Diagnostic Criteria For Et & Pd
Two sets of criteria are commonly used for the diagnosis of ET. For definite ET, the diagnostic criteria proposed by the Movement Disorder Society require the presence of persistent, bilateral postural tremor of the forearms . Kinetic tremor may be present, but is not necessary for the diagnosis . No other abnormal neurological signs may be present, except for Froments sign, which is a cogwheel phenomenon without rigidity . For definite ET, the criteria proposed by the Washington Heights-Inwood Genetic Study of Essential Tremor require the presence of moderate amplitude postural tremor as well as kinetic tremor, with the latter resulting in impairment of activities of daily living .
The UK Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank criteria require postmortem confirmation for the diagnosis of definite PD . The diagnosis of probable PD requires bradykinesia and one of the following additional features: rigidity, 46-Hz rest tremor or postural instability . In addition, three supportive features are required . The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke criteria for PD only include clinical criteria for possible PD, which require three out of four of the following features: rest tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity or asymmetric onset .
Misperception #: The Tremor Of Et Is Bilateral & Symmetric
Action tremor in patients with ET is usually, though not always, bilateral, and it is typically asymmetric . In a community-based study of 54 patients with ET, the use of clinical rating scales revealed on average a 1.32-fold sideside difference, and quantitative computerized tremor analysis revealed on average a 1.71-fold sideside difference in arm tremor severity . Unilateral arm tremor is less common, reportedly occurring in 2, 4.4 and 10% of ET cases, with values varying depending on the criteria used . One study evaluated unilateral arm tremor in 412 ET cases from 133 kindreds with presumed autosomal dominant ET . Inclusion criteria required unilateral kinetic or postural tremor for at least 5 years, without dystonic posturing or bradykinesia/rigidity . Only subjects with a first-degree relative with definite ET were included . Eighteen patients were identified as having isolated unilateral arm tremor without tremor affecting other body segments . Out of the 18 patients, 13 had a combination of postural and kinetic tremor and 5/18 had only unilateral postural tremor . Isolated unilateral postural tremor should raise the suspicion of PD, and the patient should be followed closely for the development of additional signs suggestive of PD.
Clinical pearl #3: Action tremor in ET is often but not necessarily bilateral. Small to moderate sideside differences are the rule rather than the exception.
Handwriting: A Strange Clue
Micrographia, very small and crowded handwriting, is one of the hallmark signs of Parkinson’s disease that doctors will look for it’s even one of the main reasons they’ll ask patients to fill diagnostic questionnaires out themselves. This handwriting may start off having a normal “font size”, but then gradually become smaller and smaller as the patient writes more.
People with Essential Tremor don’t have micrographia their handwriting can be affected by their condition, but it’s much more likely to become larger and more shaky .
Read Also: Dementia Associated With Parkinson’s Disease
Share This Article On Twitter
Medically Reviewed by: Dr. BautistaUpdated on: September 9, 2021
Parkinsons disease is one of the most common and well-known neurodegenerative disorders in the world. Worldwide, estimates suggest that over 10 million people currently live with Parkinsons disease. In America alone, there are about 60,000 new Parkinsons diagnoses every year.
One of the main and most characteristic symptoms of Parkinsons disease is a tremor or involuntary shaking. However, Parkinsons disease is by no means the only condition that causes a tremor. Essential tremors are also noted by shaking. Learn more about the difference between essential tremor and Parkinsons disease below.
