Between Drug Induced Parkinsonism And Parkinsonism Disease
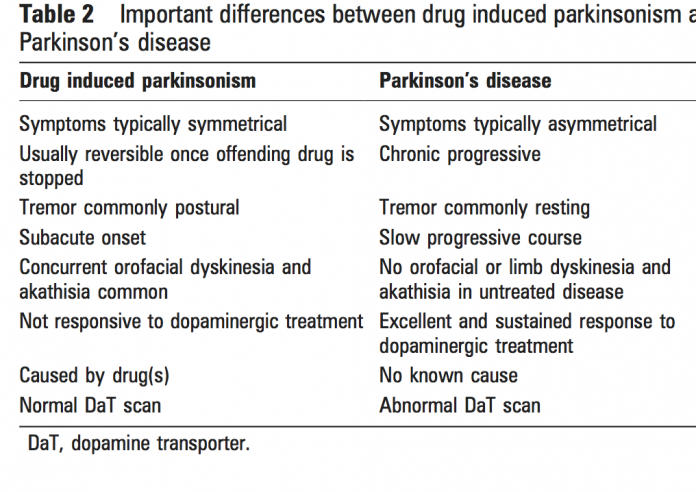
Drug-induced Parkinsonism can mimic features of Parkinsonism disease and other parkinsonian syndromes. However, there are certain clinical features that help in differentiating drug-induced Parkinsonism from Parkinsonism disease. Drug-induced Parkinsonism has a sudden and acute onset of symptoms which can be directly correlated with introduction of a new drug in the system. Drug related Parkinsonism presents itself clinically within a few days to 3 months after starting a new drug. Parkinsons disease is usually characterized by asymmetrical signs and symptoms, even at advanced stages. Drug-induced Parkinsonism usually presents itself symmetrically. Freezing, which is more common in Parkinsons disease, is a rare occurrence in drug-induced Parkinsonism. Incidence of rest tremor is more evident in drug-induced Parkinsonism than in Parkinsons disease. Studies have also known that drug-induced Parkinsonism is more common in females, whereas Parkinsons disease is more common in males. Drug-induced Parkinsonism responds to anticholinergic drugs, and Parkinsons disease responds to Levadopa.
The Connection Between Pd And Drug
In addition to potentially causing parkinsonism in the general population, these medications should definitely be avoided in people who have parkinsonism from other causes, such as PD. APDA has created a list of Medications to be Avoided or Used With Caution in Parkinsons Disease. It is important to note that there are anti-psychotics and anti-nausea medications which do not cause parkinsonism and can be used safely by people with PD.
Sometimes, a person without a diagnosis of PD is prescribed a medication which leads to a side effect of drug-induced parkinsonism. The prescribing physician may stop the new medication, but the parkinsonism does not resolve. The patient remains off the medication with continuing symptoms, and eventually is given a diagnosis of PD. In this scenario, that person most likely had dopamine depletion in the brain which had not yet manifested as a clinical symptom. The prescription medication that blocked the dopamine receptor, was the proverbial straw that broke the camels back, inducing the full-fledged symptoms of dopamine depletion and revealing that the person did in fact have PD.
The differences of PD vs drug-induced parkinsonism
There are key differences to note between parkinsonism from PD and parkinsonism as a side effect of medication.
Read Also: Parkinson Risk Factors
Parkinsonism Falls And Fracture Risk
All forms of parkinsonism, both PD and DIP, have implications for bone health. A 2014 meta-analysis on PD and fracture risk concludes that PD increases the risk of fracture.4
Given that the symptoms of parkinsonism affect balance, motor skills, gait, and the bodys ability to control movement, it is no surprise that people with PD are more likely to experience a fall than people without PD. Here is an excerpt from a 2016 study comparing the incidence of falls and fracture in PD patients:
It is estimated that 60.5% of patients with PD experience at least one fall and 39% have recurrent falls. The high frequency of falls consequently contributes to the increased risk for fractures in PD patients, which has been estimated to be approximately two times the risk in healthy controls. It has been estimated that 76% of falls in PD patients require health care services and 33% result in fractures. Falls and fractures may result in a series of unfavorable outcomes, such as disabilities and death. Furthermore, among PD patients with fractures, the mortality rate is approximately 10.6%.5
All too often, doctors prescribe these drugs without appropriate consideration of this risk. This excerpt from a study on DIP clarifies the danger of accepting a prescription of an unnecessary or inappropriate prescription drug:
Shockingly, the drugs that cause DIP are still being prescribed. This yet one more example further proving that the FDAs drug approval process is useless.
