What Genes Are Linked To Parkinsons Disease
Several genes have been definitively linked to PD:
- SNCA. This gene, which makes the protein alpha-synuclein, was the first gene identified to be associated with Parkinsons. Research findings by the National Institutes of Health and other institutions prompted studies of the role of alpha-synuclein in PD, which led to the discovery that Lewy bodies seen in all cases of PD contain clumps of alpha-synuclein. This discovery revealed the link between hereditary and sporadic forms of the disease.
- LRRK2. Mutations in LRRK2 were originally identified in several English and Basque families as a cause of a late-onset PD. Subsequent studies have identified mutations of this gene in other families with PD as well as in a small percentage of people with apparently sporadic PD. LRRK2 mutations are a major cause of PD in North Africa and the Middle East.
- DJ-1. This gene normally helps regulate gene activity and protect cells from oxidative stress and can cause rare, early forms of PD.
- PRKN . The parkin gene is translated into a protein that normally helps cells break down and recycle proteins.
- PINK1. PINK1 codes for a protein active in mitochondria. Mutations in this gene appear to increase susceptibility to cellular stress. PINK1 has been linked to early forms of PD.
- GBA . Mutations in GBA cause Gaucher disease , but different changes in this gene are associated with an increased risk for Parkinsons disease as well.
What To Do If Your Senior Has Parkinsons
If you notice Parkinsons-like symptoms in your older adult, the first thing to do is talk with their doctor. The doctor should review their complete medication history and you should let them know about any other symptoms or changes.
Important: Dont make any changes to medications without doctor approval that could cause serious problems.
Papaya Is Not The Same As Pawpaw
Unfortunately, the very healthy and nontoxic papaya fruit has been confused with the pawpaw 13-15. The papaya is in a different family , and has a completely different genus and species, Carica papaya Linn. 16. The fruit contains many antioxidants, vitamins and minerals, as well as enzymes that help digestion as well as chitinase, which has antibacterial activity 17. It also has relatively few calories . The health benefits include being hypertensive and is hepatoprotective . The fruit also has antibacterial, antihelminthic , antifungal and antimalarial properties. Fermented papaya fruits also support the immune system. The antioxidants in the fruit can help prevent heart disease, stroke, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases . An extract of the seeds is marketed as being able to rejuvenate the body and increases ones energy 17. So, the fruit of the papaya tree is quite different than the fruit of the North American pawpaw. Papaya fruits are very healthy.
In conclusion, graviola, the North American pawpaw and other fruits in the Annonaceae family can cause an atypical form of Parkinsons disease that does not respond to the standard therapy . Moreover, there is much misinformation and confusion in not just the popular literature, but also in some peer reviewed articles that have been published in scientific journals.
Don’t Miss: Postural Instability In Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinson’s disease. People with Parkinson’s-like symptoms that result from other causes are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinson’s, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to distinguish them from Parkinson’s. Since many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, it is important to make an exact diagnosis as soon as possible.
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose nongenetic cases of Parkinson’s disease. Diagnosis is based on a person’s medical history and a neurological examination. Improvement after initiating medication is another important hallmark of Parkinson’s disease.
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, it’s called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. It’s also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesn’t go away and continues to get worse over time.
Recommended Reading: Essential Oils Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Forgetfulness
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
Parkinson’s Disease And Parkinsonism
There is also another similar disease called Parkinsonism, which is a condition in which people have some of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but do not have Parkinson’s disease itself. Parkinsonism occurs when one or more of the regions of the brain that are responsible for Parkinson’s disease become damaged.
One of the early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease is a loss of the sense of smell, which can happen years before other symptoms appear. The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonism also include a fine tremor, which is very noticeable in the hands and arms and happens when the hands and arms are at rest.
Beyond loss of sense of smell and tremor, Parkinson’s is associated with several other physical symptoms, including slowness of movement , rigidity and postural instability. These symptoms can make walking or generally moving around extremely difficult and can lead to abnormal body posture. Additionally, people who have Parkinson’s disease or Parkinsonism often have very little facial expression, which is typically called a “masked face.”
