Where Is It Made In The Brain
Dopamine is produced in the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus.1 You may not remember these complicated names. That is fine! It is probably more important to know what these areas of the brain do:1,4-6
- The substantia nigra is part of the brain known as the basal ganglia. This part of the brain is responsible for making movement possible.
- The ventral tegmental area is the part of the brain that is responsible for reward and reinforcement.
- The hypothalamus has many functions. It is responsible for sleep, appetite, body temperature, and sexual arousal, among other things. The hypothalamus helps control the autonomic nervous system.
How Does Treatment Work
Currently most of the drugs that treat PD work to either replace or mimic dopamine in a persons brain.7 A few drugs work by keeping the body from breaking down dopamine, so it can stay in a persons system longer.
Doctors also think that there are other neurotransmitters that affect and are affected by PD.10 They are currently doing research to find out what these neurotransmitters are and how drugs affecting them may help with better PD treatment in the future. Hopefully, these studies will lead to better outcomes for all people with PD.
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
Don’t Miss: What Makes Parkinson’s Disease Worse
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
Histology And Proximity Ligation Assay
Immunohistochemistry was performed on free-floating sections before mounting on glass slides for imaging. Primary antibodies used for immunohistochemical analysis are listed in Table .
Table 1 Antibodies used for immunohistochemistry.
Proximity ligation assay was analyzed utilizing PLA probes and visualized with orange and far-red kits.
For quantification of immunofluorescence, confocal images of both immunohistochemistry and proximity ligation assay were taken on an Olympus IXB1 confocal. Intensity measurements were obtained in Fluoview software by circling ROIs around TH-positive neurons in the nontransduced hemisphere and TH- and GFP-positive neurons in the transduced hemisphere while blinded to the protein of interest. Intensity values of the protein of interest were compared between transduced and nontransduced TH-positive neurons. Number of objects analysis was performed in Nikon Elements software by circling ROIs around TH-positive neurons in the nontransduced hemisphere and TH- and GFP-positive neurons in the transduced hemisphere while blinded to the protein of interest. Within ROIs, a threshold was applied to the protein of interest in order to achieve unbiased counts of objects. Images to visualize DAB immunoreactivity were taken on an Olympus BX61VS microscope and analyzed for pixel saturation in CellSens software.
Don’t Miss: Trintellix And Parkinson’s Disease
Preventative Approaches: Targeting The Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
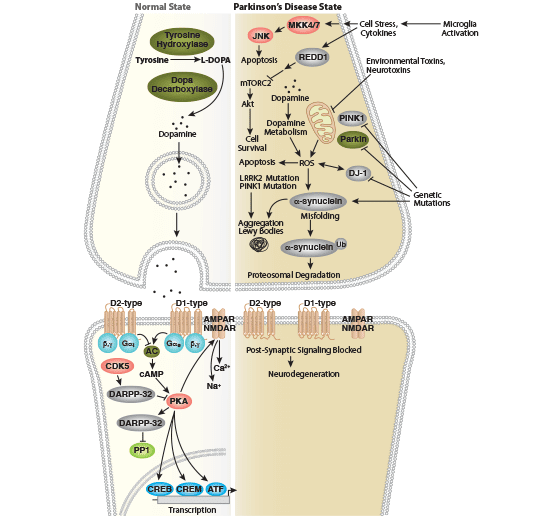
Unfortunately, although some therapies for PD produce a period of recovery for about 5 years, there is a sharp decrease in the beneficial effects of treatments thereafter . Indeed, the best approach would be to understand the relevant triggers of the disease in order to target the physiopathological mechanisms causing the death of dopaminergic neurons. Epidemiological studies have shown that less than 10% of PD cases have a strict familial etiology, while most of them are sporadic and appear to be caused by other factors associated with susceptibility genes . Although these factors are not fully understood, there is a consensus that PD is induced by a combination of age, gender, genetic background, and environmental factors. However, neither of these has, alone, been identified as a leading cause of PD . While the cellular and neurochemical mechanisms underlying PD have remained incompletely understood, what data have been collected point to heavily to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic cases of PD .
