Tackling Neuropathy Fatigue And Gi Issues In Pd
While its known as a movement disorder, people who live with Parkinsons disease experience many non-movement, or non-motor, symptoms too though not all of them are related to the disease. Peripheral neuropathy, or nervous system damage, fatigue and GI issues are common PD challenges that can also stem from other causes. Working with your doctor to identify the source of your symptoms is key to effective treatment.
This article is based on the Parkinsons Foundation Expert Briefing series Symptom Management: Is it PD, Medication or Aging? Exploring Non-motor Symptoms: Neuropathy, Fatigue, GI Issues presented by Ellen Walter, Nurse Practitioner, Cleveland Clinic, and Steven Swank, Clinical Pharmacist, University of Kansas Medical Center. Both organizations are Parkinsons Foundation Centers of Excellence.
Causes of neuropathy, fatigue and impaired gastrointestinal function during the course of PD can be wide-ranging and include everything from normal aging to .
With any health challenge, its recommended to log symptoms. This can help your doctor rule out potential causes. When did symptoms start? Are there any patterns?
More Research Is Needed
There are a limited number of studies that have investigated the relationship between the development of peripheral neuropathy and Parkinsons. Some small studies have found the frequency of neuropathies was significantly higher in PD patients than in controls.1
There are investigative questions that have been raised about a correlation of prolonged levodopa usage and according to some studies, there is insignificant evidence to link levodopa usage with the development of peripheral neuropathies in people with idiopathic Parkinsons.1
Therefore further investigation is required to evaluate whether PN could be another element of the disease or related to treatment medications, or some combination of the two.1
Median And Ulnar Neuropathy Assessment In Parkinsons Disease Regarding Symptom Severity And Asymmetry
Nilgul Yardimci
1Neurology Department, Minasera Aldan Hospital, Ahmet Taner Kislali Mah. 2741, Street No. 2 Cayyolu, Ankara, Turkey
2Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Medical Park Ankara Hospital, Kentkoop Mah., Kentkoop Parkici Yolu, Yenimahalle, Ankara, Turkey
3Biostatistics Department, Medicine Faculty, Hacettepe University, Hacettepe Mah., 06230 Ankara, Turkey
4Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Medicine Faculty, Turgut Ozal University, Alparslan Turkes Cad. No. 57, Emek, 06510 Ankara, Turkey
5Neurology Department, Medicine Faculty, Turgut Ozal University, Alparslan Turkes Cad. No. 57, Emek, 06510 Ankara, Turkey
6Neurology Department, Medicine Faculty, Gazi University, Emniyet, Yenimahalle, 06560 Ankara, Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, characterised by tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability associated with degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta and the presence of eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions .
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Parkinsons Disease Group
Firstly, the patients were examined for existence of any median or ulnar neuropathy according to the electrophysiologically diagnostic criteria based on control data performed in our laboratory.
2.2. Comparison Group
Read Also: Judy Woodruff Parkinsons
Also Check: How Fast Does Parkinson’s Disease Progress
Peripheral Neuropathy And Parkinsons Disease
Today I will address the potential link between Parkinsons disease and a common neurologic condition called peripheral neuropathy. This topic was submitted via the Suggest a Topic portal. I am grateful for your suggestions so please continue to let us know what youd like to learn more about!
In order to understand what peripheral neuropathy is and what symptoms it can cause, we will briefly review the components of the nervous system.
The 5 False Facts Your Doctor Mistakenly Promotes Neuropathy In Parkinsons
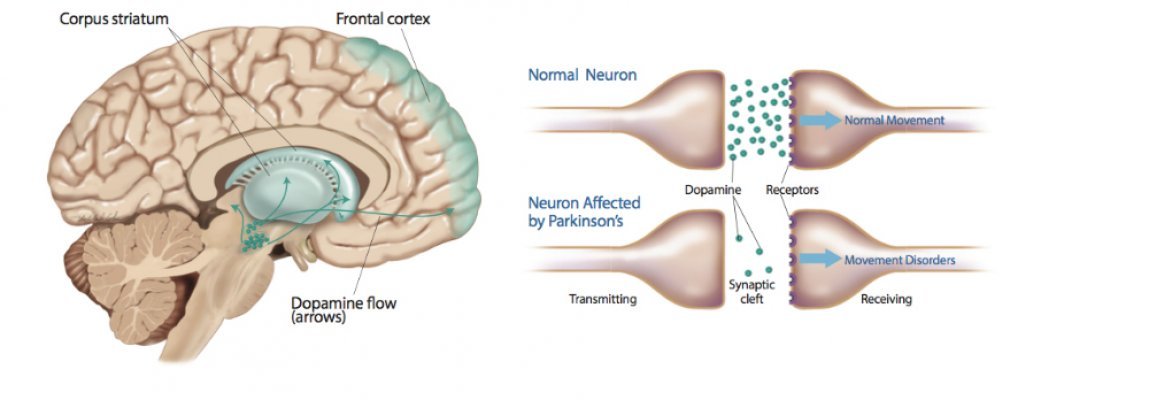
The medical community is largely responsible for this misinformation being passed on to the suffering patient. In my view it is the job and responsibility of the family doctor to teach the patient about their neuropathy problem. It is also the doctors job to train the patient in what they can do to improve and manage their neuropathy case successfully.