Synopsis
A Number Of Medications Can Lead To Dip
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when there is a loss of dopamine neurons in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter used by the brain to control bodily movements, learn and focus, and feel pleasure and enjoyment. Certain types of medications, known as dopamine antagonists, bind to and block dopamine receptors. When dopamine receptors in the brain are blocked, this can cause parkinsonism to occur. There are a number of medications that can cause DIP, including:
Don’t Miss: Weighted Bracelet For Tremors
Standard Protocol Approvals Registrations And Patient Consents
The Institutional Review Board of Severance Hospital approved this retrospective study and waived the need for informed consent as part of approval since we used retrospective de-identified data collected during outpatient visits. In addition, all methods were performed in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Some Cases Of Parkinsonism Can Be Reversed Others Cannot
In most cases, drug-induced parkinsonism can be reversed once the medication causing the problem is eliminated. However, it can take some time for an individual to return to normal. Depending on the medication and its effects, it can take anywhere from 4-18 months for DIP to resolve itself. In some cases, however, parkinsonism may continue even after the medication has been stopped for more than 18 months. This happens when an individual already has a dopamine deficit that was not caused by the medication. In these cases, that individual was already going to develop PD at some point, however DIP accelerated the process.
Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology , practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.
Also Check: Late Stage Parkinson’s Symptoms
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Which Drugs Can Cause Parkinsonism
![[PDF] Drug](https://www.parkinsonsinfoclub.com/wp-content/uploads/pdf-drug-induced-parkinsons-disease-a-clinical-review.png)
Typical antipsychotic , are the most common causative agents of drug-induced parkinsonism. It has been seen that certain atypical antipsychotics, which are thought to be free from extrapyramidal symptoms, can also induce Parkinsonism. Besides the gastrointestinal motility drugs, antipsychotics, antiepileptic drugs, and calcium channel blockers can lead to drug-induced Parkinsonism.
The most common drugs that cause Parkinsonism are listed below:
- Antiemetics 3
Don’t Miss: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinson
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative brain disorder that progresses slowly in most people. Symptoms can take years to develop, and most people live for many years with the disease. The symptoms caused by Parkinsons include an ongoing loss of motor control as well as a wide range of non-motor symptoms .
Whats The Outlook For People With Vascular Parkinsonism
Vascular Parkinsonism is a chronic condition, meaning it will always be with you. But unlike PD, it doesnt necessarily have to progress or worsen over time.
Symptoms of vascular Parkinsonism can remain steady for years if an individual maintains a healthy lifestyle and works closely with a healthcare professional to manage key risk factors. Still, because the condition is caused by vascular disease, those with vascular Parkinsonism are more likely to have cardiovascular issues, such as heart disease, that can reduce life expectancy.
While the life expectancy for someone with PD may be as long as for someone without the condition, the outlook for a person with Parkinsonism in any form isnt as encouraging. Compared to the general population, those with Parkinsonism tend to have a somewhat reduced life expectancy, especially if the condition sets in prior to age 70.
Read Also: End-stage Parkinson Disease What To Expect
Tremors Can Have Different Causes
It can be challenging to determine the exact cause of tremor, particularly if you already have a neurological condition such as Parkinsons disease . Uncontrollable tremor is a symptom of PD especially if you are taking multiple medications.2 In fact, medications can exacerbate existing tremor or cause non-Parkinsons tremor.
Medication-induced tremor is dependent on a differential diagnosis based on a physical exam and complete medical history.2
Tremor is a recognized symptom of PD and classified as a resting tremor. It is generally moderated when taking standard PD dopaminergic medications. But Parkinsons is a persistent condition so PD tremor may never go away entirely. Its common knowledge that Parkinsons affects each person differently when, how, and where you experience tremor is unique to you. Parkinsons tremor is not symmetrical it disproportionately affects one side of your body.2