What Is The Difference Between Tremors And Parkinson’s Disease
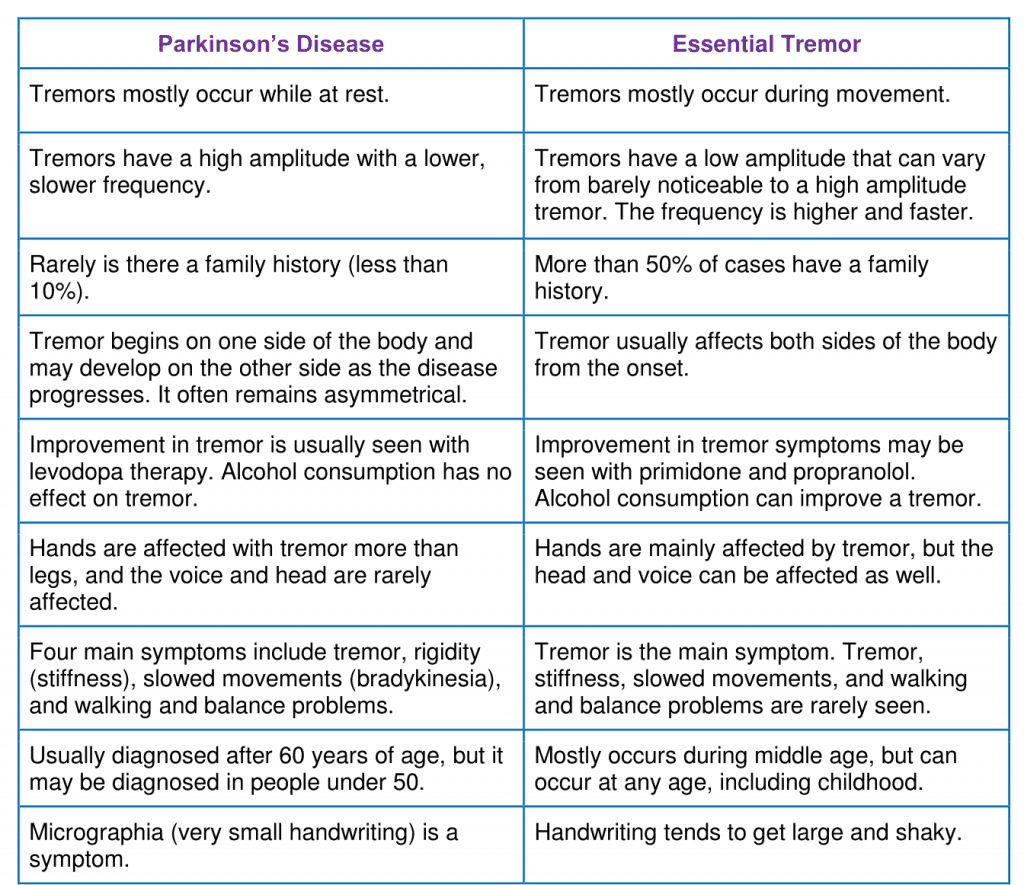
While the majority of Parkinson’s patients experience tremors,not everyone who has tremors has Parkinson’s. Tremors are also asymptom of other conditions, such as traumatic brain injury, stroke, certainmedicines, alcohol poisoning or anxiety.
Tremor is an unintentional, rhythmic musclecontraction that leads to shaking in one or more parts of thebody. Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that causes tremors,stiffness in limbs and loss of coordination.
The most significant difference between tremor associated withParkinson’s disease and tremor associated with other conditions is thatParkinson’s tremor is typically a “resting tremor,” meaning it ispresent when an individual is at rest and goes away when the individual isactive. Tremors in most other conditions are classified as “actiontremor,” meaning shaking increases when a person is active and decreaseswhen the person is at rest.
While Parkinson’s is typically the most widely-known disease associatedwith tremor, a condition called essential tremor is more common, affectingapproximately 5% of people aged 65 and older.
Read Also: How Long Can Someone With Parkinson’s Drive
Summary Essential Tremor Vs Parkinsons Disease
Essential tremor is a neurological disease with autosomal dominant inheritance, which primarily characterizes the development of bilateral, low amplitude tremor whereas Parkinsons disease is a movement disorder characterizes a decline in the dopamine level of the brain. Essential tremors have an autosomal dominant inheritance, but Parkinsons disease does not have such a genetic predisposition. This is the main difference between essential tremors and Parkinsons disease.