This evidence suggests that preventing mitochondrial dysfunction can be a key therapeutic goal to achieve as stand-alone or adjunctive therapy against PD.
Living With Parkinson Disease
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Renal Failure
Parkinsons Disease Medications Are Designed To Increase Dopamine Levels In The Brain Or Slow The Breakdown Of The Brains Dopamine Lessening The Tremors And Other Symptoms
Story by: David Steen Martin on September 17, 2021
Parkinsons disease medications are designed to increase dopamine levels in the brain or slow the breakdown of the brains dopamine, lessening the tremors and other symptoms.
Dopamine is a chemical involved in movement, and its decrease in the brain is central to Parkinsons disease. By the time someone starts experiencing symptoms, dopamine levels in the basal ganglia already have dropped an estimated 50% to 75%.
Walking, movement and tremor can be managed better with Parkinsons disease medications.
Levodopa, which the brain converts to dopamine through a natural process, is the gold standard for treatment, according to Justin T. Phillips, M.D., medical director of movement disorders at the Norton Neuroscience Institute Cressman Parkinsons & Movement Disorders Center.
Common misconceptions about levodopa prompt some patients to wait before taking. Some patients worry they will develop a tolerance for the drug and it will stop working, it is only effective for a certain amount of time or that will cause the disease to progress faster.
All of these are myths, Dr. Phillips said. In addition to being the most effective medication, levodopa also tends to have fewer side effects, particularly in the long term.
Levodopa should be started as soon as troubling symptoms begin, according to Dr. Phillips. It will lessen disability in the long run, though it will require adjustments over time.
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
Also Check: How Do You Know If Someone Has Parkinson’s Disease
What Not To Eat If You Have Parkinson’s
Don’t eat too many sugary foods and drinks as these can negatively impact your immune system. Opt for naturally sweetened food and reduce your sugar intake to manage Parkinson’s symptoms. Don’t eat too much protein. Consuming lots of beef, fish, or cheese may affect the effectiveness of certain Parkinson’s medications.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsonâs disease can include:
- Walking slowly leaning forward with small steps
- Memory problems
People with Parkinsonâs disease often show minor symptoms at first. The symptoms may begin on only one side of the body. Symptoms often become more pronounced over time.
Parkinsonâs disease itself isnât fatal, but it has no cure. Symptoms like frequent falling can lead to injury and death.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
How To Determine The Dopamine Level In The Brain Of Parkinsons Patients
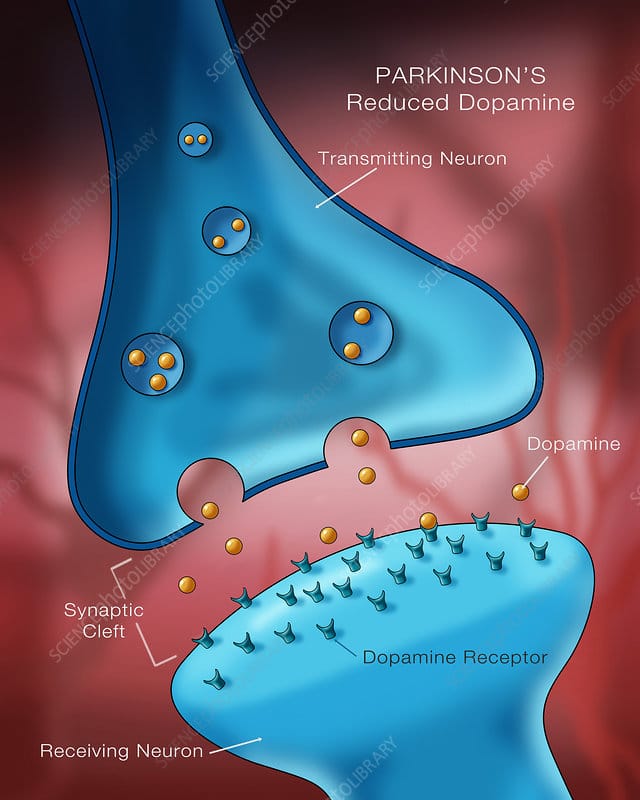
There is no rigorous method that could directly access to Dopamine and monitor its changes in the brain. The currently used methods rely on brain imaging techniques which do not reliably detect and measure Dopamine changes in the human brain.
