What Is Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are special because theyre undifferentiated, meaning they have the potential to become many types of specialized cells.
You might think of stem cells as natural resources for your body. When your body needs a specific type of cell from bone cells to brain cells an undifferentiated stem cell can transform to fit the need.
There are three main types of stem cells:
- Embryonic stem cells: These cells are pluripotent, meaning they can transform into the many types of cells found in your body. As the name suggests, theyre found in embryos.
- Somatic stem cells: Also called adult stem cells, these mostly perform repair functions. They can still transform, but not into as many types of specialized cells as embryonic stem cells can.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells : These stem cells are made by genetically changing cells that have already matured.
Stem cell therapy is the use of stem cells usually from a donor, but sometimes from your own body to treat a disorder.
Because Parkinsons disease leads to the death of brain cells, researchers are trying to use stem cells to replace brain cells in the affected areas. This could help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Relative Optimism In The Long Haul
Even so, Im more optimistic here than in some other areas of stem cell translational research.
For instance, when we look at the arena of stem cells for COPD, which often includes no actual stem cells, most of what is going on is not approved by the FDA. Some of it is probably illegal. Its not even clear to me how stem cells in most cases would help COPD.
The cell therapy and stem cells for autism space is extremely active even commercially at clinics, yet we mostly dont even know what causes autism and it is a highly heterogeneous collection of conditions. Here again, we have many folks doing stuff they shouldnt too.
Another example is the field of stem cells for heart disease, which has been wracked by controversy and misconduct.
Stem Cells For Parkinsons Disease Are Safe And Effective
According the Venkataraman and colleagues, A subjective improvement was found in symptoms like facial expression, gait, and freezing episodes 2 patients have significantly reduced the dosages of PD medicine. These results indicate that our protocol seems to be safe, and no serious adverse events occurred after stem-cell transplantation in PD patients.
As stated in a 2005 study held by Brian Snyder,
Stem cells offer the potential to provide a virtually unlimited supply of optimized dopaminergic neurons that can provide enhanced benefits in comparison to fetal mesencephalic transplants. Stem cells have now been shown to be capable of differentiating into dopamine neurons that provide benefits following transplantation in animal models of Parkinsons disease.
You May Like: How Long Do Elderly Live With Parkinsons
Also Check: How To Determine If Someone Has Parkinson’s
The Many Types Of Stem Cells
While the regenerative power of stem cells is at the cutting-edge of research, people have known that our tissues and organs have the capacity to regrow for thousands of years. The regenerative ability of the liver even features in Greek mythology. The myth goes that when Prometheus defied the gods they sentenced him to eternal torment, each day a vulture would eat his liver only for it to regrow as fast as it was damaged.
We now know that the ability of our tissues to regrow is due to the presence of stem cells. But its not just when cells get damaged that stem cells are activated, there are types of stem cells that are active throughout our lives.
Whatever your age, your body is many years younger. This is because almost all of our organs and tissues contain adult stem cells that can turn into many different types of cells and help our body to replace old or damaged tissues. But adult stem cells can only develop into a limited number of cell types. For example, bone marrow stem cells naturally develop into blood cells but not brain cells.
Adult stem cells were first discovered in the 1960s, and we now know they can be found all over the body, including in our brains. Some forms of adult stem cells already provide vital treatments. For instance, bone marrow contains adult stem cells that make all our different blood cells which means that bone marrow transplants from healthy donors can be used to treat blood disorders like leukaemia.
You May Like: Sam Waterston Parkinsons
Medications For Parkinsons Disease

Currently, the most common medication for managing the symptoms of Parkinsons disease is a drug called levodopa. The brain converts levodopa to dopamine, helping replace the neurotransmitters loss.
Since levodopa can cause nausea, the medication is almost always administered with a companion drug, carbidopa, which manages stomach upset and nausea symptoms.
Unfortunately, levodopas absorption is inconsistent because it takes a long path from the small intestine through the blood to the brain. The inconsistency can lead to a rise and fall in the brains dopamine levels.
