How Do I Prevent Falls From Common Hazards
- Floors: Remove all loose wires, cords, and throw rugs. Minimize clutter. Make sure rugs are anchored and smooth. Keep furniture in its usual place.
- Bathroom: Install grab bars and non-skid tape in the tub or shower. Use non-skid bath mats on the floor or install wall-to-wall carpeting.
- Lighting: Make sure halls, stairways, and entrances are well-lit. Install a night light in your bathroom or hallway and staircase. Turn lights on if you get up in the middle of the night. Make sure lamps or light switches are within reach of the bed if you have to get up during the night.
- Kitchen: Install non-skid rubber mats near the sink and stove. Clean spills immediately.
- Stairs: Make sure treads, rails, and rugs are secure. Install a rail on both sides of the stairs. If stairs are a threat, it might be helpful to arrange most of your activities on the lower level to reduce the number of times you must climb the stairs.
- Entrances and doorways: Install metal handles on the walls adjacent to the doorknobs of all doors to make it more secure as you travel through the doorway.
Deep Brain Stimulation And Respiratory Failure
DBS is an effective strategy for the treatment of advanced PD, thus improving motor fluctuations and bradykinesia.
Nonetheless, the classical target of the subthalamic nucleus -DBS reserves stimulation-induced side effects in the long-term period, comprising gait and speech impairment, as well as a progressively worsening of tremor. In this scenario, only few papers have specifically investigated respiratory failure. In particular, STN-DBS may increase the risk of a fixed epiglottis and modify velopharyngeal control these effects seem to strictly depend on frequency parameters, with low-frequency stimulation leading to a clinical improvement, whereas higher frequencies are associated with a detrimental effect on velopharyngeal control .
In support of this view, Hammeret al. have recently found that in STN-DBS patients, respiratory changes do not correlate with limb function, but speech-related respiratory and laryngeal control may benefit when the stimulation is delivered at low frequencies and shorter pulse width . In addition to stimulation frequency, other factors may account for these correlations, including variability in localisation of the active DBS electrodes, individual variability in somatotopic organisation of STN, stimulation fields and potential current spread beyond the STN target . Data on the relationship between respiratory changes and novel DBS targets, such as the pedunculopontine nucleus , have not been extensively reported so far.
Billy Connolly Jokes About Parkinsons During Drug Discussion
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive nervous system disorder that cannot be cured, although the sooner it is picked up the better. Steps can be taken to slow down its progression, helping a person with Parkinson’s to maintain quality of life for as long as possible. The symptoms of Parkinson’s are mainly related to movement because it leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain. However, occasionally the symptoms can appear in unusual areas of the body including in the way you .
You May Like: What Color Is The Ribbon For Parkinson’s
Lack Of Oxygen To The Brain In Parkinson’s Disease
and hence low oxygenation levels through poor breathing are likely to make the neurological situation worse.
Furthermore, these unhealthy breathing patterns are still apparent in many people with PD even when the medications are working well and the other main motor symptoms are alleviated. Speaking with many people with PD about this, the realization usually occurs that poor breathing habits were already ingrained years before diagnosis, and often are life-long patterns. It seems therefore that issues with breathing may be more causal of other symptoms, or at least an exacerbating factor of PD, rather than just an effect of the disease.
Sleep Disorders In Parkinsons Disease

Parkinsons sleep apnea: Sleep apnea is a sleep-related breathing disorder in which the person stops breathing for brief moments throughout the night. This can cause the individual to awaken abruptly in order to resume breathing. Sleep apnea sufferers often wake up tired, may experience headaches and jaw pain, and may have other health problems, like hypertension and diabetes.
Some studies have shown that up to 20 percent of Parkinsons disease patients suffer from sleep apnea, compared to five percent of the general population. The good news is, sleep apnea can easily be treated with a continuous positive airway pressure device.
Parkinsons insomnia: Insomnia in Parkinsons disease occurs in up to 30 percent of patients. Insomnia can be a sign of anxiety and may also be linked to depression the two other symptoms of Parkinsons disease that may explain its high occurrence. Medication for Parkinsons disease may contribute to insomnia as well, and thus some adjustment of insomnia treatment may be required.
Therapy may help resolve insomnia issues, and practicing good sleep hygiene only using the bed for sleeping, for example may help improve the condition.REM behavioral disorder: The REM sleep phase is when our dreams form and occur. REM behavioral disorder is when a person acts out their dreams. Generally, this is harmless, but it can increase the risk of injury and danger for the sleeper, especially if motor function is impaired.
Related Reading:
Read Also: Life Expectancy After Parkinson’s Diagnosis
Medical Recognition Of Breathing Disorders
The existence of these breathing disorders have been known about, but largely ignored, in medical circles, for decades. Indeed, L.C. Lum, a cardiologist at Papworth & Addenbrookes Hospitals, Cambridge, UK, wrote an article on this entitled Hyperventilation: the Tip of the Iceberg in 1975. Here are some relevant excerpts:
“…this syndrome… shows up in medical clinics under many other guises. This is merely the tip of the iceberg the body of the iceberg, the ninety nine per cent who do not present , presents a collection of bizarre and often apparently unrelated symptoms, which may affect any part of the body, and any organ or any system. The many organs involved are often reflected in the number of specialists to whom the patient gets referred, and my colleagues have variously dubbed this the multiple doctor or the fat folder syndrome. Indeed the thickness of the case file is often an important diagnostic clue.”
Lum lists many symptoms, many of which are also common in PD: palpitations, disturbance of consciousness/vision, shortness of breath. “asthma” chest pain, dysphagia, muscle pains, tremors, tension, anxiety, fatigability, weakness, exhaustion, sleep disturbance nightmare, constipation, diarrhea, twitching eyelids, headache, giddiness, difficulty in breathing, weak limbs, painful limbs, vague pain, weakness, irritability, insomnia.
What Causes Of Shortness Of Breath
People with Parkinsons may experience varied respiratory symptoms, ranging from shortness of breath without exertion to acute stridor, the sudden onset of high-pitched breathing sounds when taking a breath. Dysfunction can be caused by a variety of factors including physiological restrictive changes in the lungs, upper airway obstruction, and response to medications.1,3
Also Check: What Do Parkinson’s Patients Usually Die From
Lessons From Fascia Decompression
Another seminal source of information which affirmed for myself the critical role of breathing in health and disease, especially the movement of the diaphragm, was the book
by Deanna Hansen. Deanna writes
It is through proper mechanics of the body that we maintain the optimal tissue temperature. The diaphragm muscle is situated in the core of the body, acting as the ceiling to the abdominal organs and the floor to the heart and lungs. When we inhale, the muscle moves down in the core and the belly extends when we exhale, the muscle moves up and the belly squeezes small. Breathing with the diaphragm muscle is like turning on the furnace in the body. This muscles action regulates the core temperature with its continual movement up and down through proper inhalation and exhalation. Correct posture is required to support the diaphragms shape and action. When we collapse into the core from unconscious posture, the diaphragm doesnt have the opportunity to move in the way in which it is designed.”
Correct posture is required to support the diaphragms shape and action. When we collapse into the core from unconscious posture, the diaphragm doesnt have the opportunity to move in the way in which it is designed.
and that fixing these fascial issues will be key to progressive symptom reduction. Deannas work thus points us to the conclusion that correcting diaphragm dysfunction and unhealthy breathing patterns will, in turn, be vital for mending the fascia.
What Do The Lungs Do
When you breathe in, your lungs take in oxygen, which is then circulated around your body, providing you with energy.
Exercise causes the lungs to increase their rate of breathing to match the action of the heart, which works harder to pump blood faster round the body, particularly to the muscles. The lungs and ribcage are flexible enough to expand like bellows. They adjust to the need for deeper, bigger breaths.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How To Test Your Lungs At Home
If youre worried about your breathing, or you feel that your ribcage is so stiff you cannot take a deep breath, your GP can arrange a test to diagnose any lung problems. This uses a spirometer, which measures the amount of air you can inhale and exhale.
However, there are more fun ways to test this for yourself. Below are four simple checks that will also strengthen your lungs and keep your ribcage flexible. If you find some of these tests difficult, such as becoming light-headed or out of breath, then you know you have some work to do in strengthening your lungs.
Breathing muscles
Using a mirror, watch your body as you breathe. We naturally breathe in using the diaphragm, a large muscle at the base of our ribcage, so you should see your belly expand and your lower ribs move outward. These areas sink back to their normal position when we breathe out. If your ribcage is stiff, you may chest breathe, where you see the upper chest inflate and your shoulders move up and down. This wastes energy and is not an efficient way of breathing. Your GP can refer you to a physiotherapist if you need to learn better breathing techniques.
Lung power
Ribcage flexibility
Exercises you can do at home
This is only a start though, and its best to seek better and more specific advice from your GP to keep your lungs fit and healthy.
Research Is Underway To Further Understand The Cardiac Effects Of Parkinsons
It is possible to image the sympathetic nervous system of the human heart by injecting a radioactive tracer, meta-iodo-benzyl-guanidine, . Development of this technique, known as MIBG cardiac imaging, holds much promise as a test to confirm the diagnosis of PD , to identify those who are at risk of developing PD in the future, and to distinguish PD from related disorders. MIBG cardiac imaging is still considered an experimental procedure for detection of PD and is not yet in use as a clinical tool for this purpose.