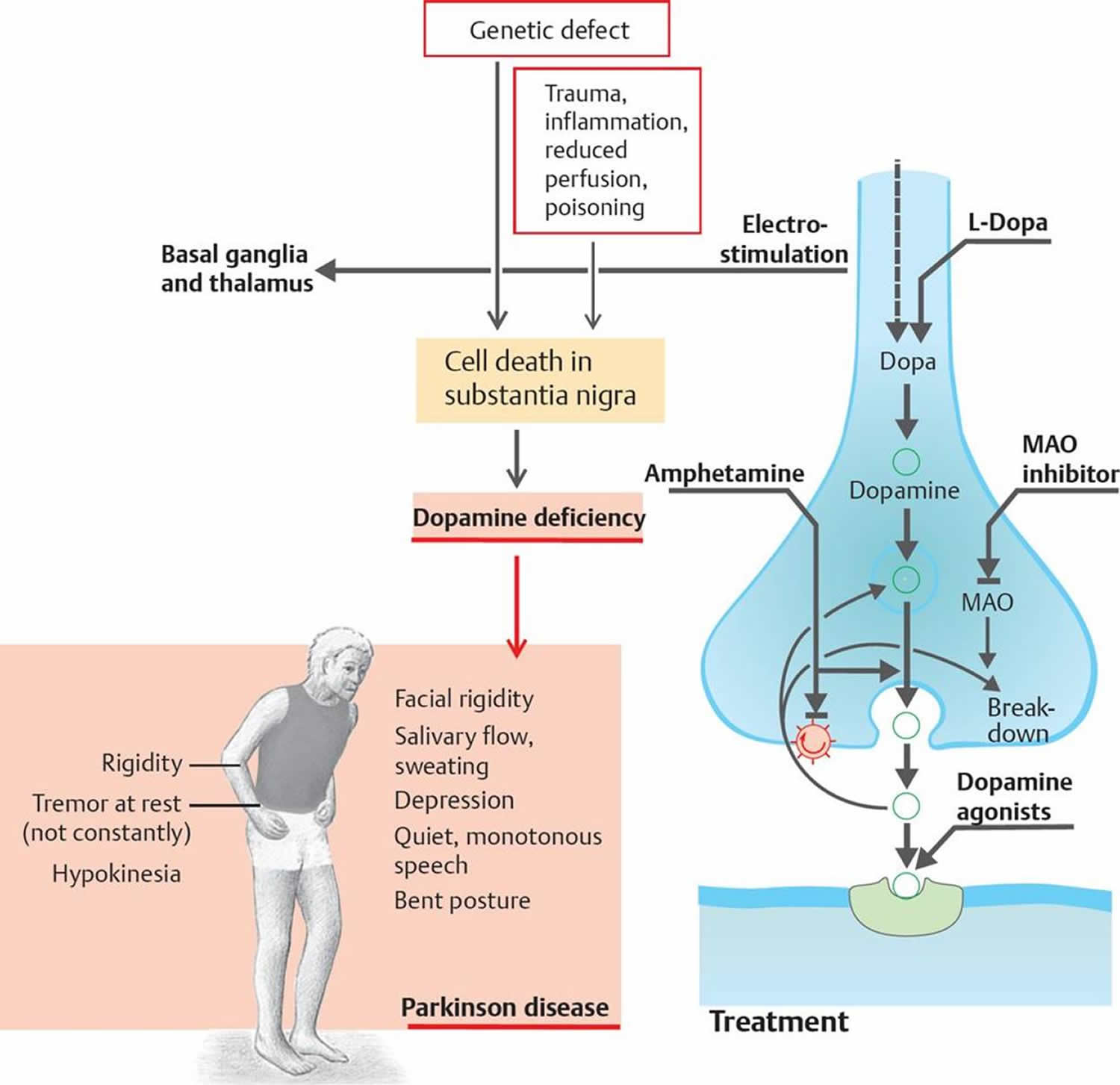
The areas of the brain involved in Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonism are called the substantia nigra and the basal ganglia. Parkinson’s disease is normally caused by slowly progressive degeneration of these two areas, which control the rhythm and smoothness of our movements and the tone of our muscles. As the substantia nigra and the basal ganglia degenerate, the typical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease begin to emerge.
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsonism Falls And Fracture Risk
All forms of parkinsonism, both PD and DIP, have implications for bone health. A 2014 meta-analysis on PD and fracture risk concludes that PD increases the risk of fracture.4
Given that the symptoms of parkinsonism affect balance, motor skills, gait, and the bodys ability to control movement, it is no surprise that people with PD are more likely to experience a fall than people without PD. Here is an excerpt from a 2016 study comparing the incidence of falls and fracture in PD patients:
It is estimated that 60.5% of patients with PD experience at least one fall and 39% have recurrent falls. The high frequency of falls consequently contributes to the increased risk for fractures in PD patients, which has been estimated to be approximately two times the risk in healthy controls. It has been estimated that 76% of falls in PD patients require health care services and 33% result in fractures. Falls and fractures may result in a series of unfavorable outcomes, such as disabilities and death. Furthermore, among PD patients with fractures, the mortality rate is approximately 10.6%.5
All too often, doctors prescribe these drugs without appropriate consideration of this risk. This excerpt from a study on DIP clarifies the danger of accepting a prescription of an unnecessary or inappropriate prescription drug:
Shockingly, the drugs that cause DIP are still being prescribed. This yet one more example further proving that the FDAs drug approval process is useless.
Synopsis
What Is The Prognosis
The average life expectancy of a person with PD is generally the same as for people who do not have the disease. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available for people with PD. However, in the late stages, PD may no longer respond to medications and can become associated with serious complications such as choking, pneumonia, and falls.
PD is a slowly progressive disorder. It is not possible to predict what course the disease will take for an individual person.
One commonly used scale neurologists use for describing how the symptoms of PD have progressed in a patient is the Hoehn and Yahr scale.
Also Check: Is Parkinson Disease Genetic
When To Be Suspicious Of Medications
In many cases, symptoms of Parkinsons could be caused by a new medication that was started a few days or a few months ago.