Additionally, the treatment becomes less effective over time, as the cells that convert levodopa to dopamine continue to decline. There are several other medications aimed at reducing Parkinsons symptoms. However, they all have some limitations.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Stages And Symptoms
Stem Cell Treatments In The Future Of Parkinsons Disease Management
Although there are a number of challenges brought about with stem cell-based treatments for PD, it seems probable that these treatments will progress to the clinic in the short- to medium-term future. While development of optimized products has been necessarily slow and iterative, the field is now asking questions about how these treatments can be scaled and deliveredthis demonstrates the progress that has been made with these approaches.
As has been discussed, the purpose of stem cell treatments is predominantly to treat the motor symptoms of PD. They will not have any disease-modifying effect and will not treat the major non-motor symptoms which can be particularly disabling in some patients. While these techniques can form one arm of the future of PD treatment, they will likely be combined with other novel treatments targeting alpha-synuclein pathology . It may be possible for stem cell-based regenerative therapies to be employed to restore the function of dopaminergic neurons that have already been lost, while novel disease-modifying drugs could be used to prevent ongoing neuronal death.
Stem Cell Therapy In Parkinson’s Disease
Embryonic stem cells : ES cells have attracted great attention as an alternative source for the generation of dopamine neurons because they can be continually expanded with high potential for differentiation. As they are pluripotent stem cells, they are able to form all three embryonic germ layer lineages following induced differentiation. Many studies have focused on optimizing the differentiation of ES cells into dopamine neurons. Among them, systematic and efficient induction systems for dopamine neurons have been reported by several groups , The prospect that ES cells can produce a sufficient number of dopamine neurons for transplantation therapy is particularly appealing, both for clinical and industrial use. At the same time however, their clinical application is limited because of their ability to form tumors and the ethical problems surrounding the use of using fertilized human eggs to establish the ES cell lines .
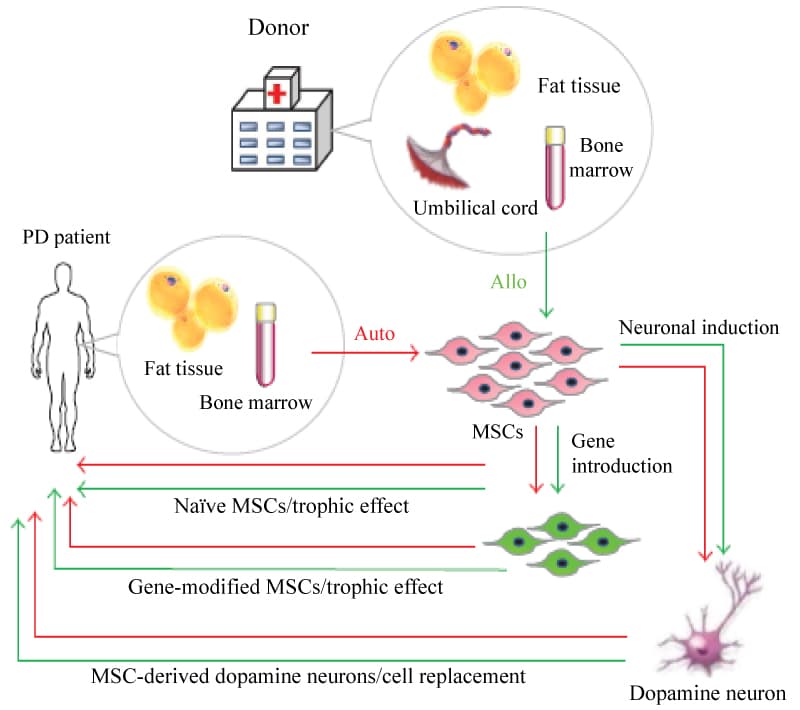
Mesenchymal stem cells :
Figure 9: Strategy for MSC transplantation in PD patients. View Figure 9
These findings stimulated the advancement of regenerative medicine aimed at the generation of desired cells from MSCs. To date, various cell types, such as mesodermal lineage cells , as well as endodermal lineage cells and ectodermal lineage cells have been induced from MSCs in vitro by the use of cytokines, trophic factors or gene introduction .
Figure 10: Production release of dopamine. View Figure 10
Also Check: Can You Drive With Parkinson’s Disease
Scientists Have Made A Breakthrough In The Development Of A Nasal Spray For Parkinsons Disease Treatment
Researchers from the University of York have developed a new gel that can adhere to tissue inside the nose alongside the drug levodopa, helping deliver Parkinsons disease treatment directly to the brain.
