During And After Treatment
During the treatment, you will lie down on the treatment bed inside the MRI scanner. The medical team will be in the control room and you will be conscious and able to communicate with them. Your head will be positioned in the focused ultrasound helmet which is filled with water, and you will have a blanket to keep you warm.
Use Of Anticholinergic Medication In Pd
Anticholinergic medication was prescribed to 2597 of 8620 patients with PD trihexyphenidyl was prescribed more than benztropine . Anticholinergic use was observed to be higher in PD+D than in PD-D . The number of PD patients concurrently prescribed anticholinergic and anti-dementia medications was 1006 (25.9% of PD+D patients.
You May Like: Parkinsons Support Group Connecticut
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Recommended Reading: Can Drugs Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Why Is Pd More Common In The Elderly
As we age, damage to our body builds up very slowly. It can take a long time for us to notice. For example, people who live with osteoarthritis have had small amounts of damage to their joints over and over.
As a young adult, they may not notice any joint issues. However, at some point, the joints build up enough damage that they start to experience pain or stiffness. This can happen to individual cells too.
The biggest risk factor for PD is age. Dopamine-producing neurons can die slowly over time. This can build up for years before symptoms of PD are apparent.3
Are There Medicines To Treat Pdd
Though there is no cure for PDD yet, there are medications that help manage the symptoms. These medications are called cholinesterase inhibitors, and they can help if a person with PDD is having memory problems. Some examples of these medicines are donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine. Sleep problems may be managed by sleep medications such as melatonin.
Because people with PDD are usually very sensitive to medications, any new medication, even one that is not being used for the brain, needs to be reviewed with the persons provider to avoid potential contraindication.
Also Check: Ed Begley Jr Parkinsons
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Caregiver Support Groups
Clinical Symptoms Of Pd And Ageing
Ageing can produce axial impairment of gait and postural control in PD due to the combined effect on non-dopaminergic and dopaminergic pathways. Older PD patients are more liable to suffer side effects of anti-cholinergic medications, such as confusion and hallucinations, because of the increasing cholinergic deficit in PD with age. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia may reduce with age, possibly because younger onset patients demonstrate a higher rate of dopamine turnover relative to production when compared with older patients. One of the difficulties extrapolating the evidence base for the use of many anti-parkinsonian medications to older people is the exclusion of older people from trials, which may lead to an over- or underestimation of the efficacy of treatments in older people .
How To Treat Parkinson’s
Since there is no known treatment for Parkinson’s, treatment is all about symptom management. There are different medications, surgeries, and other methods to help with the symptoms.
Medicines used to treat Parkinsonâs often:
- Increase dopamine levels
- Affect other brain chemicals in your body
- Help control other symptoms not related to movement problems
The most common medication for Parkinsonâs is called levodopa, or L-dopa. Levodopa helps the brain make more dopamine. Unfortunately, levodopa can cause nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and sleep difficulties. That is why people usually take a medication called carbidopa alongside levodopa. Carbidopa helps to reduce those side effects.
People who take these medications should always consult their doctor before they stop taking them. Suddenly stopping these medications can have serious and unwanted effects.
Other medications that people take for Parkinsonâs include:
- Medications that mimic dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors, which slow down a dopamine-killing enzyme
- COMT inhibitors, which break down dopamine
- Amantadine, which helps reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs that reduce tremors and muscle stiffness
Other ways to treat Parkinsonâs symptoms include physical, occupational, and speech therapies. These can help with the physical, vocal, and mental effects of Parkinsonâs. You can also use exercise and diet to help with muscle and balance issues.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: Doctors Who Treat Parkinson’s Disease
Short Term Risks Day Of Treatment Up To 3
- The most common potential risks associated with the Exablate Neuro device and thalamotomy procedure are transient numbness and tingling. These sensations are typically mild to moderate in intensity and can last as briefly as the length of the sonication or up to several days. Headaches or head pain during sonication and imbalance or unsteady were other potential risks, but most often ended shortly after treatment.
- Nausea/Vomiting were also reported in some instances. It is unclear if this is related to medications used during the treatment or the procedure itself.
- You may experience bruising in the area of the iv catheter following the procedure similar to that experienced after blood draws. Any bruising should resolve on its own within a week.
Parkinsonism And Brain Pathology
There were 1,373 deaths after an average of nearly 7 years of follow-up with 1,187 autopsies . At the time of these analyses, the uniform neuropathological examination was complete for 1,160 . Mean age at death was 88.3 years 64.5% were women. At their last visit, about 10 months before death, more than 70% had either parkinsonism or possible parkinsonism ).
Description of Neuropathologies: AD pathology was the single most common pathology . One or more of the four vascular pathologies were present in more than 4/5 of the cases . Nigral Lewy body pathology was present in more than 1/5 and moderate/severe nigral neuronal loss was present in more than 1/10 and nigral Lewy bodies together with moderate/severe nigral neuronal loss was present in 1/10 .
Ordinal logistic regression models were employed to examine which neuropathologies were associated with parkinsonism. Each model included terms for one of the seven neuropathologies and controlled for age, sex, and education. Each of the four vascular pathologies was associated with parkinsonism but not AD pathology, Lewy body pathology, or nigral neuronal loss . Arteriolosclerosis and atherosclerosis showed independent associations with parkinsonism when all seven pathologies were included in a single model . These results were unchanged when we excluded cases with a history of PD proximate to death
Read Also: What Does Parkinson’s Affect
Resources For People Newly Diagnosed With Parkinson’s
You have Parkinsons disease. Four words that come with a diagnosis full of questions and uncertainty. However you choose to start processing, youre not alone. The Michael J. Fox Foundation has developed resources to help individuals and families move through the earliest days with Parkinsons disease and beyond.
Wondering where to start? , “Navigating Parkinson’s: Your Guide to the Early Years,” for insights, wisdom and practical perspectives on everything from finding acceptance to navigating doctors appointments.
A Golden Opportunity to Speed a Cure
Understandably, few people think about participating in research following a Parkinsons diagnosis. But people at this early stage of disease are in a unique position to help speed new treatments. The Parkinsons Progression Markers Initiative is our landmark study on a mission to stop the disease. If youre recently diagnosed and not yet taking medication, call 877-525-PPMI or email to get started.
Your First Year with Parkinson’s: Practical Tips for the Road Ahead
A Parkinsons diagnosis can bring many questions and emotions. But the good news is that you dont have to figure out everything at once. Movement disorder specialist Rachel Dolhun, MD, shares tips for making your way forward.
Moving Online: Experiences And Potential Benefits Of Digital Dance For Older Adults And People With Parkinsons Disease
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations School of Psychology, College of Social Sciences and Law, University College Dublin, Dublin Ireland, Division of Psychology Communication and Human Neuroscience, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Biology Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
-
Roles Methodology, Project administration, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Mark Morris Dance GroupDance for PD, Brooklyn, NY, United States of America
-
Roles Methodology, Project administration, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Faculty of Education, Royal Academy of Dance, London, United Kingdom
- Charlotte Growcott,
Roles Formal analysis, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Division of Psychology Communication and Human Neuroscience, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Biology Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
- Ellen Poliakoff
Roles Methodology, Visualization, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Division of Psychology Communication and Human Neuroscience, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Biology Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
You May Like: Things To Help Parkinson’s
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition

When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
You May Like: Is Diarrhea A Symptom Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
What Can You Do If You Have Pd
- Work with your doctor to create a plan to stay healthy. This might include the following:
- A referral to a neurologist, a doctor who specializes in the brain
- Care from an occupational therapist, physical therapist or speech therapist
- Meeting with a medical social worker to talk about how Parkinsons will affect your life
For more information, visit our Treatment page.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Cause Dry Mouth
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
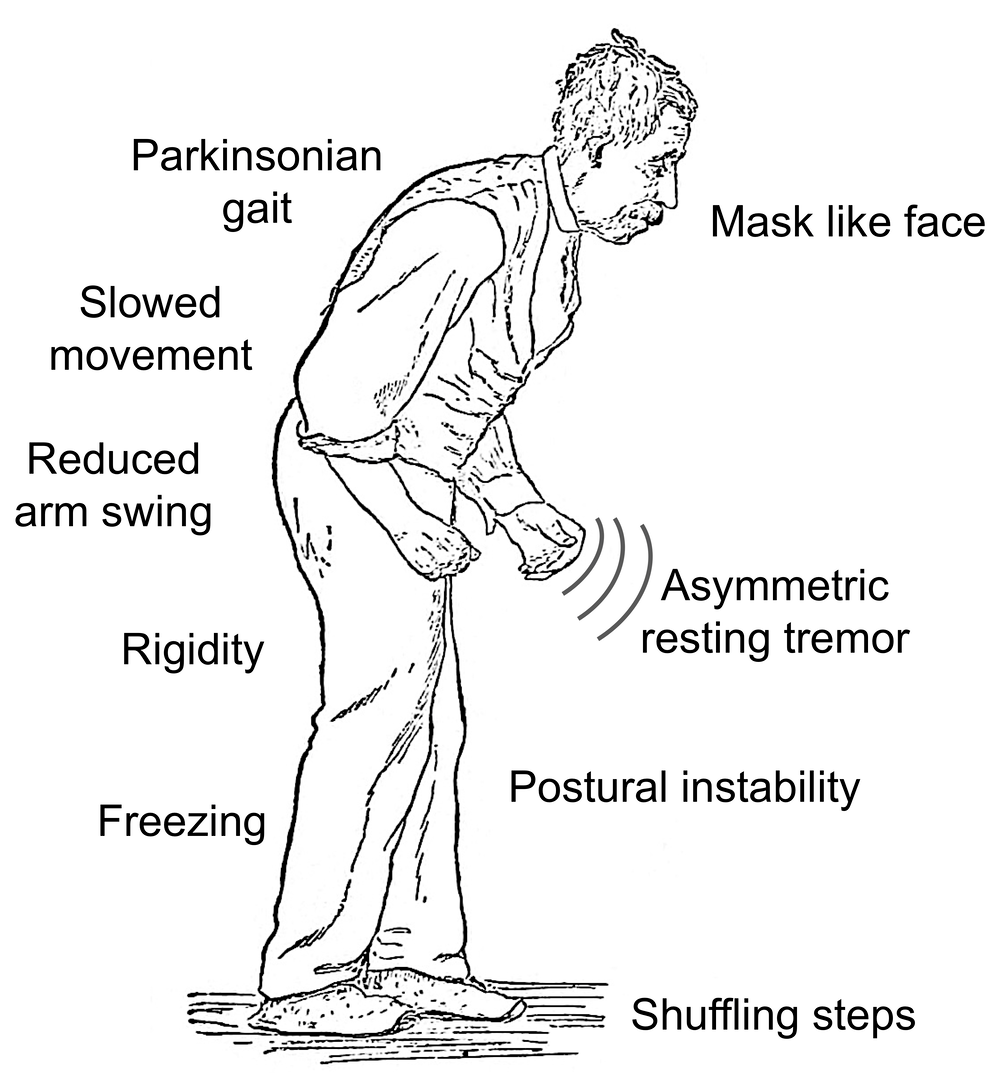
What Are The Symptoms
PD symptoms do not predictably differ according to age. However, everyone experiences PD slightly differently. Different people develop different symptoms at different times.3
The most common motor symptoms of PD include:3
- Tremor at rest, such as a tremor in a finger, hand, or foot