Recently, neuroscientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge have developed a method to measure Dopamine in the brain for a long period of time, more than a year. They have designed a sensor which they believe could be used to monitor the changes in Dopamine levels in brain areas where Dopamine is highly concentrated. The sensor is so small that it can be implanted in different parts of the brain. The sensor has been successfully tested on animals and hopefully will be available for human trials in the near future.
Also Check: What Drugs Make Parkinson Worse
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Or When Should I Seek Care
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended, or if you notice changes in your symptoms or the effectiveness of your medication. Adjustments to medications and dosages can make a huge difference in how Parkinsons affects your life.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you should go to the hospital or seek medical care. In general, you should seek care if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
Linking The Catecholaldehyde Hypothesis To Synuclein
A pivotal study by Burke et al. in 2008 demonstrated that in vitro DOPAL incubation with Syn monomers triggers a dose-dependent protein aggregation. Similarly, SDS-resistant aggregates of Syn were detected by Western Blot in lysates from SH-SY5Y cells after administration of DOPAL in the medium. The process was observed also in vivo upon direct DOPAL injection into rat SNpc, which resulted in dopaminergic neuron loss and accumulation of Syn high molecular weight species . Since then, other groups provided further insights into the DOPAL-dependent Syn aggregation process. Inhibition of DA uptake into synaptic vesicles by reserpine administration to dopaminergic PC12 cells, induced DA cytosolic build-up with consequent cytotoxic accumulation of DOPAL and induction of Syn oligomerization . Furthermore, redox active metal ions i.e. Cu, Fe, Mn, whose levels are increased in parkinsonian SNpc , were shown to accelerate DOPAL-induced Syn oligomerization in PC12 cells . On the same ground, in vitro assays revealed a modulating effect of N-terminal acetylation and familial mutations on DOPAL-induced Syn oligomerization .
Fig. 4
Recommended Reading: Do All Parkinson’s Patients Have Lewy Bodies
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Pivotal Pathological Mechanism Of Parkinsons Disease
Mitochondria are complex cytosolic organelles of eukaryotic cells whose primary function is the generation of cellular energy in the form of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Mammalian mitochondria contain between 2 and 10 mitochondrial DNA molecules encoding 22 transfer RNAs, two ribosomal RNAs, and 13 polypeptides, each of which is part of the respiratory chain and the oxidative phosphorylation system . The mitochondrial respiratory chain contains four protein complexes that form the site of oxidative phosphorylation. This site is responsible for NADH and FADH2 oxidation, co-occurring with the movement of protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space. This movement produces an electrochemical gradient denoted as mitochondrial membrane potential . This gradient stimulates the ATP synthase to reduce molecular oxygen and synthesize ATP. This step is fundamental in aerobic metabolism and constitutes the primary provider of ATP at the final stage of cellular respiration . Nevertheless, the biological function of mitochondria goes far beyond energy production and includes the metabolism of lipids and amino acids and the support of intermediate metabolic pathways, such as the Krebs cycle.
How Is A Diagnosis Made
Because other conditions and medications mimic the symptoms of PD, getting an accurate diagnosis from a physician is important. No single test can confirm a diagnosis of PD, because the symptoms vary from person to person. A thorough history and physical exam should be enough for a diagnosis to be made. Other conditions that have Parkinsons-like symptoms include Parkinsons plus, essential tremor, progressive supranuclear palsy, multi-system atrophy, dystonia, and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Don’t Miss: How You Get Parkinson’s Disease
Can Dopamine Be Used To Treat Parkinsons
If Parkinsons disease is caused by a drop in dopamine, it might make sense that replacing that dopamine would stop the symptoms and halt the progression of the disorder. But its not that easy.