Reference:
1. Kumar, Parveen J., and Michael L. Clark. Kumar & Clark clinical medicine. Edinburgh: W.B. Saunders, 2012. Print. Ser. 8.
Image Courtesy:
1.8376271918 by _DJ_ via Flickr2.Writing by a Parkinsons disease patientBy Jean-Martin Charcot via Commons Wikimedia
Clinical Situation #: Pd Or Pd+et
Clinical summary
A 65-year-old man with rest tremor and rigidity in the right arm is diagnosed with PD. Five years later, he develops a postural tremor of his right arm, which occurs after a latency of 10 s and a frequency similar to his 4-Hz rest tremor.
A re-emergent tremor with similar frequency to the patients rest tremor is consistent with a diagnosis of PD. There are no additional features to suggest ET.
Also Check: Beginning Of Parkinson’s
Risk Factors For Essential Or Benign Tremor
The medical professionals have long time ago concluded what are the risk factors for one person to develop Essential Tremor. The two main risk factors regarding essential or benign tremor are:
- Genetic mutation.
- Age.
Whether you know it or not, essential or benign tremor can be passed from a parent to a child. The genetic pattern of inheriting this neurological disorder is autosomal dominant inheritance. That makes essential or benign tremor an autosomal dominant disorder. Only one mutated gene in the parents genetic structure is enough to make a person suffer from Essential Tremor later in its life.
If you have a parent that was diagnosed with essential or benign tremor, you have a 50% for developing that neurological disorder yourself. The most common genetic mutations that cause essential or benign tremor are the mutations of the genes such as LINGO1 and HAPT1.
If you are 40 years or less old, you do not have to worry at all about developing essential or benign tremor. This neurological illness only affects the people 40 years or above old.
Misperception #: Bradykinesia = Pd
Bradykinesia is a cardinal sign of PD. Although bradykinesia is not traditionally associated with ET, there have been several studies that report the contrary. One study quantified rapid alternating pronation-supination movements in 10 ET cases, 20 mild to moderate PD cases and 10 controls . Post hoc analysis demonstrated that rapid alternating movement cycle duration was statistically longer in ET cases compared with controls, and similar to PD cases . Another study, involving 61 ET cases and 122 controls, evaluated performance in four timed tests involving hand movements, as well as walking and visual reaction time . ET cases compared with controls had longer mean finger tapping times and mean visual reaction times . Another study reported reduced arm swing in 18/136 clinically diagnosed ET cases . While a small proportion of ET cases may exhibit slower movement times than controls, a reduction in amplitude and cessation of movement during rapid successive movements has not been demonstrated in ET.
Clinical pearl #6: Slower movement times may be observed in some patients with ET, yet other features of bradykinesia have not been demonstrated in ET.
Read Also: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s 2018
Misperception #: Action Tremor = Et & Not Pd
Action tremor is the hallmark feature of ET and can be further subdivided into postural, kinetic and intention tremors. Yet just as rest tremor may occur in patients with ET, conversely, action tremor may be found in patients with PD. Indeed, it is not uncommon to encounter patients with PD who have various forms of action tremor. Below, we discuss postural, kinetic and intention tremors separately.
Clinical pearl #2: Although action tremor is the hallmark feature of ET, it is commonly found in patients with PD as well. When evaluating kinetic tremor in a particular patient, comparing it to other tremor types within that patient may help distinguish PD from ET. Thus, kinetic tremor is generally of greater amplitude than postural tremor in ET whereas the converse has been reported in PD. Intention tremor with limb dysmetria is more suggestive of ET than PD. Some of the clinical features of action tremor may similarly suggest one disorder or another. Thus, a postural tremor whose frequency is similar to the 4- to 6-Hz rest tremor of PD is suggestive of PD. A postural tremor with a significant latency is also more characteristic of PD.
