Surgery To Implant The Deep Brain Stimulation Device
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical implantation of an electrical device into the brain. A neurosurgeon uses imaging scans to pinpoint the right spot in the brain for implanting the electrode.
When surgeons have determined the correct location, they create a small opening in the skull and insert a thin, insulated wire, through which they insert the electrode. Surgery to implant the electrode takes about four hours and requires general anesthesia. You may then stay overnight in the hospital for observation.
The next day, doctors perform the second part of the surgery, which involves connecting the insulated wire to a battery-operated pulse generator that is implanted under the skin near the collarbone. Most people can return home after this procedure.
Several days after the surgery, you meet with your neurologist, who programs the pulse generator. Pushing a button on an external remote control sends electrical impulses from the pulse generator to the electrode in the brain.
People who use deep brain stimulation work closely with their neurologist to find the combination of settings that best controls their symptoms. After several visits, they are able to control the strength of the electrical impulses on their own. Following this adjustment period, most people require only occasional maintenance visits.
A Stanford Neurosurgeon Answered Questions About Deep Brain Stimulation
Stanfords Parkinsons Community Outreach Program hosts a quarterly deep brain stimulation support group meeting for those wanting to learn more about this surgical treatment for Parkinsons disease . The June 2020 meeting featured Dr. Daniel Kramer, a neurosurgeon and clinical instructor at Stanford, who answered audience questions pertaining to DBS.
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinsons
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider will schedule visits to see you after your procedures. Programming visits occur with your neurologist, and youll need to make appointments to see them. The goal of those visits is to find the settings that work best and don’t cause side effects that disrupt your life.
Regular visits with your healthcare provider are also common to monitor your condition, symptoms and to adjust medications or other treatments as needed. The schedule for these visits is something that your provider will discuss with you.
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Physical Therapy
Latest Developments In Dbs Surgery And Future Enhancements
In this one hour and twenty one minute webinar Stanford neurosurgeon Jaimie Henderson, MD, reviewed the steps a person with Parkinsons can expect before, during, and after DBS surgery. He also outlined the differences between DBS systems as well as recent and anticipated advancements in DBS technology before taking questions from listeners.
How Does Dbs Work
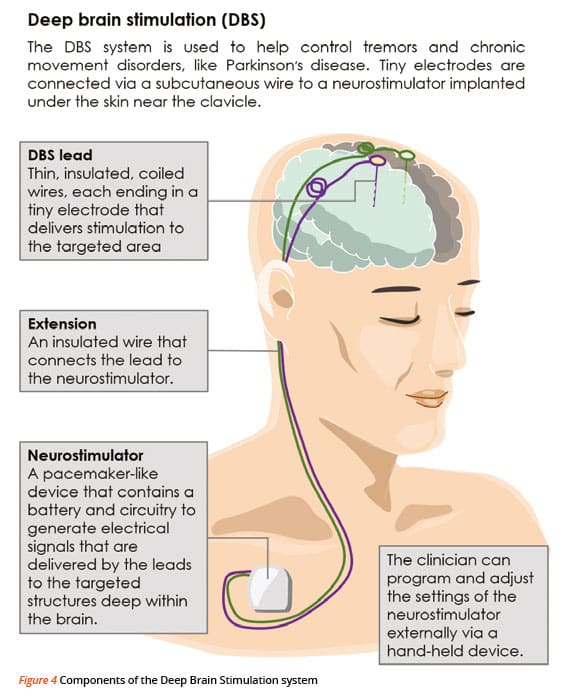
In DBS surgery, electrodes are inserted into a targeted area of the brain, using MRI and, at times, recordings of brain cell activity during the procedure. A second procedure is performed to implant an impulse generator battery , which is similar to a heart pacemaker and approximately the size of a stopwatch.
The IPG is placed under the collarbone or in the abdomen and delivers an electrical stimulation to targeted areas in the brain that control movement. Those who undergo DBS surgery are given a controller to turn the device on or off and review basic parameters such as battery life.
Recommended Reading: How To Lose Weight With Parkinson’s Disease
Approaches: Rtms As A Therapy
The effects of rTMS usually last about 30-60 minutes in humans, depending on protocols and usage patterns, such as pulse number, rate and intensity12. Of course, if this were the only effect, rTMS would not make real sense. Permanent changes are crucial for using it as a therapy.
Repeated induction of plasticity seems to fill that gap by creating temporary changes for a long time . This seems to depend on the number of sessions, so protocols of 10 or more days of use are often applied. So far, depression may warrant therapies of up to six weeks, at least 20-30 sessions for best effects13. The idea is to create structural and functional changes gradually, to âregularizeâ the neuronal interconnections.
In order to apply rTMS, the patient must be seated or in a ârelaxedâ position, in a comfortable environment. Some even consider using rTMS prior to physical or psychological therapy, which seems to cause dramatic changes and increases its effectiveness dramatically14. We will discuss the pathologies where rTMS has proven to be effective, going deeper into their theoretical bases and the various studies that corroborate these data.
Suggested Relative Criteria For Ineligibility
1) Any cognitive disorder that may interfere with adequate understanding about the treatment procedures , or potential for worsening or interference with daily activities after surgery significant impairment of semantic or phonemic verbal fluency in the preoperative evaluation
2) Untreated, unstable or recurrent major depression
3) In general, there is a reluctance to recommend surgery in patients of advanced age , as the risk/benefit ratio is less favorable due to cumulative comorbidities and cognitive burden3737. Okun MS, Foote KD. Parkinsons disease DBS: what, when, who and why? The time has come to tailor DBS targets. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010 Dec 10:1847-57. https://doi.org/10.1586/ern.10.156
4) UPDRS Part III with a score lower than 30/108 in defined OFF, representing a low functional disability in the absence of significant therapeutic effect of levodopa2828. Lang AE, Houeto JL, Krack P, Kubu C, Lyons KE, Moro E et al. Deep brain stimulation: preoperative issues. Mov Disord. 2006 Jun 21:S171-96. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20955
Don’t Miss: Nyu Langone Parkinson’s Center
How Does Dbs Compare To Other Methods Of Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
As in Hardys case, every patients treatment begins with medication until it is determined that they can benefit from DBS. Medications are always tried first. Unfortunately, we can only get so far with medications. Oftentimes, many patients try them, and they may work for a little while, said Dr. Sheth.
But at some point, oftentimes the medications stop working as much because the disorder tends to progress over the years. It could get worse, and the medicines may not be able to keep up. Many of the medicines themselves have their own side effects. So, you get to a point where perhaps the medicines are helping to a degree, but they’re causing their own side effects, and exactly when we get to that point is when we introduce the idea of a surgical therapy like DBS.
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation Or Dbs
Deep brain stimulation, or DBS, is often described as a pacemaker for the brain. It works much like a pacemaker, sending electrical signals to the brain instead of the heart. DBS is primarily utilized for patients who have Parkinsons disease, dystonia, or essential tremor, and who cant adequately control their disease with medication. Before any patient is considered for the surgery, they are evaluated by the U-M interdisciplinary team. That team includes a neurosurgeon, neurologist, clinical neuropsychologist, speech pathologist, social worker, and other team members who ensure that you and your family understand the procedure and discuss your expectations and concerns.
Its important to understand that DBS does not offer a cure for your disease, but a way to manage it more effectively. It can offer many benefits, including the need to take less medication and therefore experience fewer medication side effects.
Read Also: Brain Implant Parkinson’s Disease
Experience Fewer Symptoms With Deep Brainstimulation
For patients with movement disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor, an effective treatment is available to help significantly reduce their symptoms and make performing daily activities easier.
For appointments
Deep brain stimulation is a therapy used to treat multiple disorders. The most common disorders include Parkinsons disease and essential tremor. It can be used to improve a patients:
- Abnormal muscle activation
It is also being studied in a few psychiatric conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, Tourettes syndrome, depression and addiction.
About DBS surgery
The procedure involves placement of an electrode or lead into a deep structure of the brain typically, one on each side of the brain. These electrodes are secured in place with a plastic cap and connected to extension wires that are tunneled underneath the skin to an implanted generator placed under the skin just below the collar bone, similar to a pacemaker.
The generators last for 3-15 years depending on type implanted and patient use. They are replaced with a simple outpatient surgery. The overall risk of the operation is very low but not zero. In depth discussion with your neurologist and surgeon is needed to determine if you are an appropriate candidate and your risk of the operation.
For above images: ©2021 Medtronic. All rights reserved. Used with the permission of Medtronic.
What Risks Come Along With Doing Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS is a surgical procedure. As with any surgery there are some risks associated with it. Some of the risks of DBS include infection and bleeding. Your neurosurgeon may discuss some additional risks with you. Studies have shown that any risks are relatively small, but they should be kept in mind when considering DBS.
Read Also: How To Diagnosis Parkinson’s Disease
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work
Movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease and other neurological conditions are caused by disorganized electrical signals in the areas of the brain that control movement. When successful, DBS interrupts the irregular signals that cause tremors and other movement symptoms.
After a series of tests that determines the optimal placement, neurosurgeons implant one or more wires, called leads, inside the brain. The leads are connected with an insulated wire extension to a very small neurostimulator implanted under the persons collarbone, similar to a heart pacemaker. Continuous pulses of electric current from the neurostimulator pass through the leads and into the brain.
A few weeks after the neurostimulator has been in place, the doctor programs it to deliver an electrical signal. This programming process may take more than one visit over a period of weeks or months to ensure the current is properly adjusted and providing effective results. In adjusting the device, the doctor seeks an optimal balance between improving symptom control and limiting side effects.
You May Like: On-off Phenomenon
Which Brain Targets Should Be Used To Implant The Dbs Lead
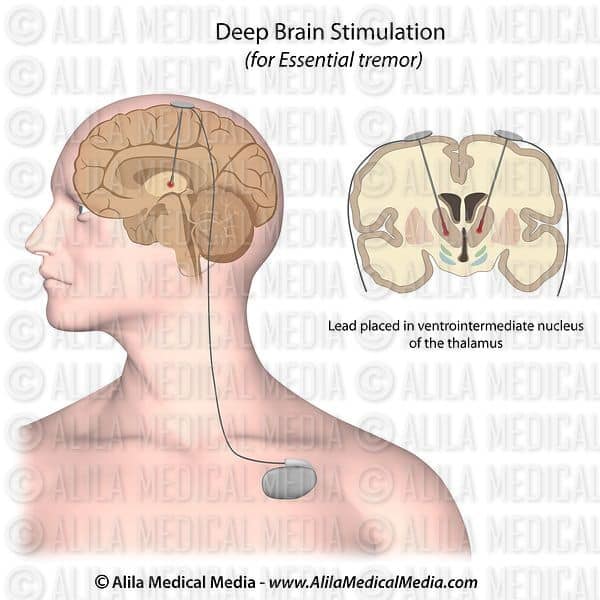
- There are three brain targets that the FDA has approved for use in Parkinsons: the subthalamic nucleus and the globus pallidus interna are the most common.
- The target choice should be tailored to a persons individual needs.
- There are many ongoing studies that will help refine target choice for individual people.
- Although the picture is not yet clear on the issue of target choice, the STN seems to provide more medication reduction, while GPi may be slightly safer for language and cognition.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson Disease Be Cured
Historical Perspective Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Prior to the discovery of levodopa, surgical interventions were the most efficacious treatment for PD symptoms, but primarily focused on the reduction of bothersome tremor. Early approaches targeted the pyramidal tracts, with lesioning either at the point of origin in the cortex or the descending pathways through the brainstem and cervical spinal cord . Although tremor was reliably improved following surgery, hemiparesis was an inevitable consequence. However, in 1952, Dr. Irving Cooper inadvertently interrupted the anterior choroidal artery while performing a mesencephalic pedunculotomy in a patient with PD. Ligation of the vessel was required, though what resulted was a serendipitous reduction in rigidity and tremor with preservation of motor and sensory function. Cooper reasoned the favorable outcomes were due to infarction of the medial globus pallidus. An expansion of ablative stereotactic surgery followed, aided by the earlier development of the stereotactic frame and methods of targeting deep brain structures, including the basal ganglia and thalamus. However, the success of these approaches was limited, partly because of inaccurate, imprecise, and inconsistent targeting. Moreover, intentionally created bilateral brain lesions frequently led to irreversible deficits in speech, swallowing, and cognition.
What Benefits Does The Procedure Offer
DBS is not a cure for Parkinsons, but it may help control motor symptoms while allowing a reduction in levodopa dose. This can help reduce dyskinesias and reduce off time. DBS does not usually increase the peak benefits derived from a dose of levodopa the best levodopa response before DBS is a good indicator of the best response after DBS. But it can help extend the amount of on time without dyskinesias, which may significantly increase quality of life.
DBS does not provide most patients benefit for their non-motor symptoms, such as depression, sleep disturbance, or anxiety. DBS also does not usually improve postural instability or walking problems. If a symptom you have does not respond to levodopa, it is not likely to respond to DBS.
Don’t Miss: Personal Training For Parkinson’s Disease
Suggested Criteria For Surgical Eligibility
1) High level of certainty about the diagnosis of idiopathic PD using the Queen Square Brain Bank diagnostic criteria3333. Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinsons disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Mar 55:181-4. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181 or the new international Parkinson and Movement Disorders Society criteria22. Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinsons disease. Mov Disord. 2015 Oct 30:1591-601. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26424. An alternative diagnosis of atypical or secondary parkinsonism should be carefully excluded
2) Clinical progression for a minimum of four years is additionally useful for improving the certainty of a clinical diagnosis of idiopathic PD
4) Exceptions to the need for levodopa responsiveness include patients with severe disabling resting tremor, resistant to dopaminergic therapy. In these patients, the symptomatic benefit is likely, regardless of the levodopa challenge test response
8) The following attributes give support to the surgical eligibility: young age onset, severe tremor, need to reduce medications, nocturnal akinesia.
Who Is A Candidate For Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS is more than just a surgical procedure. It involves a series of evaluations, procedures, and consultations before and after the actual operation, so people interested in being treated with DBS should be prepared to commit time to the process.
For example, those who do not live close to a medical center that offers DBS surgery may need to spend significant time traveling back and forth to appointments.
The procedure, as well as the pre-operative evaluation and post-operative follow-up, can be expensive depending on the persons insurance coverage. DBS surgery is an FDA-approved treatment for Parkinsons disease, and Medicare and most private insurers cover the procedure, but the extent of coverage will depend on each persons individual policy.
Prospective patients should have realistic expectations about DBS results. Although DBS can improve movement symptoms of Parkinsons disease and greatly improve quality of life in properly selected patients, it is not likely to return anyone to perfect health.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Foods To Avoid
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation For The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
Objective/Rationale:Current treatments for Parkinsons disease are either associated with side effects, expensive, or their efficacy diminishes over time. Thus, the development of practical, inexpensive and effective long-term, adjunct treatments is needed in PD research. Transcranial direct current stimulation may represent one such intervention with a realistic potential to be translated into clinical practice. The goal of this project is to identify the optimal stimulation parameters for the application of tDCS to improve motor and cortical function in PD.
Project Description:The project comprises two studies designed to examine the efficacy of different tDCS protocols of improving motor function in PD. The first study will determine the optimal timing of tDCS relative to practice of a motor task to improve motor performance, whereas the second study will examine the optimal intensity of tDCS to improve motor performance. The studies will also determine if motor performance improvements attained in a task practiced in association with tDCS can be generalized to non-trained tasks such as a common clinical measure of motor function and various functional manual dexterity tests. Additionally, transcranial magnetic stimulation will be performed before and after the tDCS interventions to assess selected cortical pathways that are commonly impaired in PD and determine the extent to which tDCS impacts these pathways.
Living With A Dbs Device
Batteries most often last three to five years, but this can vary. Rechargeable batteries may last up to 15 years.
There are several precautions related to electrical/magnetic devices that are important, but usually easy to accommodate. Items such as cell phones, computers, and home appliances do not generally interfere with the stimulator. Keep your stimulator identification card handy when you are out and about, in your wallet or purse.
Theft Detectors
Be aware that some devices may cause your transmitter to turn on or off. This includes security monitors that might be found at the library and retail shops.
If this occurs accidentally, it is not usually serious, but may be uncomfortable or result in your symptoms worsening if the stimulator is turned off. When you visit stores with these devices, you can ask to bypass the device by presenting your stimulator identification card.
Home Electronics
Keep the magnet used to activate and deactivate the stimulator at least 12 inches away from televisions, computer disks, and credit cards, as the magnet could potentially damage these items.
Air Travel/Metal Detectors
Talk to TSA personnel when traveling by plane, as the metal in the stimulator may set off the detector. If you are asked to go through additional screening with a detector wand, its important to talk to the person screening you about your stimulator.
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
Occupational Electromagnetic Concerns
Also Check: Possible Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Happens After Deep Brain Stimulation
Your healthcare provider will schedule a follow-up appointment that will take place within a few weeks of the pulse generator implantation procedure. At this appointment, they’ll start programming the pulse generator.
All pulse generators now in use have a wireless antenna built-in. That allows your healthcare provider to access and program the device from outside your body. Finding the right settings for the pulse generator may take some time and additional visits for adjustments.
Most pulse generators have special batteries that have long lifespans. Standard batteries for these devices last about three to five years. Some devices use rechargeable batteries, which can last about nine years. Replacing the battery also takes a surgery procedure, but this is usually shorter and quicker than the original surgery to implant the pulse generator. You’ll still go home the same day for battery replacements.