In other cases, it could be caused by medications that start out at one dose and are increased to higher doses. If the dose increases move too quickly, that can also cause these symptoms.
Other factors also make it more likely that someone will develop Parkinsons symptoms from medications. These include having a history of:
- Dementia
- Strokes or transient ischemic attacks
- Parkinsons in the family
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are:
- tremor or shaking, often when resting or tired. It usually begins in one arm or hand
- muscle rigidity or stiffness, which can limit movement and may be painful
- slowing of movement, which may lead to periods of freezing and small shuffling steps
- stooped posture and balance problems
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease vary from person to person as well as over time. Some people also experience:
- loss of unconscious movements, such as blinking and smiling
- difficulties with handwriting
- drop in blood pressure leading to dizziness
- difficulty swallowing
- sweating
Many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease could be caused by other conditions. For example, stooped posture could be caused by osteoporosis. But if you are worried by your symptoms, it is a good idea to see your doctor.
Also Check: Mannitol Parkinson’s
How Do Doctors Diagnose Parkinsonism
No single test exists for doctors to diagnose Parkinsonism.
A doctor will start by taking a persons health history and review their current symptoms. They will ask for a medication list to determine if any medicines could be causing the symptoms.
A doctor will likely also order blood testing to check for underlying potential causes, such as thyroid or liver problems. A doctor will also order imaging scans to examine the brain and body for other causes, such as a brain tumor.
Doctors can perform a test that tracks the movement of dopamine in the brain. This is known as the DaT-SPECT test.
The test uses radioactive markers designed to track dopamine in the brain. This allows a doctor to watch the release of dopamine in a persons brain and identify the areas of the brain that do or do not receive it.
Because Parkinsonism does not respond to typical treatments and can have a variety of symptoms, doctors can have difficulty coming to a quick diagnosis. It may take time for doctors to rule out other conditions and begin to make treatment recommendations.
What Diseases And Conditions Resemble Parkinsons Disease
PD is the most common form of parkinsonism, in which disorders of other causes produce features and symptoms that closely resemble Parkinsons disease. Many disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of PD, including:
Several diseases, including MSA, CBD, and PSP, are sometimes referred to as Parkinsons-plus diseases because they have the symptoms of PD plus additional features.
In very rare cases, parkinsonian symptoms may appear in people before the age of 20. This condition is called juvenile parkinsonism. It often begins with dystonia and bradykinesia, and the symptoms often improve with levodopa medication.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How Is A Diagnosis Made
Because other conditions and medications mimic the symptoms of PD, getting an accurate diagnosis from a physician is important. No single test can confirm a diagnosis of PD, because the symptoms vary from person to person. A thorough history and physical exam should be enough for a diagnosis to be made. Other conditions that have Parkinsons-like symptoms include Parkinsons plus, essential tremor, progressive supranuclear palsy, multi-system atrophy, dystonia, and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Sadly, no.
It is not possible to prevent Parkinsons disease, but some believe that lifelong healthy habits may reduce ones risk of developing the condition. Some medications may also relieve some of its symptoms.
In some PD patients, particularly those who are at the late stage of the disease, surgery may be an option to help improve symptoms.
Some experts also advise doing rpeventive measures such as wearing gloves and other protectvie equipment when applying pesticides as it may help protect you against the disease.
Read Also: How Does Someone Get Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
Diagnosis And Management Of Parkinsons Disease
There are no diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. X-rays, scans and blood tests may be used to rule out other conditions. For this reason, getting a diagnosis of Parkinsons may take some time.
No two people with Parkinsons disease will have exactly the same symptoms or treatment. Your doctor or neurologist can help you decide which treatments to use.
People can manage their Parkinsons disease symptoms through:
- seeing a Doctor who specialises in Parkinsons
- medication
- multidisciplinary therapy provided for example, by nurses, allied health professionals and counsellors
- deep brain stimulation surgery .
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Can The Various Stages Of Parkinsons Disease Be Identified
Parkinsons disease is a progressive disease associated by progressive symptoms in various stages. The symptoms associated with the five stages include-
Stage 1- This stage is characterized by the mildest form of Parkinsons. The symptoms are not so severe to interfere with daily tasks and overall lifestyle. Friends and family members may notice some sort of changes in the way the patient walks, his posture and some facial expression. One of the distinct symptom of Parkinsons is the tremors are other problems in movement and exclusive to one side of the body. If doctor is consulted at this stage, the prescribed medication can help ease out the symptoms at this stage.
Stage 2- This phase is considered to be the moderate form of Parkinsons because the symptoms get distinctively noticed by people. Muscle stiffness is quite common at this stage. It must be remembered that although there may be an increase of tremors and irregular posture, stage 2 does not impair the balance of the patient.
Stage 3- The patient may experience a turning point in this stage as along with the symptoms he may not be able to maintain his balance and experience decreased reflexes. Movements become slower and falls become common. Medication along with occupational therapy may be advised.
Stage 4- It becomes impossible to even stand without assistance at stage 4. Living alone may make daily tasks impossible and dangerous. Thus the patient will need a caregiver from this stage.
Also Read:
