Assessment Of The Efficacy Of Cell Transplants With Immunostaining Characterization
In the case of mDA progenitor neuron specifications, positive gene expression of common transcription factors FOXA2, LMX1A, and OTX2 and negative markers such as Afp, Gata4, and Brachyury have been quantitatively analyzed . More importantly, the upregulation and downregulation of these markers at a given stage in vitro governs the efficiency of cell fate determination. Unfortunately, these markers have been shown to coexpress in the diencephalic progenitor cells of the subthalamic nucleus . Furthermore, the expression of the positive genetic marker for DA neurons, tyrosine hydroxylase , a rate-limiting enzyme in dopamine synthesis , and the levels of GIRK2 have also been observed in many cell types in vitro . Moreover, common positive markers used to isolate high-quality DA progenitor cells include EN1 and SPRY1 Nurr1 FOXA2, LMX1B, and MSX1 , and the bicoid-related homeodomain factor Ptx3/Pitx3 . It is noteworthy that some discrepancies have been found with the requirement for the presence of floor plate-specific cell surface marker CORIN expression . A more recent study has identified a cell surface marker integrin-associated protein as a positive marker for FOXA2-positive DA progenitor cells .
Which Stages Of Parkinson’s Disease Can Be Treated With Stem Cells
The treatment of Parkinsons Disease with any stem cell method is independent of the stage. Stem cells secrete many healing factors, which can potentially induce a flourishing effect on local resident cells, as well as anti-inflammatory effects wherever they are deployed. This has very positive effects on PD at all stages. However, anticipated results may vary are depending on the progression the treatment plan and the side medications. Contact us for a consultation.
Assessment Of The Efficacy Of Cell Transplants With Imaging
Last, concurrent with the high demand for the optimization of cell graft visualization in PD, growing emphasis has been placed on enhancing the sensitivity and precision of the spatiotemporal resolution of functional neuroimaging. En route to successful cell transplantation as a therapeutic regenerative method for Parkinsons disease, neuroimaging techniques have to be employed for better patient care. Some key features required to elucidate the therapeutic efficacy of transplanted cells for clinical diagnostics are innervation, survival, differentiation, and functional biochemistry composition. Furthermore, it is crucial that these imaging techniques are time efficient, safe, non-invasive, and allow repeated measures in an individual to determine longitudinal post-operative progression in patients with cell transplantation . In this section, we summarize the pros and cons of current imaging modalities used in tracking cell grafts in PD and their respective biomarkers .
Table 2. Imaging modalities used in cell transplantation for PD.
Also Check: What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Parkinson’s
Stem Cells Have More Variety Than Id Thought
Kim referred to this particular study as very unusual and exceptional because it was the first trial of its kind. It reported successfully using Lopezs own skin to create induced pluripotent stem cells, which are cells that are reprogrammed to behave like stem cells. Those cells, which are autologous, were then transplanted into the Parkinsons patients brain. This is different from embryonic stem cells , which is an allogeneic approach.
OK, what do autologous and allogeneic mean? Allogeneic stem cells are not taken from ones own body, while autologous stem cells are created from ones own body.
Kim explained: There are different approaches, such as fetal cells and embryonic stem cells. These approaches could be complementary and not exclusive. For instance, the ESC-based approach may be more economic and fast because the cells can be available for many patients. However, these cells are allogeneic and need immunosuppression. In contrast, autologous cell transplantation does not need immunosuppression but will take more time and budget. Once FDA approval is obtained, these different approaches can be compared with each other.
Morning Bradykinesia Common Device

Bradykinesia is an early motor symptom of Parkinsons marked by slowness or difficulty in movement. Over time, it may lead to freezing of gait, which occurs when a person feels as though their feet are glued to the ground, making it difficult to take a step forward. It also may lead to a shuffling walk with very small steps, a flat facial expression, and a limited ability to perform everyday tasks.
While it is not known what exactly causes bradykinesia to occur, inflammation may play a role.
Mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells a type of cell that can give rise to almost any cell in the boy present in multiple tissues in the body, including the umbilical cord, bone marrow, and fat. These cells have anti-inflammatory properties and may help treat the condition by modulating the immune system and easing inflammation.
In this clinical trial , researchers are testing the safety and tolerability of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients aged 55 or older whove had bradykinesia for at least three months. Its primary goal is to measure the number of side effects and serious side effects for the duration of the study.
The therapy involves a procedure called an allogeneic stem cell transplant, during which the patients received mesenchymal stem cells from a healthy donor via an intravenous infusion to replace their diseased or damaged cells.
Also Check: What Chemicals Can Cause Parkinson
Phase Iia Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial: Mesenchymal Stem Cells As A Disease
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| Recruitment Status : Active, not recruitingFirst Posted : August 10, 2020Last Update Posted : February 10, 2022 |
What Are Stem Cells
Stem cells are a class of immature cells that are able to differentiate, or mature, into specialised cell types. They are found in many parts of the body. In nature, stem cells come from two main sources: embryos , and adult tissue , and are generally characterised by their potential to differentiate into particular cell types, such as skin, muscle or bone. In recent years, stem cells have also generated mature, specialised cells such as skin cells.
As well as the ability to differentiate into another cell type with a specialised function, stem cells are also characterised by the fact that they are able to divide and multiply to form copies of themselves.
These two distinct properties mean stem cells can serve as an internal repair system, dividing without limit to replenish other cells.
Read Also: Is Frozen Shoulder A Sign Of Parkinson’s
Potency Hypothesis Of Stem Cell Therapies
Stem cells possess the potential to communicate with the immune cells that elicit inflammation and by natural, so far not understood mechanisms may inhibit this immune-over-reaction. Furthermore, stem cells have the ability to stimulate regeneration of tissue thereby counteracting the loss of function.
A Decade In The Making
Nearly one million people are living with Parkinsons disease in the United States alone, according to the Parkinsons Foundation. About 60,000 people are diagnosed with Parkinsons each year, and that number is expected to rise to 1.2 million by the end of this decade. It is the fastest rising neurological disorder in the world, with the global number of diagnosed people doubling from 3 to 6 million people between 1990 and 2015. If this development continues, the number of cases will again have doubled by 2040.
If the rate at which Parkinsons growth continues, were going to outgrow the capacity to be able to handle all of the consequences of letting a chronic neurodegenerative disease go unchecked, Michael S. Okun, a neurologist at the University of Florida and one of the worlds leading Parkinsons scientists, told The Daily Beast.
After decades of research, what we know so far is that Parkinsons is caused when dopamine-producing nerve cells in the brain die too fast. Often called the happy hormone, dopamine is critical for relaying signals from the brain that give orders of movement to different body parts. A dearth of dopamine will cause tremors and slowed movement. These symptoms only worsen over time, and make it extremely difficult to do even the simplest activities in the late stages of the illness.
And Parkinsons can lead to cognitive effects as well, such as short-term memory loss, difficulties with staying focused, and challenges with impulse control.
Also Check: Is Double Vision A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Phase 1 Trial Of Stem Cells In Treating Bradykinesia To Open In Us
The participants will be followed for a year by IMAC doctors and physical therapists. The trial enrolled a total 15 patients five in each dosing group ages 55 or older, who began experiencing bradykinesia for at least three months before enrollment. Participants were allowed to continue treatment with levodopa or other standard treatment.
The trial is underway at three of IMACs U.S. clinical centers: Chesterfield, Missouri Paducah, Kentucky and Brentwood, Tennessee.
Bradykinesia is one of the early signs of Parkinsons disease. It is characterized by slow movements, delayed reaction times, and decreased amplitude of movements that is, smaller movements.
Although the mechanisms underlying bradykinesia are not completely understood, it is generally accepted that inflammation is one of its key drivers.
Stem cells are characterized by their ability to divide indefinitely while giving rise to various cell types, prompting its interest as a regenerative medicine for disorders like Parkinsons.
MSCs are a subtype of stem cells that are found across different tissues, but at high rates in the umbilical cord. Other tissues include the bone marrow and fat. They have anti-inflammatory properties, supporting their potential to treat bradykinesia by easing inflammation.
Ricardo Knight, MD, the medical director of the Mike Ditka IMAC Regeneration Center in Arlington Heights, Illinois, is the trials lead investigator.
Compelling Stem Cell Research In Japan About To Begin
On July 30, 2018, Kyoto University announced that a clinical trial using stem cells to treat Parkinsons disease is set to begin.
This trial will recruit seven patients and will use induced pluripotent stem cell-derived dopamine producing cells. These cells are created as follows: Adult skin or blood cells are taken from a donor and reprogrammed in a cell culture dish to revert to an embryonic state. Then, these cells, referred to as IPS cells, are further treated to become dopamine producing neurons. This trial will be the worlds first using IPS cells for the treatment of Parkinsons disease. The engineered IPS cells will be injected deep within the brain, in the basal ganglia, where the ends of the dopamine producing neurons live. Only patients who live in Japan are eligible for the trial.