Dopamine from a medication or injection cant penetrate the blood-brain barrier. That makes it an ineffective treatment.
An amino acid called levodopa can help increase levels of dopamine in the brain. If given as a medication, it can cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, levodopa is converted to dopamine.
Levodopa wont replace all of the lost dopamine, but it can help to reduce symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Its particularly helpful with movement control.
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Painful
Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Cured
No, Parkinson’s disease is not curable. However, it is treatable, and many treatments are highly effective. It might also be possible to delay the progress and more severe symptoms of the disease.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Parkinson’s disease is a very common condition, and it is more likely to happen to people as they get older. While Parkinson’s isn’t curable, there are many different ways to treat this condition. They include several different classes of medications, surgery to implant brain-stimulation devices and more. Thanks to advances in treatment and care, many can live for years or even decades with this condition and can adapt to or receive treatment for the effects and symptoms.
Downstream Effects Of Dopal Accumulation: Oxidative Stress Mitochondrial Dysfunction And Cell Death
A further analogy with DA is that also DOPAL quinones could covalently modify mitochondrial protein, possibly affecting mitochondrial physiology . In the work by Kristal et al., isolated mitochondria from mouse liver were exposed to DOPAL resulting in an increased opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore at concentrations close to physiological ones . Later studies reported that DA oxidation to quinones induced mitochondria swelling and reduced respiratory activity, suggesting the induction of the mPTP opening . An analogous effect was ascribed to DAQs derived from enzymatic oxidation of DA, specifically addressing the modulation of mPTP opening to DAQs . As a consequence, both DA and DOPAL-derived quinones could be responsible for the activation of the apoptotic pathway. On the other hand, DOPAL-induced decreased cell viability was assessed by measuring Lactate Dehydrogenase release in the extra-cellular space, which is an accepted indication of necrosis .
Don’t Miss: What Tests Determine Parkinson Disease
Precision Medicine In A Preventive Approach
The failure of current therapies for PD may be due to the heterogeneity of syndromes collectively referred to as PD. While all converge in the massive loss of DA neurons in the midbrain alongside the appearance of Lewy bodies, different etiologies of PD have been found. Some of these etiologies specifically affect the DA neurons, while others may overlap with comorbid conditions such as AD and other synucleinopathies. Based on this idea, the multiple hit hypothesis was proposed, in which the basis for selective neuronal death is a combination of toxic stress, induced by DA oxidation or mitochondrial dysfunction, co-occurring with inhibition of neuroprotective responses, such as follows after the loss of parkin function .
This said, the bright side of PDs multifactorial etiology provides an opportunity for more personalized treatment regimens. Precision medicine is driven to improve specific molecular alterations and treat particular subtypes of PD . Personalized medicine is not a novel treatment approach outside of PD, and it is currently used in an array of conditions, such as oncology and cystic fibrosis . The slow development of PD gives a unique opportunity to study the patients genome and environmental factors to target the causes of the disease in each specific group of patients .
How Long Does It Take For L
In the beginning. When you first start taking levodopa, you feel a noticeable improvement in your Parkinson’s symptoms that is maintained throughout the day. Your medicine effectively tops up dopamine levels within your brain for several hours, so most people get effective symptom control with three doses per day.
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Disease Deadly
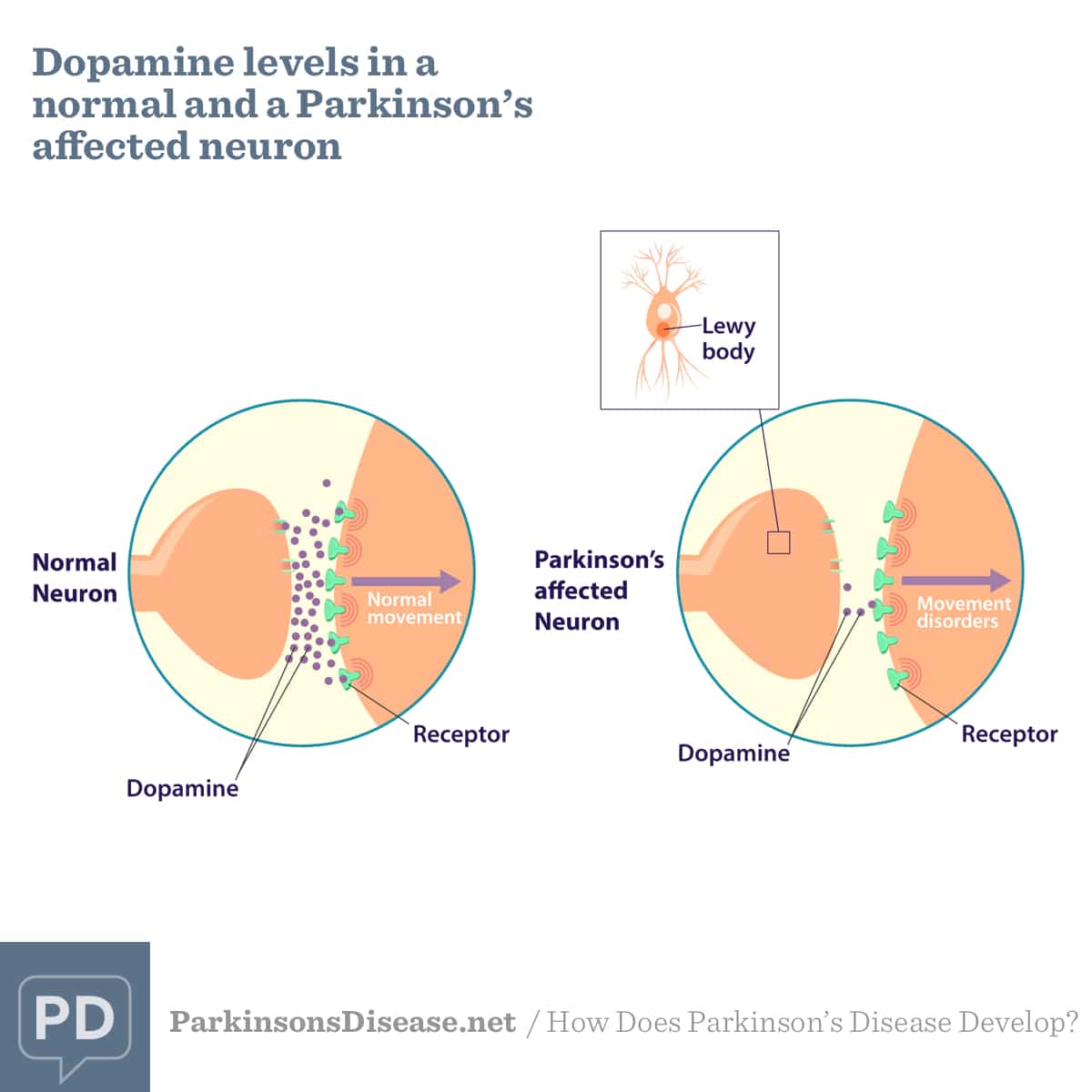
What Is Dopamines Connection To Parkinsons Disease
For people with Parkinsons disease, dopamine levels are too low. As the dopamine starts to fall, signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease will begin to reveal themselves. That means the smooth, controlled body movements may be replaced by symptoms like tremor or stiffness in limbs. Fluid motions may become slow, shaky, and halted.
Dopamine levels may be significantly reduced by the time these symptoms are noticeable. Some of the earliest signs of Parkinsons disease arent as obvious, and they may occur years before the more significant motor problems arise. These symptoms include:
- difficulty concentrating
Its not clear why dopamine levels drop off in people with Parkinsons disease, but the lower the level of dopamine, the more likely you are to experience symptoms of the disorder.
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke , the symptoms of Parkinsons disease typically begin to appear when a persons brain has lost 60 to 80 percent of their dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra. That means the drop in dopamine may be happening long before symptoms are recognized and your doctor begins the work of trying to determine whats causing issues.