Parkinsons disease is a condition in which parts of the brain become progressively damaged over many years. This leads to a reduction in dopamine in the brain, which plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. The main symptoms include involuntary shaking, slow movement, and stiff and inflexible muscles.
You May Like: Cinnamon And Parkinsons Disease
Cell Assessment Of Differentiated Da Neurons
Understanding the key type of DA neurons required to achieve downstream restoration of PD pathology is essential. The mesotelencephalic DA system in the midbrain contains two main groups: the A9 neuronal clusters of the nigrostriatal DA pathway located in the zona compacta, the substantia nigra involved in the control of posture, and the A10 neurons located in the ventromedial mesencephalic tegmentum that regulates the locomotor activity and emotional behavior . Dysfunction of the nigrostriatal system has been linked to Parkinsonism and later to schizophrenia, drug addiction, and depression . Differences between the two DA cell populations have been observed in neurochemistry and in spontaneous neuronal firing . More importantly, A9 neurons display significantly enhanced levels of neuromelanin pigmentation as compared to other dopamine-producing neurons . This could account for the association of early loss of A9 DA neurons in Parkinsons disease with increased vulnerability upon disease progression with the relative preservation of A10 DA neurons .
Generally, stem cells are differentiated into specific nigra A9 DA neurons in large quantities prior to PD transplantation. This step has been thoroughly reviewed by many articles such as in Fan et al. and, thus, will not be further discussed here. However, we focus on developments in technology in cell assessment of differentiated DA neurons.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease A Mutation
We Take A Look At The Science Behind Trials That Aim To Slow And Reverse Parkinsons By Using Stem Cells Or Other Cell Therapies
Parkinsons is caused by the loss of brain cells that produce the chemical dopamine. Research over the last few decades has focused on finding ways to slow or stop this loss to slow the progression of Parkinsons. Indeed, there are ongoing trials of promising therapies that aim to protect and nurture remaining dopamine-producing cells. But with half these cells lost or damaged by the point of diagnosis, a cure for Parkinsons may also require a therapy that can reverse the damage that has already been done this is where cell-based therapies that aim to replace those cells come into their own.
Does It Work Efficacy Of Commercial Stem Cell Clinics
Commercial clinics do not as a rule publish their results in peer-reviewed journals to demonstrate to the scientific community that the treatments work. Rather, they usually rely on anecdotes from patients as proof of efficacy. Some clinics are tracking their results by measuring variables such as quality of life before or after the procedure. However, without comparing the patients to a similar group who does not receive the treatment, it is hard to know whether any improvement is due to placebo effect or to the treatment itself.
Also Check: What Drugs Make Parkinson Worse
Mda Cell Dosage For Transplantation
Typically, 200,000420,000 dopamine neurons reside in human midbrain, and it is estimated that 50% loss of those DA neurons leads to the PD symptom . According to preclinical studies using fetal tissue or hPSC-derived mDA cell, 12002400 surviving TH + neurons in rat, 13,000 in primate, 40,00080,000 in the human brain may be required to achieve a meaningful therapeutic effect . The current bottleneck in delivering cells to the brain is that typically less than 10% of grafted mDA neurons survive following transplantation . Multiple factor may contribute to poor mDA neuron survival including mechanical trauma, growth factor deprivation, initial lack of vascularization, hypoxia and free radical production, or excessive extracellular concentrations of excitatory amino acids in the host brain .
Why Is Stem Cells Treatment Better Than Conventional Treatment Approach For Treating Parkinsons
Conventional treatment approaches highly invasive associated with many side effects. Although stem cells can naturally heal the body from damage and regenerate lost neurons to improve impaired functions. Additionally, since the bodys own cells are used for repairing, the entire treatment is minimally invasive without any side effects.
Recommended Reading: On Off Phenomenon
You May Like: Are There Different Stages Of Parkinson’s Disease
New Medications For Off Time
A number of new medications approved recently are designed to reduce OFF time. These medications fall into two major categories:
- Medications that lengthen the effect of a carbidopa/levodopa dose
- Medications that are used as needed if medication effects wear off
Well give specific examples below. In general, new medications that extend the length of a carbidopa/levodopa dose are used if OFF time is somewhat predictable and occurs prior to next dose. New medications that are used as needed are most beneficial when OFF time is not predictable.