The adult cells to be reprogrammed will be taken from donors, and not from the trial patients, which means that at least initially, an immunosuppressant medication will be administered to those in the trial to prevent rejection of the cells.
One concern of using IPS cell-derived dopamine producing neurons in humans was that the cells, once injected into the brain would not engraft correctly into the brain and could even cause tumors. To address this concern, the Kyoto group tested these cells in monkeys and last August. The cells that were injected survived and functioned as dopamine neurons. In addition, after two years of observing the monkeys, no tumors were seen.
You May Like: What Are The End Stages Of Parkinson’s
What Is Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are special because theyre undifferentiated, meaning they have the potential to become many types of specialized cells.
You might think of stem cells as natural resources for your body. When your body needs a specific type of cell from bone cells to brain cells an undifferentiated stem cell can transform to fit the need.
There are three main types of stem cells:
- Embryonic stem cells: These cells are pluripotent, meaning they can transform into the many types of cells found in your body. As the name suggests, theyre found in embryos.
- Somatic stem cells: Also called adult stem cells, these mostly perform repair functions. They can still transform, but not into as many types of specialized cells as embryonic stem cells can.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells : These stem cells are made by genetically changing cells that have already matured.
Stem cell therapy is the use of stem cells usually from a donor, but sometimes from your own body to treat a disorder.
Because Parkinsons disease leads to the death of brain cells, researchers are trying to use stem cells to replace brain cells in the affected areas. This could help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Gmp Cryopreservation Of Cells
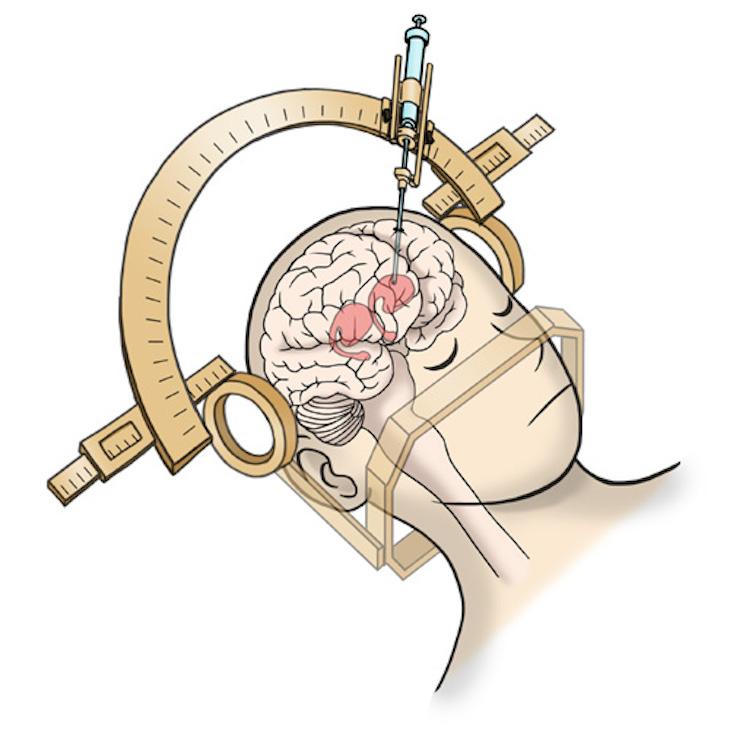
The generation of good manufacturing practice -compliant, deliverable midbrain DA progenitors/neurons optimized for cell-based therapy for PD is a major challenge. Currently, a diverse collection of clinical-grade hESC lines are available as starting material to generate GMP-compliant mDA progenitors/neurons. In fact, GMP compliant differentiation protocols and reagents have been successfully applied to generate GMP mDA neurons .
You May Like: How Do You Prevent Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons Disease is a degenerative nervous system condition that affects ones movement. Symptoms often start quite gradually, with minor issues such as small tremors within the extremities . Currently, there is no cure for Parkinsons Disease but certain medications do have the capacity to help manage symptoms. Some doctors may also recommend surgery to address certain symptoms, which involves regulating certain areas of the brain.
How Are Clinical Trials Conducted
Clinical trials that test drugs or interventions are conducted in a series of carefully monitored phases designed to answer specific questions.