- Rigidity of limbs, neck, or shoulder
- Impaired balance when standing up , which can lead to falls
- Slowness of movement or gradual loss of movement , such as slower walking, decreased blinking, or slower facial expressions
- Difficulty swallowing
- Speech issues, such as slurred speech, abnormally long pauses, or hoarseness
- Sleep issues, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep , restless legs syndrome, or acting out dreams
You May Like: Is There A Connection Between Parkinson’s And Neuropathy
Medication Goal: Replace Or Preserve Dopamine
In PD, the brain cells or neurons that produce dopamine are injured, which leads to most of the movement problems in PD. Replacing or preserving dopamine levels is the goal of PD medications.
There are three basic types of PD drugs:
- Levadopa is converted into dopamine in the brain.
- Dopamine agonists act like dopamine in the brain to mimic its effects.
- The third group blocks the metabolism or breaking down of dopamine in the brain so that it lasts longer.
Please feel free to ask questions about any of your Parkinsons medicine with your doctor, physician care assistant , nurse or pharmacist.
What Other Things Help
There are various ways to help a person with PDD. Speech therapy may help improve communication between people with PDD and others. Physical therapy may help strengthen and stretch stiff muscles and help to prevent falls.
Research has shown that physical exercise helps to enhance brain health and improves mood and general fitness. A balanced diet, enough sleep and limited alcohol intake are other important ways to promote good brain health. Other illnesses that affect the brain, such as diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol, should also be treated if present.
Read Also: Why Is Parkinson’s Disease More Common In Males
Nership With A Specialist
Neurologists, particularly those who specialize in movement disorders, can be helpful at all stages of PD patient care. They have clinical experience with the various causes of parkinsonism and phenotypes of PD. As the disease progresses, partnering with a specialist is helpful for both the increased complexity of PD management, consideration of DBS, and to assure that proper management of non-PD medical illnesses can continue.
Can Older Adults With Parkinsons Enjoy Normal Lives

By Annette Campbell 9 am on February 10, 2021
Parkinsons disease is classified as a neurological disorder, which means it affects nerve cells that transmit signals to and within the brain. The Parkinsons Foundation estimates about 1 percent of all seniors have some form of this condition. However, having Parkinsons doesnt mean your senior loved one cant still live a normal life. Today, were going to focus on what can be done to achieve this goal.
You May Like: Deep Brain Stimulation Parkinsons Video
Read Also: How To Reverse Parkinson’s Naturally
Complications Of Parkinsons And Covid
It has been found that motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease may become worse due to COVID-19 infection.
Other studies showed an increase in symptoms from Parkinsons disease during the pandemic, even without COVID-19 infection, due to a lack of physical activity and the need for people with Parkinsons to isolate themselves from others to reduce the risk of infection. Worsening symptoms included:
- Psychologic distress
Long COVID-19 symptoms may continue well after the initial infection has resolved. COVID-19 infection has been associated with long-term effects on the following body systems:
- Heart: Heart muscle damage has been found in patients with COVID-19. This could lead to a weakened heart muscle or heart failure.
- Lungs: Damage to the air sacs in the lungs by pneumonia from the virus can cause difficulty breathing after the infection has resolved.
- Brain: Some people who had COVID-19 developed strokes, and many report difficulty thinking or concentrating.
One article estimated that at least 10% of people diagnosed with COVID-19 will be considered a long-hauler currently it is unknown which patients are at a higher risk for developing long COVID-19 symptoms.
Many long-haulers initially had mild symptoms, did not require hospitalization, and did not have other comorbidities.
At this time, it is not known if having Parkinsons disease increases the risk of being a long-hauler. Research is ongoing to help answer these questions.