===> How To End Peripheral Neuropathy < < <
Many neuropathy patients, suffering with foot or hand pain, tingling, numbness, burning, and other evasive and hard to describe neuropathy symptoms, dont even know the name of their condition! And while others do, that is essentially all they know. With this in mind I want to address some of the most commonly INCORRECT facts that suffering neuropathy patients have been told, or come to understand, due to the lack of patient education by the medical community.
1. Neuropathy comes with age, and there is nothing you can do about it.This statement is only partially correct, inasmuch as aging can contribute to the increased onset and intensity of the neuropathy condition. There are however, many simple techniques and procedures that any person can learn which will offset many of these effects of aging as they relate to peripheral neuropathy.
4. Neuropathy just gets worse with time, and you have to accept that you are stuck with it.
Neuropathy in Parkinsons
Also Check: New Parkinson’s Treatment 2021
Things That Really Bother Me About Life With Parkinsons
Peripheral neuropathy, or damage to the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, often leads to weakness, numbness, and pain, usually in the hands and feet, resulting in problems with balance and mobility.
While some studies suggest peripheral neuropathy is a feature of Parkinsons, others indicate that the use of levodopa could aggravate neuropathy.
Most of this research used traditional electrophysiological testing methods that can only measure damage to large nerve fibers responsible for detecting vibrations and sensing movement, but not damage to small nerve fibers, which relay information about pain and temperature.
The Neurometer is a more sensitive and non-invasive neurodiagnostic device that evaluates the function of more than 90% of sensory nerve fiber types, including large myelinated fibers, medium-size myelinated fibers, and small unmyelinated fibers. Of note, myelin is a fat-rich material that surrounds nerve fibers to increase the speed of electrical signals.
Researchers at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University in China applied the Neurometer to determine the functional status of each type of peripheral nerve fiber in a group of Parkinsons patients. They investigated both peripheral neuropathy and the potential the impact of levodopa therapy.
A group of 22 age-matched healthy adults was assessed as a control group for comparison. Blood levels of vitamin B12, folic acid, and homocysteine were measured in all participants.
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinsons is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
You May Like: What Are The First Stages Of Parkinson’s Disease
Favorite Resources For Online Support
If youre active on social media, stop by the Our Neuropathy Friends Facebook page and join the discussion. Comprising more than 4,000 members, this website is an excellent place to connect with people who understand your situation firsthand. Ask questions, share tips, or relate your personal experiences.
Youve come to the right place if you need help finding a support group for neuropathy. This site provides information about online and local support groups in your area, and you can read articles on neuropathy and get information on clinical trials.
You May Like: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinsons
The 5 False Facts Your Doctor Mistakenly Promotes Neuropathy And Parkinsons Disease
The medical community is largely responsible for this misinformation being passed on to the suffering patient. In my view it is the job and responsibility of the family doctor to teach the patient about their neuropathy problem. It is also the doctors job to train the patient in what they can do to improve and manage their neuropathy case successfully.
===> How To End Peripheral Neuropathy < < <
Many neuropathy patients, suffering with foot or hand pain, tingling, numbness, burning, and other evasive and hard to describe neuropathy symptoms, dont even know the name of their condition! And while others do, that is essentially all they know. With this in mind I want to address some of the most commonly INCORRECT facts that suffering neuropathy patients have been told, or come to understand, due to the lack of patient education by the medical community.
1. Neuropathy comes with age, and there is nothing you can do about it.This statement is only partially correct, inasmuch as aging can contribute to the increased onset and intensity of the neuropathy condition. There are however, many simple techniques and procedures that any person can learn which will offset many of these effects of aging as they relate to peripheral neuropathy.
4. Neuropathy just gets worse with time, and you have to accept that you are stuck with it.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Cause Low Blood Pressure
Evaluation And Treatment Of Constipation In Neurological Diseases
In evaluation of the neurologically diseased patient with respect to gastrointestinal dysfunction, a combination of a carefully taken history , including actual medication, and physical examination including digital exploration, will be adequate in most cases. Patients may present with abdominal discomfort or pain, and investigations generally do not detect any abnormalities. Based on history alone, it may prove to be difficult to differentiate slow colonic transit time and outlet obstruction. Severe cases of constipation secondary to slow colonic transit, may present with decreased appetite and not uncommonly with nausea, but rarely with vomiting.