A recent research study was conducted in monkeys in which the destruction of the sympathetic nerves of the heart was chemically induced to mimic the changes that are seen in PD. The cardiac system was then imaged using a number of new-generation radioactive tracers, which bind to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. This model system may help to shed light on the molecular changes that accompany the loss of the sympathetic nerves of the heart and can also be used to track the response of the cardiac system to therapeutic agents.
Also Check: Which President Had Parkinson’s Disease
Memory Or Thinking Problems
Having issues with thinking and processing things could mean your disease is progressing. Parkinsons is more than a movement disorder. The disease has a cognitive part as well, which means it can cause changes in the way your brain works.
During the final stage of the disease, some people may develop dementia or have hallucinations. However, hallucinations can also be a side effect of certain medications.
If you or your loved ones notice that youre getting unusually forgetful or easily confused, it might be a sign of advanced-stage Parkinsons.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
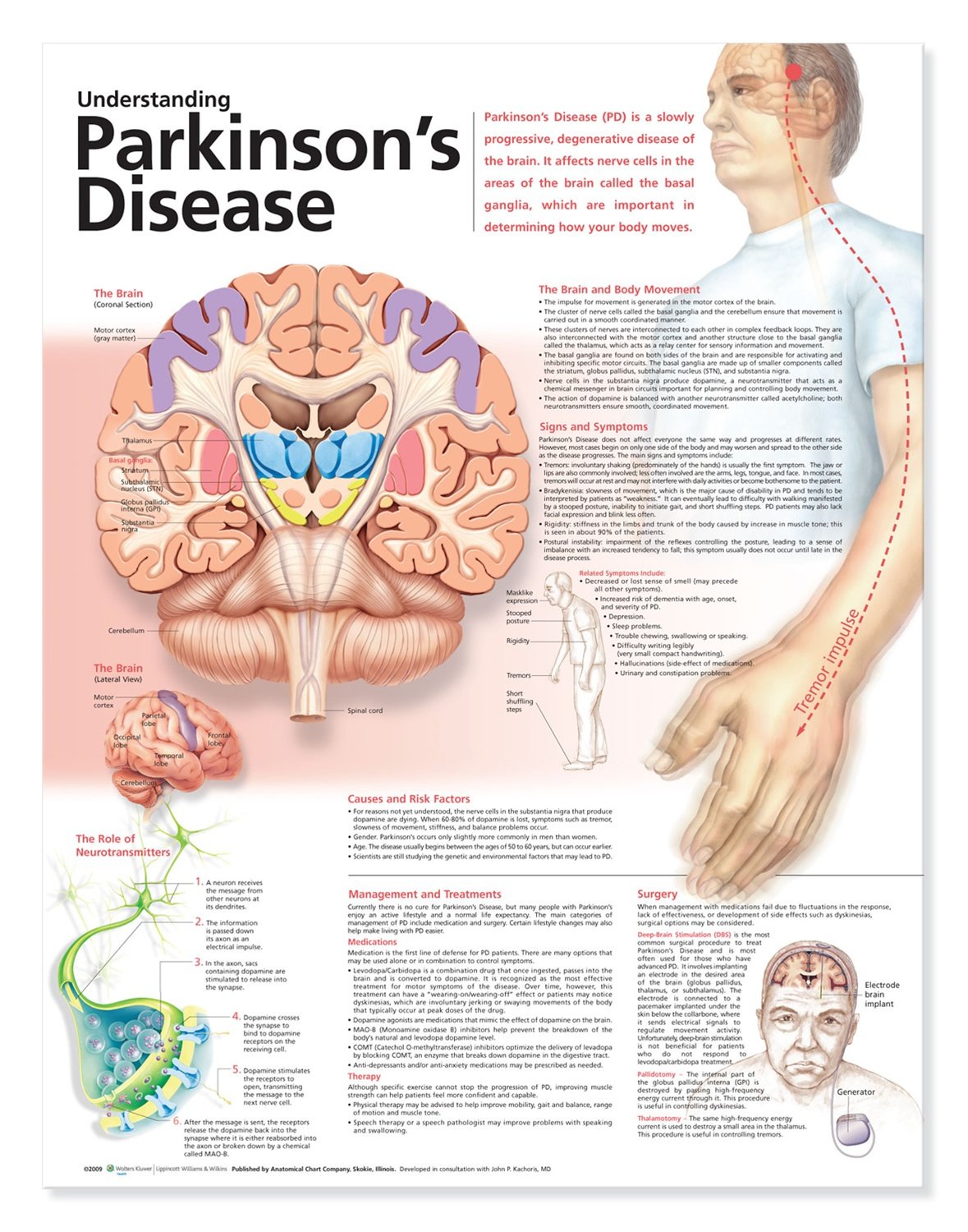
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
You May Like: Can Alcoholism Mimic Parkinson’s
The Issue Of Pneumonia In Parkinson’s Disease
Aspiration pneumonia represents a dramatic complication that may explain the acute/subacute onset of fever and respiratory insufficiency in a PD patient. Physiologically, swallowing requires adequate coordination between pharyngeal and respiratory musculature, but this mechanism is frequently impaired in PD . Dysphagia is typical in the advanced stages of disease, on average 1011years after motor symptoms onset , when bradykinesia, rigidity and dyskinesias are predominant however, a cough dysfunction in more than 50% of asymptomatic PD patients has been demonstrated and this may also contribute to silent aspiration and increased risk of pneumonia . Moreover, in these patients the cough mechanism becomes weak because of cough reflex impairment and chest wall rigidity, further increasing the risk of aspiration . A blunted urge to cough , a respiratory sensation that precedes the cough reflex, is also present and correlates with the severity of dysphagia and consequently, with an increased risk of aspiration .