New medications that lengthen the effect of a dose of carbidopa/levodopa
- Istradefylline is an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist which was approved in the US in 2019 as an add-on therapy to levodopa for treatment of OFF time in PD. Unlike many of the other medications, it has a novel mechanism of action and is the first medication in its class to be approved for PD. It acts on the adenosine receptor, which modulates the dopaminergic system, but is not directly dopaminergic. The drug was developed in Japan and underwent clinical trials both in Japan and in the US.
- Opicapone is a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor that is taken once a day. It was approved in the US in 2020 as an add-on therapy to levodopa for motor fluctuations.
New formulations of levodopa designed to be used as needed if medication effects wear off
Other medications used as needed if medication effects wear off
Why Choose Our Stem Cell Clinic For Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic and degenerative neurological disorder that leads to the loss of neurons in the brain. This leads to uncontrolled shaking, muscle rigidity, and difficulty with walking, speech, and cognition. The stem cell therapy we offer at Shifa Rejuvenation Clinic has been shown to be an effective treatment for Parkinsons Disease.
We use Superior Quality Stem Cells which can help reverse the damage done by Parkinsons disease while also providing relief for patients who suffer from chronic pain.
Also Check: Do Statin Drugs Cause Parkinson’s
What Have Clinical Trials Found
Until the discovery of the process of creating iPSCs, the only stem cell therapies for Parkinsons disease required the use of embryonic stem cells. This came with ethical and practical challenges, making research more difficult.
After iPSCs became available, stem cells have been used in clinical trials for many conditions involving neural damage with overall mixed results.
The first clinical trial using iPSCs to treat Parkinsons disease was in 2018 in Japan. It was a very small trial with only seven participants. Other trials have been completed using animal models.
So far, trials have shown improvement to symptoms affecting movement as well as nonmotor symptoms such as .
Some challenges do arise from the source of the stem cells.
Stem cell therapy can be thought of as being similar to an organ transplant. If the iPSCs are derived from a donor, you may need to use immunosuppressant drugs to prevent your body from rejecting the cells.
If the iPSCs are derived from your own cells, your body might be less likely to reject them. But experts believe that this will delay stem cell therapy while the iPSCs are made in a lab. This will probably be more costly than using an established line of tested iPSCs from a donor.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative illness that attacks the bodys central nervous system. This progressive disease causes damage to the brains nerve cells particularly those responsible for the production of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Dopamine is a naturally occurring substance that regulates the messages sent from the brain to the bodys muscles. When these messages are interrupted by Parkinsons disease, the patient experiences problems with movement and the coordination of muscles. Up to 80% of a sufferers cells are affected, which means the condition is irreversible. Despite worldwide research, there is no cure for Parkinsons.
Recommended Reading: What Age Does Parkinsons Start
Personalized Stem Cells Improved Motor Symptoms And Depression Signs In Monkeys Modeling Parkinsons Disease Paving The Way For Trials In Human Patients
Current treatments for Parkinsons disease alleviate symptoms, but lead to involuntary muscle spasms and do not prevent the loss of neurons that underlie the disease. Transplanting stem cells from fetal tissue has shown enough promise to warrant clinical trials, but the approach is ethically complex and the outcomes are inconsistent, likely because of differences between donor tissues.
In a recent study published in Nature Medicine, researchers reported that transplanting personalized induced pluripotent stem cells into the brains of rhesus monkeys modeling PD not only improved motor function and neuron growth over a two-year period, but also boosted the animals moods.1
The findings indicate clinical potential for using stem cells derived from the patient, known as autologous stem cell therapy, to treat PD. This study is the culmination of University of Wisconsin neuroscientist Su-Chun Zhangs career-long goal to repair damaged or lost function in the brain.
This work confirms the long-term efficacy of an autologous approach in a non-human primate model, said Penny Hallett, co-director of the Neuroregeneration Research Institute and psychiatrist at Harvard Medical School in Belmont, Massachusetts. Hallett was not part of the new research, but her work helped to lay the foundation. In a 2015 study published in Cell Stem Cell, she and her team provided the first proof-of-concept data for an autologous iPSC approach for PD treatment in a non-human primate model.2