Stercoral diarrhoea is a bothersome symptom and though the impaction is evident to the physician, it may prove difficult to treat.
Patients, who have difficulty in evacuating the rectum, generally have outlet obstruction and neoplasia needs to be excluded.
In female patients with severe constipation and difficulty with defecation, it is important to exclude rectoceles, which are mostly asymptomatic but sometimes can cause incomplete emptying.
Table 1
Figure 1 outlines a possible strategy for management and drug treatment in constipated patients.
Figure 1
Nerve Conduction Studies Hrus And Diagnosis Criteria Of Pnp
All patients underwent electrophysiological examination performed by a board-certified neurologist with the use of a Medtronic four channel electroneurography device . Motor studies of tibial and median nerve as well as sensory studies of sural and median nerve were done bilaterally maintaining skin temperature at 36°C and were referenced to normal values. Nerve HRUS examination was performed with an Affinity®70G ultrasound system with an 18-MHz linear array transducer as described previously. It was performed bilaterally at entrapment and nonentrapment sites. The entrapment sites included the median nerve , the ulnar nerve , and fibular nerve . The nonentrapment sites contained the median nerve , the ulnar nerve , and the fibular nerve . In order to avert anisotropy, the transducer was kept perpendicular to the nerves and no additional force was applied while the extremities were kept in neutral position to avoid nerve deformation. The measurement of CSA was performed at the inner border of the thin hyperechoic epineural rim by a continuous tracing technique.
The diagnosis criteria for PNP were determined by nerve conduction studies. The lower value of bilateral conduction was regarded to detect early PNP. In order to include and analyze neuropathy groups with different severity in NCS we defined three PNP subgroups based on normal values .
Recommended Reading: What Happens When You Have Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinsons may experience some of these more common hallmark symptoms:
- Bradykinesia slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
Black And Hispanic People And Neuropathy
Determining which racial and ethnic groups experience neuropathy the most may be complicated by the type of neuropathy, as well as the differing ways that people communicate their pain to others, including their healthcare providers.
The FDA reports that American Indians/Alaska natives , Hispanics , Black people and Asian Americans have higher rates of diabetes than white people .
Yet in a December 2017 study of more than 1,900 people who had painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy symptoms, which was published in Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology, Black and Hispanic participants were less likely than white participants to rate their pain as moderate or severe. Also, significantly fewer Black and Hispanic individuals reported having received a painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy diagnosis. However, higher proportions of those who were Black and Hispanic reported difficulty communicating with their healthcare provider about their pain symptoms, and feeling less comfortable about doing it. They were also younger, on average, than white participants. Researchers said more research in diverse populations is needed to understand the disparities.
However, a November 2015 study published in Clinical Cancer Research found that women of African descent being treated for breast cancer with specific chemotherapy drugs known as taxanes were more likely to report painful neuropathy symptoms than women of European descent.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Bike Therapy
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Massage Is Good For Parkinson’s Disease
Favorite Resource For Diet Advice
The FPN is an amazing resource for food and nutrition advice. Controlling blood sugar starts with good nutrition. The site offers basic diet tips for controlling blood sugar, as well as tips for eating to help beat inflammation. This resource also guides you in grocery shopping for healthy foods and using supplements for neuropathy.
For more on how to build an anti-inflammatory diet, check out our article.
Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinsons disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple systems atrophy and corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinsons UK website.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2019 Next review due: 30 April 2022