Causes: Parkinsons Vs Essential Tremor
The cause is largely unknown for both Parkinsons and essential tremor. However, there are theories about what may cause these conditions.
In regards to essential tremor, John Hopkins Medicine notes that there is a theory that the condition may be caused by miscommunication between the cerebellum and other parts of the brain. There is also believed to be a genetic predisposition for developing essential tremor. You may be 50% more likely to develop essential tremor if your parent has the condition.
It is also important to note that certain factors can also cause other types of tremors. For example, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, certain medications, thyroid overactivity, and toxins like lead and mercury can produce tremors that might be confused with this condition.
In regards to what causes Parkinsons disease, the direct cause as to why specific individuals develop Parkinsons is unknown. However, what happens within the body that causes Parkinsons symptoms to manifest, is the gradual loss of brain cells that are responsible for producing dopamine. When this happens, it can interfere with normal body movement, leading to patients to exhibit the common symptoms of Parkinsons.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Brain Changes In Essential Tremor
Neuropathologists have studied the brains of people with essential tremor after their death. The results are suggestive but conflicting. Some people have described changes in the cerebellum, a region of the brain commonly associated with movement and coordination. Furthermore, some studies have described a higher chance of finding Lewy bodies, usually considered to be a sign of Parkinson’s disease, in part of the brainstem known as the locus coeruleus.
Some pathologists believe that these are signs that essential tremor may be a neurodegenerative illness along the lines of Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s disease. Other studies have found that people with essential tremor may be at an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Perhaps there is a common predisposition towards neurodegeneration that links tremor with these other disorders.
On the other hand, others state that the increased risk of developing other diseases may be simple misdiagnosis meaning that perhaps some people who initially were said to have essential tremor had an unusual presentation of Parkinson’s or another known movement disorder. These researchers believe that there is no current need to call essential tremor degenerative itself.
Clinical Situation #: Et+pd
Clinical summary
A 45-year-old woman develops a bilateral action tremor than progressively worsens over the ensuing 15 years. Kinetic tremor is more severe than the postural tremor and she subsequently develops a postural head tremor. At 60 years of age, she develops a rest tremor in the right arm accompanied by bradykinesia .
The bilateral, progressive action tremor of long duration suggests ET and the subsequent development of a postural head tremor supports the diagnosis. The patient subsequently develops two parkinsonian signs, satisfying criteria for a clinical diagnosis of PD. The patient thus has a combination of ET+PD.
Don’t Miss: What Color Is The Ribbon For Parkinson’s
Distinguishing Essential Tremor And Parkinsons Disease
While most people are familiar with Parkinsons Disease , Essential Tremor is much more common1.
If you are experiencing shaking of your hands, a neurologist specializing in movement disorders can perform testing to diagnose your condition. This may include holding your arms straight out in front of your body, touching your finger to your nose, and drawing spirals on a piece of paper. Additional testing or imaging scans may also be required as part of the diagnosis.
While only a qualified physician can provide a diagnosis, there are several key symptoms that differentiate Essential Tremor from other conditions such as Parkinsons Disease.
Are There Surgical Options For Essential Tremor
Deep brain stimulation is a therapeutic option for those with severe disabling ET not already managed by medications. DBS is often described as a pacemaker for the brain. It works much like a pacemaker, sending electrical signals to the brain instead of the heart. It is primarily utilized for patients who have Parkinsons disease, dystonia, or essential tremor, who cant adequately control their disease with medication.
Thalamotomy, involving the destruction of tremor producing cells in the brain region called the thalamus, is another surgical option. Using a small temperature-controlled electrode, a permanent lesion is created in the thalamus that helps to stop tremor without disrupting sensory or motor control.
Talk to your doctor about surgical and non-surgical options that are right for you.