Phase I trial: researchers test a new drug or treatment in people for the first time. A small group of people, typically fewer than 100, are monitored to evaluate the drug or treatment’s safety, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side-effects.
Phase II trial: study the effectiveness of a drug or treatment in a larger group of people.
Phase III trial: the study drug or treatment is given to a large group of several hundred to several thousand people. This large-scale testing gives more detailed information about the drug’s benefits, effectiveness, range of possible side effects, and compare it with standard treatment or placebo.
Phase IV trial: usually conducted on treatments that have already been Food and Drug Administration approved and is available to the general population. These trials help monitor the safety of the intervention in a larger population and obtain additional information about the benefits and use of the intervention.
Don’t Miss: Sudden Onset Parkinson’s Disease
What Types Of Cells Are Used In Parkinsons Disease Stem Cell Treatment
TruStem Cell Therapy provides access to treatment that utilizes a patients stem cells isolated from their own bone marrow. There are multiple inherent benefits afforded by the utilization of bone marrow derived stem cells as Bone marrow and bone marrow components function in various diverse, innate therapeutic capacities.
Hematopoietic stem cells , found within BM, are the bodys source of most cells found in the peripheral or circulating blood. These include red blood cells and white blood cells . Evidence suggests that BM-derived monocytes may act to improve certain neurodegenerative conditions. In this disease environment exhausted microglia cannot efficiently clear A deposits, leading to peptide buildup and neurodegeneration. In this state, monocytes easily bypass the compromised blood-brain-barrier, adhere to A positive veins, then phagocytose and transport peptide from the brain microvasculature into the circulating blood.
In addition to HSCs, mesenchymal stem cells are also contained within BM. Evidence suggests MSCs can enter the circulating blood during injury and have been shown to readily home to areas of injury or inflammation. Once at these damaged tissue sites, MSCs can exert both protective cellular and immunomodulatory effects believed to be critical in many neurological conditions.
Next Step: Human Trials
Dr. Kordower told MNT that the results of this study give him great confidence going forward into patients.
Dr. Kordower will be a principal investigator in a clinical trial that he expects to take place in 2023, which will study a specific population of individuals with PD who have mutations in the Parkin gene .
These individuals experience degeneration of the dopamine system. While they experience motor dysfunction typical with PD, they do not develop cognitive decline or dementia. So, that makes the perfect test to see whether cell replacement strategies can be helpful, Dr. Kordower told MNT.
If the trial is successful, larger trials may follow in a broader population of people with PD. However, it is important to note that while the findings from this study are promising, results from animal models do not always translate into human clinical trials.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Go Into Remission
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s DIsease can include a variety of symptoms that vary in severity and type amongst the affected population. Early signs of the condition can sometimes go unnoticed but as the disease progresses one can expect these symptoms:
- Difficulty speaking
- Difficulty writing
- Loss of automatic movements
- Slowed overall movement
- Muscle stiffness
Red Flags Raising Concerns About A Medical Tourism Facility
Claims of efficacy only based on patient testimonialsClaims of multiple diseases being treated with the same type of stem cellUnclear documentation of the source of the cells or how the treatment will be doneClaims of little or no riskHigh cost of treatment or hidden costsSuggestions that repeat treatments may be needed if not initially successful
You May Like: New Treatments For Parkinson’s Disease 2021
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies For Neurodegenerative Diseases
While there have been significant advances in the symptomatic management of these diseases that improve quality of life and at times survival, the available medications likely only slow the progression of neuronal death by a few months. The idea of using cell therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases has been around for decades, most notably in Parkinson’s Disease where a variety of cell transplant investigations have been performed with success.
According to a recent study conducted by Nathan P. Staff et al,
“The precise mechanism by which MSCs may exert beneficial effects in neurological disease is still being elucidated, but it appears that multiple different mechanisms may contribute. First, MSCs have been shown to secrete neurotrophic growth factors, including glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor , vascular endothelial growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor ,which can be further enhanced under specific culture conditions.Neurotrophic growth factors have been shown to improve neuronal survival in a number of preclinical models of neuron injury, including ALS, PD, and MSA transgenic animalsand nerve injury models. â Second, MSCs strongly modulate the immune system and can aid wound healing, and this mechanism has been exploited in disorders such as graft versus host disease and Crohnâs disease. From a neurodegenerative perspective, it has become increasingly recognized that neuroinflammation plays a significant pathomechanistic role.”