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Parkinsons And Alzheimers
Read Also: What Is Dystonia In Parkinson’s Disease
Laboratory Assessment Of Pnp In Pd
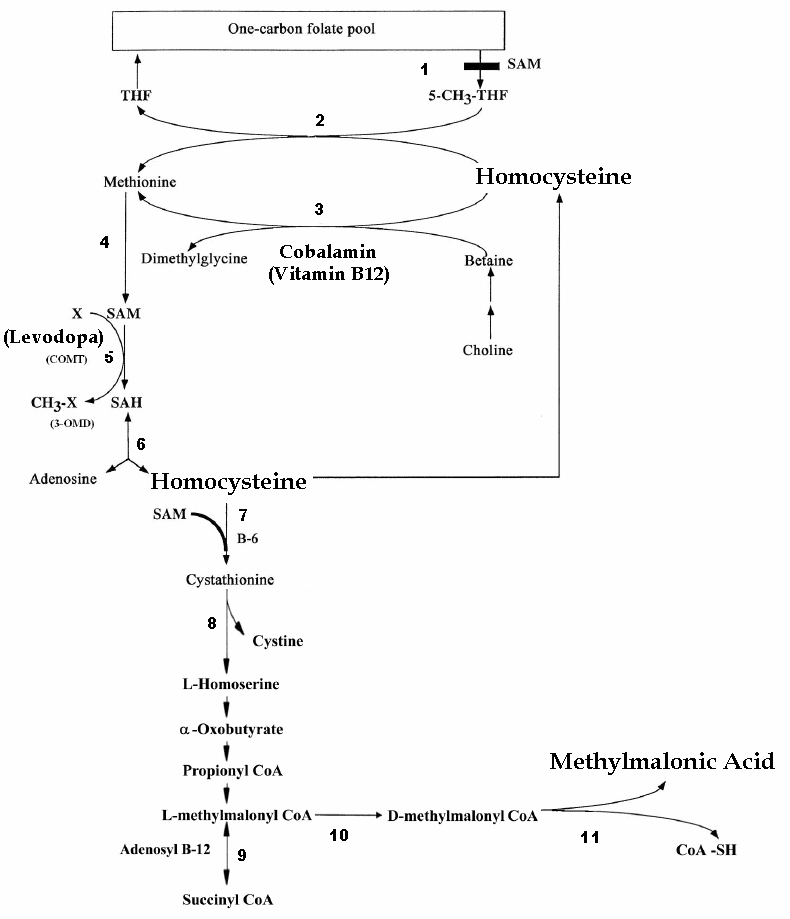
In addition, we performed a broad analysis of serum parameters that could be associated with PNP. There were no age independent effects for other etiologies of PNP such as deficits of folate, cobalamin, methylmalonic acid, and homocysteine. Of interest, when age was included as a confounder LED did not correlate significantly with tibial nerve cMAP or with HRUS pathology .
What Is The Link Between Them
Peripheral nervous system dysfunction is not uncommon in PD.3 The possibility that PD be considered a systemic disorder could account for the many experiences of neuropathies reported.1
Studies have looked at common Parkinsons hallmarks such as levodopa exposure, vitamin B deficiencies, and alpha-synuclein deposits, as all playing a role in PN dysfunction.3
Scientists have looked at long term levodopa use combined with vitamin B deficiencies as possible conditions that could contribute to the development of PN. Levodopa exposure, particularly by infusion, could be a determinant of neuropathy development compared to oral levodopa and other kinds of dopaminergic treatment.3
Alpha-synuclein proteins, a structural characteristic of Parkinsons disease, have been identified in the small nerve fibers of the PNS. This has led to the need to further investigate whether specific features of Parkinsons may predispose people to develop peripheral neuropathy.3
Read Also: How Is Parkinson’s Tested
The Use Of Levodopa And Peripheral Neuropathy
There are reports in the literature that levodopa use may increase the risk of peripheral neuropathy, although other studies suggest that this is not the case. There are studies that demonstrate for example, that cumulative Levodopa exposure correlates to prevalence of PN in people with PD. Other studies however, demonstrate no difference in the prevalence of PN whether the person was treated with Levodopa or not, suggesting that Levodopa treatment does not play a role in development of PN.
Another area of research that emerges from the literature is the potential role of Vitamin B12 deficiency in the development of PN in those with PD. Some studies suggest that Vitamin B12 deficiency is a more common cause of PN among those with PD than those with PN who do not have PD.
There is also research that suggests that levodopa treatment may contribute to PN through impairment of Vitamin B12 metabolism, leading to Vitamin B12 deficiency. Taking COMT inhibitors such as Entacapone may protect against this complication.
Regardless, if PN is diagnosed in anyone, whether they have PD or not, and whether they take Levodopa or not, Vitamin B12 and various other markers of Vitamin B12 metabolism should be tested. If Vitamin B12 levels are low or even low-normal, a person should take Vitamin B12 supplementation, which may help with the symptoms of PN. Other causes of PN, many of which can be checked with various blood tests, should be investigated as well.
Potential Pathogenic Mechanisms Of Peripheral Neuropathy In Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease Patients
The studies to date have been descriptive and associative in nature only. The precise pathogenic mechanisms for the development of peripheral neuropathy in IPD patients remain speculative. Before considering the mechanisms by which methylmalonic acid and/or homocysteine may be pathogenic, other considerations require discussion.
As mentioned, considerations for genetic influences are important. The potential implications of parkin mutations given the expression of parkin mRNA in peripheral nerve may be of importance, but only a small percentage of IPD patients with parkin mutations appear to have an axonal form of peripheral neuropathy . The relationship of concurrent peripheral neuropathy to the so called Parkinsons Plus forms of disease, such as with multiple system atrophy must also be considered patients with multiple system atrophy frequently have an axonal peripheral neuropathy present . Associations such as this may suggest a neurodegenerative pathogenesis for peripheral neuropathy rather than a deficiency. Indeed, patients with greater severity and longer duration of IPD were more susceptible to development of peripheral neuropathy in our studies as well . Further studies will be required to determine if the peripheral neuropathy present in IPD patients develops in an analagous fashion to the central nervous system neurodegeneration in IPD.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Affect Blood Pressure