Effects Of Dopaminergic Therapy: Risk Or Protection
Studies have provided controversial results about the therapeutic effects of dopaminergic stimulation, and the role of drugs commonly used in the treatment of PD is still debated, strictly depending both on disease stage and administration modality.
Most papers strengthen the role of anti-Parkinsonian drugs as a protective factor against the development of respiratory failure. Levodopa increases inspiratory muscle function in anaesthetised dogs , and dopamine improves diaphragm function during acute respiratory failure in patients with COPD . In early stages, the levodopa equivalent daily dose does not correlate with pulmonary functional testing as the disease progresses, anti-Parkinsonian medications may be responsible for the maintenance of the maximal inspiratory mouth pressure and sniff nasal inspiratory pressure . Accordingly, bedtime controlled-release levodopa is associated with less severe obstructive sleep apnoea in PD . Because dopamine is not known to increase muscle strength, it may ameliorate respiratory function by improving muscle coordination by a central activity .
Many authors have investigated the effect of dopaminergic therapy on aforementioned respiratory dysfunction, especially on obstructive and restrictive patterns .
Main findings of major studies we considered about the effects of dopaminergic drugs on respiratory parameters and respiratory dysfunctions
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Types Of Eye Movements
There are three kinds of eye movements that can change with PD:
- Saccadic rapid eye movements direct us to gaze at a specific object or to read lines of print.
- Pursuit eye movements allow us to follow an object as it moves.
- Vergence eye movements allow us to move our eyes in different directions2
Changes to these eye movements due to Parkinsons can also result in different kinds of visual difficulties. The inability to control eye movements can lead to involuntary blinking, double vision and other motor issues that can affect visual acuity.
Dry eyes can be treated with drops or ointments, warm wet compresses, but are not generally cured. The blink reflex can be impacted by PD. This manifests as either a slowing of the reflex, appearing as inappropriate staring, dry or burning eyes and by reduced vision. Blepaharospasm and apraxia are two common eyelid motion issues. Blephararospasms are eyelid spasms that cannot be controlled, cause eyelids to squeeze, and can be relieved with Botox injections. Apraxia is a condition that makes it difficult to open eyes. There are specialized lid crutches and cosmetic tape that can be applied to hold the eyelids open.2
Abnormal Lung Function Found In Patients With Early
Results of a study on patients with early-stage Parkinson disease add to the evidence showing an association between PD and pulmonary function and point to the potential use of respiratory center drive to identify early PD.
Results of a study on patients with early-stage Parkinson disease add to the evidence showing an association between PD and pulmonary function and point to the potential use of respiratory center drive to identify early PD.
Prior research has shown that impaired pulmonary function is a nonmotor symptom of PD that increases disability in patients with PD, and respiratory complications are associated with greater mortality. However, most of the studies involved patients with advanced-stage PD. The researchers of the current study set out to investigate the link between pulmonary function and early-stage idiopathic PD, as well as the role of respiratory center drive, which is measured by airway occlusion pressure and is associated with the level of muscular activity when breathing in.
The study, published in Frontiers in Neurology, enrolled 43 patients with idiopathic PD and 41 healthy controls from the hospital at Tianjin Medical University in China. The patients had a mean disease duration of 1.67 years, and their mean total levodopa equivalent dose was 313.18 mg. The control participants were matched to the patients on age, sex, and body mass index.
Reference
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