Read Also: How Much Does Carbidopa Levodopa Cost
Signs & Symptoms: Is It Essential Tremor Or Parkinsons
In order to start managing your condition and receive the treatment you need, you should be aware of the most common signs and symptoms as well as the key differences between essential tremor and Parkinsons. After all, the first step in getting care as early on as possible is self-awareness that you might be suffering from one of these conditions.
File A Paraquat Claim With The Help Of Our Skilful Legal Team
With over 25 years of experience in pursuing compensation on behalf of victims of toxic exposure, our attorneys are ready to provide your family member with quality legal assistance if they were exposed to paraquat and developed Parkinson’s disease. Because we are aware that individuals who struggle with this brain disorder have a difficult time explaining their situation, your help will be essential in the legal process. However, the legal process will require minimal involvement on your part, as the only documents you will need to send our legal team are evidence of paraquat exposure and proof of diagnosis for your family member. The rest of the paperwork will be efficiently taken care of by our resourceful legal experts on your behalf.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Life Expectancy Early Onset
What Is Essential Tremor
Similar to Parkinsons disease, essential tremor is a neurological disorder, and it typically gets worse over time, resulting in severe symptoms. Although essential tumor is usually not dangerous on its own, its effects can be devastating and cause difficulties in your career and everyday life making it a severe tremor.
While it is not as well-known as Parkinsons disease, essential tremor is actually more common than Parkinsons. Essential tremor affects about 5 percent of people over the age of 50, though tremor syndrome symptoms can initially appear in a persons 40s.
There is no known cause for essential tremor syndrome. Some theories suggest that the disorder causes problems within the cerebellum, which is the part of the brain responsible for movement and balance.
Essential tremor does not have a known cure or treatment, but medication and practical measures can help you manage your symptoms and tremor frequency. Medications for essential tremor usually involve beta blockers, like propranolol, or anti-seizure medications. If medication does not have any meaningful effect, your doctor may recommend surgery.
Differences Between Essential Tremor And Parkinsons Disease
- Leo Nguyen
There are an estimated 10 million people with essential tremor in the United States. Essential tremor is a neurological condition characterized by involuntary, rhythmic shaking or tremors. These tremors interfere with important tasks like drinking, eating, or writing legibly. Tremors are also present in those with Parkinsons disease, a disease affecting the nervous system that is also symptomized by muscle inflexibility and slowed movement. Because tremors are a symptom of both Parkinsons disease and essential tremor, its often hard for people to tell the difference between the two conditions. Though Parkinsons disease and essential tremor have a common symptom, they are not equal.
For those with Parkinsons disease, tremors typically occur during rest and are known as resting tremors. People with essential tremor mostly have tremors during times of activity. Because these tremors occur during activity or action, they are known as action tremors.
In addition to type, the tremors of Parkinsons disease and essential tremor also differ in frequency and magnitude. Tremors related to Parkinsons disease usually occur more frequently over time and are more forceful than those related to essential tremor. Individuals with essential tremor may see a fluctuation in the frequency of their tremors throughout the day, ranging from high to low.
Note: This article is written for informational purposes only and does not replace a proper medical diagnosis
Also Check: Parkinson Disease Genetic Link
What Medications Are Typically Prescribed To Treat Essential Tremor
There are several medications available to help manage ET symptoms. It is important to work with your doctor to find a medication that is right for you. In addition, it is equally important to make sure that a high enough dose of medication is taken for it to be effective. Provided below is a list of common medications used for ET with upper limits of the dose by which we would expect an effect on tremor. If your physician has not prescribed doses of these medications similar to the ones listed, you may consider going back to your physician to try higher doses before considering other treatment options, such as deep brain stimulation.
Doses of Essential Tremor Medications:
- Primidone – Up to 350 milligrams daily
- Propranolol – Up to 320 milligrams daily
- Topiramate – Up to 400 milligrams daily
- Clonazepam – Up to 6 milligrams daily
- Gabapentin – Up to 2700 milligrams daily
- Mirtazepine – Up to 45 milligrams daily
