Pramipexole Dihydrochloride Extended Release
Available Doses: .375 mg, .75 mg., 1.5 mg, 2.25 mg, 3 mg, 3.75 mg, 4.5 mg
Typical Treatment Regimen: 1.5 to 4.5 mg once per day
Side Effects: nausea, lower blood pressure, leg swelling, confusion, sleep attacks, compulsive behaviors like gambling
Indications for Usage: or combination therapy for slowness, stiffness and tremor
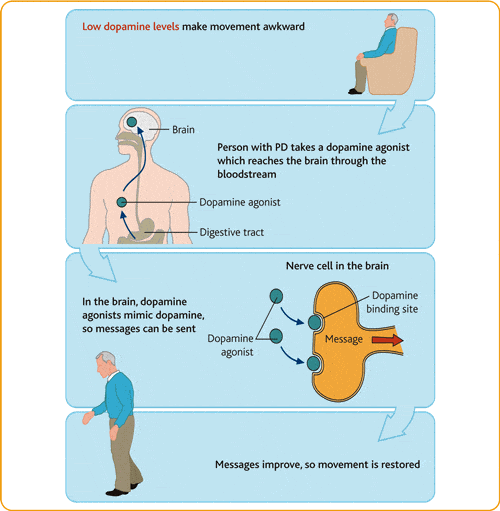
What Is A Dopamine Agonist And How Does It Work
Dopamine agonists are a type of medication often used to treat Parkinsons. Dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine a type of neurotransmitter that coordinates movement. It is also linked to other factors, such as motivation, addiction, attention, sleep and heart rate.
In Parkinsons, the nerve cells that form dopamine die, leading to symptoms which can include tremor, rigidity, tiredness, depression and pain.
Dopamine agonists bind to the receptors on nerve cells that detect natural dopamine, so can help to treat symptoms of the condition.
Nicola Pavese, professor of clinical neuroscience and consultant neurologist at Newcastle University, UK, says: Unfortunately, we cannot use dopamine itself as a drug because, due to its chemical characteristics, it would not cross the defensive barrier between the blood and the brain, and therefore would not reach the neurons where it is needed.
Dopamine agonists are molecules that have a chemical structure and pharmacological action similar to dopamine but have the advantage of easily crossing the blood-brain barrier and act directly on the sites of action of dopamine . They are therefore used to replace the missing dopamine in the brains of people living with Parkinsons.
First Reports Of Levodopa Adverse Events
The initial paper by Cotzias et al. on the first proper drug trial of l-dopa gave little attention to any motor adverse effects associated with this new form of therapy although they mentioned anorexia, nausea, vomiting, faintness and hematologic changes. However, in their 1969 paper, these authors described l-dopa induced dyskinesias as well as the mental symptoms of irritability, anger, hostility, paranoia, insomnia and awakening effect.
Recommended Reading: Which Structures Of The Body Deteriorate During Parkinson’s Disease
Therapeutic Benefits Of Levodopa With Adjuncts
L-dopa is rapidly metabolized leading to off periods as it expires. These off periods are associated with the emergence of dyskinesia, dystonia and choreic type movements. L-dopa is converted to dopamine by the enzyme dopa-decarboxylase in both the peripheral and central nervous system. This led to the clever strategy of developing carboxylase inhibitors and blocking their transit across the blood brain barrier prevented the conversion of l-dopa to dopamine in the peripheral system, thereby maximally preserving l-dopa for enzymatic processing to dopamine in the brain. This not only extended central therapeutic effect of each dose but also reduced the peripheral adverse cardiovascular and gastrointestinal effects.
Carbidopa and benserazide are peripherally acting decarboxylase inhibitors which when given with l-dopa produce a 4-fold increase in available dose for conversion to dopamine.
Sinemet and Madopar combine decarboxylase inhibitors and l-dopa into a single tablet usually in ratios of 1:10 e.g. 10/100 and 25/250 mg strength tablets although the most common strength prescribed is 25/100mg.
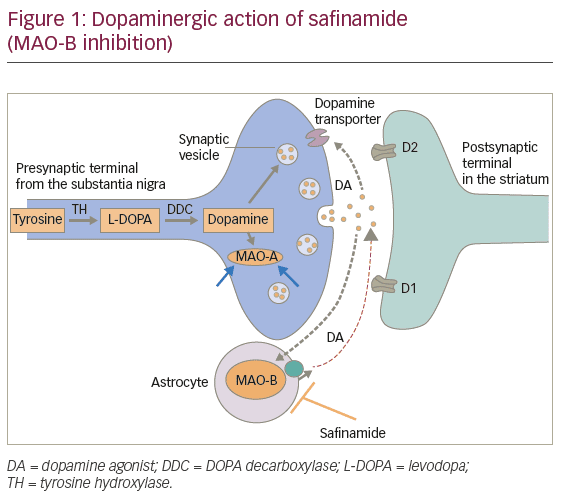
The next class of drugs developed were the inhibitors of monoamine oxidase-B . These potentiate l-dopa by approximately one third, by inhibiting the brain metabolism of both endogenous and therapeutically-derived dopamine. Selegiline and rasagiline do this.
Types Of Dopamine Agonist Drugs
Below are the types of dopamine agonist drugs. The generic names are written in bold and the brand names are written underneath in bullet points.
Pramipexole
- Mirapexin prolonged release
Rotigotine
- Apo-go pre-filled pen for Intermittent injection
- Dacepton cartridge for Intermittent injection
- Apo-go pre-filled syringe for infusion
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Alzheimer’s
Ropinirole Prolonged Release Tablets
Prolonged-release tablets release your medication slowly throughout the day. This can give you more control of your symptoms. They can be taken alone to try and delay the need for you to take levodopa. This can be helpful because levodopa becomes less effective over time.
You should take these tablets once a day. These tablets can be taken with or without food.
It is important that you take these tablets whole. They must not be chewed, crushed or divided into pieces.
At first, your specialist will prescribe you a low dose of Ralnea XL, Requip XL, Spiroco XL, Ipinnia XL, Raponer XL or Ropilynz XL. This will usually be once per day for an initial period of 1 week. Your healthcare professional can then increase your daily dose until it is right for you and your symptoms.
In some cases, a high-fat meal may create issues so speak to your specialist if you think that food is creating problems when you take your medication.
Tell your doctor if you experience side effects from any of these prolonged-release tablets as other forms of ropinirole medication may be more suitable for you.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsonâs disease can include:
- Walking slowly leaning forward with small steps
- Memory problems
People with Parkinsonâs disease often show minor symptoms at first. The symptoms may begin on only one side of the body. Symptoms often become more pronounced over time.
Parkinsonâs disease itself isnât fatal, but it has no cure. Symptoms like frequent falling can lead to injury and death.
Also Check: How Does Sinemet Help Parkinson’s
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Providers should monitor patients on dopamine agonists for any signs and symptoms of CNS depression, orthostatic hypotension, or electrolyte imbalance. Patients should be closely monitored by clinicians and the collaboration of all interprofessional healthcare team members, especially during the titration period. Baseline complete blood count with differential, liver function test, BUN/Cr should be obtained before starting the medication, and cardiovascular evaluations are necessary. Patients treated with dopamine agonists might not be aware of the symptoms of orthostatic hypotension. The clinician should consult with a pharmacist on the appropriateness of the agent selected correct dosing and have the pharmacist check for drug interactions on the patient’s medication profile.
Dopamine Agonists For Parkinsons Disease Therapeutic Effects And Side Effects
Dopamine agonists are a class of drugs that are used to treat Parkinsons disease symptoms. Generally, they are prescribed for patients under 60 years of age or for those whose symptoms are not well-controlled by a drug called levodopa, which is used as first-line therapy for Parkinsons disease. In some patients, dopamine agonists are used alone. In others, they are used in a combination with levodopa.
You May Like: How Does A Person Die From Parkinson’s
Systematic Review And Characteristics
In this meta-analysis, 20 eligible RCTs involving 6,560 patients were included . The included PD patients with motor fluctuations received eight different treatments .
Figure 1 presents network plots of comparisons for primary and secondary outcomes. Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of the studies. Supplementary Appendix 3 presents the risk of bias assessment for studies contributing to analyses of each outcome. Supplementary Appendix 3 also presents moderate- to high-quality evidence in primary outcomes using the GRADE approach.
Figure 1. Network plot of outcomes on time without troublesome dyskinesia, ON time, OFF time, UPDRS III, UPDRS II, and TEAE. The size of the nodes corresponds to the number of participants assigned to each treatment. Treatments with direct comparisons are linked with a line its thickness corresponds to the number of trials evaluating the comparison.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients in the studies included in the NMA.
On Time Without Troublesome Dyskinesia
To provide patients with increased ON time without dyskinesia, 5/6 drugs were significantly more efficacious than the placebo . No significant difference was observed among these drugs. The top three ranked drugs were apomorphine , pramipexole_IR , and ropinirole_PR .
Figure 2. Forest plot of primary outcome on time without troublesome dyskinesia. The size of the node corresponds to the weight in the comparison. MD, mean difference CrI, credible interval.
Figure 3. The surface under the cumulative ranking curve for competing interventions based on ON time without troublesome dyskinesia, on time, OFF time, UPDRS III, UPDRS II, and TEAE. The x-axis represents the ranking, and the y-axis represents cumulative probabilities. The greater the surface under the cumulative ranking, the greater the benefit of the intervention. SUCRA, surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
Read Also: Will Parkinson’s Kill You
Physicians Desk Reference Or Bnf And Prescription Safety
This is exactly what most clinicians rely on. But in the case of dopamine agonists, the BNF still reveals omissions and inconsistencies. Dopamine agonists are listed under 2 different sections, Dopaminergic drugs for the treatment of parkinsonism and Endocrine Drugs. The information reported for the same drugs differs between sections. For instance, bromocriptine is noted for hypersexuality and increased libido in the Endocrine Drugs section but not in the Parkinsonian Treatment section. The Parkinson section has a for ICD whereas the Endocrine section does not.
Cabergoline is marketed as Cabaser and Dostinex by Pharmacia/Pfizer. As a Parkinsons treatment Cabaser is listed. In the Endocrine section both Dostinex and Cabaser are noted. Since 2004, Dostinex has been marketed online as a sex enhancing drug. On the website Buy-Dostinex.com, it is marketed as The Sex Drug. The advert states Dostinex, also known as cabergoline can make sex better, much better for almost anyone, thats the reason some refer to it as The pleasure drug or the Miracle drug.
Throughout this period, cabergoline was not listed as associated with the side effects of hypersexuality or increased libido. In fact by 2008, after the regulator asked for warnings for the entire class of dopamine agonists, cabergoline was still the only dopaminergic drug which did not report increased libido and hypersexuality!
Ive Just Been Prescribed A Dopamine Agonist What Should I Be Aware Of
It is very important to mention the slightly higher risk of developing impulse control disorders, particularly pathological gambling, compulsive shopping, and hypersexuality as these could have important financial and social repercussions, says Pavese.
The possible occurrence of excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks should also be discussed, particularly with regards to driving.
I believe that it is very important for the patients, when possible, to take time to learn more about the different classes of medications that are available for Parkinsons and how they work so that they can participate in a discussion with their physicians and nurse specialists to choose the best treatment for their specific needs.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Physical Therapy Big
Rationale For Levodopa And Dopamine Agonists
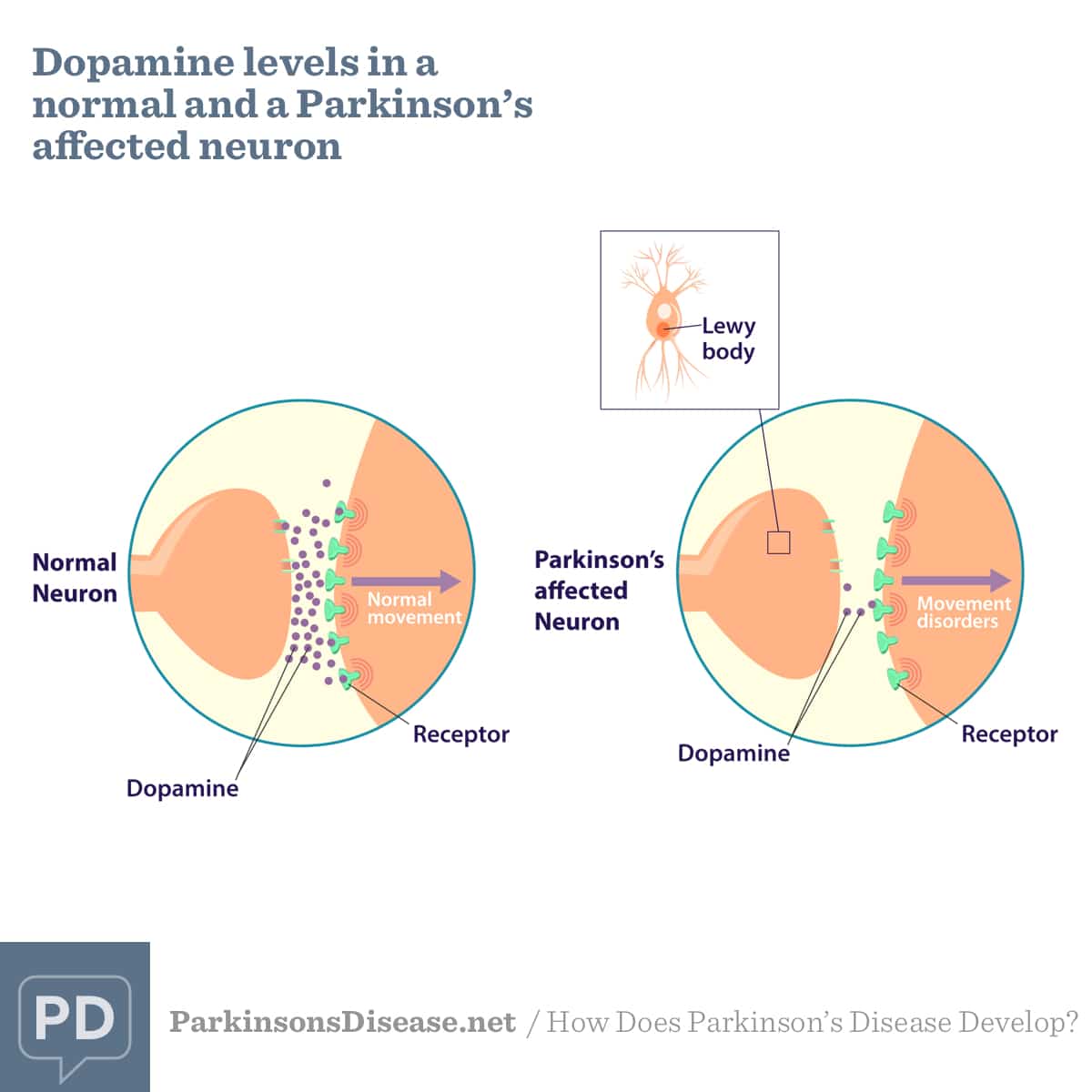
The recognition that Parkinsons disease is caused by a depletion of the neurotransmitter dopamine came from post mortem studies reported by Oleh Hornykiewicz in 1960. His studies concluded that the caudate and putamen of patients suffering from Parkinsons disease showed a marked depletion of dopamine. He later showed a link between striatal dopamine deficiency and most of the motor symptoms now associated with Parkinsons disease. Subsequent studies implicated a nigrostriatal pathway which extends between the cell bodies of the substantia nigra to their nerve terminals within the striatum. Experimentally induced damage to this pathway in laboratory rodents produced a movement disorder comparable to Parkinsons disease.
These findings signaled a role for l-dopa in re-establishing neurochemical levels of dopamine within this neurodegenerative disease. Intravenous injection of l-dopa to a Parkinsons disease patient produced dramatic benefit and from this, the era of dopamine and levodopa therapy was born . Subsequent trials reported benefits for the akinesia, rigidity and tremor associated with Parkinsons disease in ~75% of cases, although full remission was never achieved.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsonâs disease is an illness in the brain that affects many different parts of the body.
Your brain has different areas that deal with separate body parts. Cells in these brain areas are called neurons.
Neurons send electrical signals to each other to direct your body. Signals between neurons tell your body to move, make you feel pain and other sensations, manage your breathing, and perform many more needed functions.
Chemicals called neurotransmitters help these electrical signals travel between neurons throughout the brain. For example, dopamine is a chemical that plays a role in movement, motivation, and other behaviors.
The part of the brain that helps with movement and produces dopamine is called the basal ganglia. In cases of Parkinsonâs disease, cells in this area of the brain become damaged and produce less dopamine and other important neurotransmitters. This can cause problems with moving, thinking, and other functions.
Parkinsonâs disease isnât contagious. It usually appears in people around age 60 and older. People as young as their early twenties can get diagnosed with Parkinsonâs disease, though.
You May Like: How Does Amantadine Work For Parkinson’s
What Are Some Possible Side Effects Of The Dopamine Receptor Agonists
Dopamine agonists have many of the side effects of other dopaminergic agents. These include hallucinations and orthostatic hypotension . Leg swelling can also occur. Dopamine agonists can induce sleepiness as well as sleep attacks and must be used with great caution in those patients who are driving. Compulsive behavior is a well described side effect and could take the form of over-shopping, over-eating, gambling or hyper-sexuality.
In some patients, a withdrawal syndrome can be experienced as the dopamine agonist is lowered and stopped. Symptoms of the withdrawal syndrome can include anxiety, pain, depression, and even suicidality. Patients should be warned about the possibility of experiencing withdrawal when a dopamine agonist is tapered so if they experience these symptoms, they can modify how the medication is weaned off.
Dopamine Agonist Drugs: An Introduction
Dopamine agonist drugs trick your brain into thinking they are dopamine. This means they can mimic the way dopamine works which can reduce your symptoms.
Dopamine agonists are typically prescribed in the earlier stages of Parkinsons but everyone is different and you could be prescribed them at any time if it is right for you.
Treatment with dopamine agonists has to be started carefully. The dose is gradually increased until you and your specialist team are happy that your symptoms are under control.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Medical Marijuana For Parkinson’s Disease
Fast Facts About Dopamine Agonists
- mimic the actions of dopamine in the body to aid in symptom relief
- useful for early treatment of Parkinsons symptoms, especially in people less than 60 years old
- fewer movement-related side effects compared to levodopa for Parkinsons treatment
- newer DA medications bind more selectively to dopamine receptors and have less heart-related side effects
- extended release formulations of newer DA medications lower the burden of taking multiple doses throughout the day
- manipulation of dopamine can cause serious side effects including compulsive behavior and other mental health problems
- can cause dizziness, fainting, or sudden sleepiness which is dangerous for tasks that require alertness like driving
- can cause withdrawal syndrome including sudden high fever, muscle stiffness, kidney failure, and other problems with sleep, mood, and pain if stopped abruptly
indicates there are two major groups of dopamine receptors, D1 and D2, with subgroups under them which are responsible for many behavioral, hormonal, and muscle related effects in our body.
The D1 group includes D1 and D5 receptors, and the D2 group includes D2, 3, and 4.
Each is found in different areas throughout our body and responsible for important actions from how we move to how we learn. Lack of dopamine in our cells affects our bodies in many negative ways.
Taking Dopamine Agonist Drugs: Pramipexole And Ropinirole
Below we have included the different forms of pramipexole medication and an overview of how to take them.
The most recent and complete information on your specific drug will be on your patient information leaflet that comes with your medication packet. Always read it carefully before you start your treatment.
For detailed information you should follow the advice of your specialist or Parkinsons nurse about how to take pramipexole so that it works well for your Parkinsons.
Pramipexole drugs are also used to help your symptoms when your levodopa medication causes you to experience wearing off and dyskinesia. This could be motor fluctuations, or wearing off before your next dose of levodopa is due.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Huntington’s Disease And Parkinson’s Disease
How Do Dopamine Agonists Cause Their Effects
Dopamine depletion in the brain is the main reason why people develop Parkinsons symptoms. Restoring its amount in the brain by using dopamine as a drug would have been an ideal treatment option. Unfortunately, this is not possible because dopamine cant cross the blood-brain barrier to reach the brain. The blood-brain barrier, as the name indicates, is a barrier that prevents the entry of toxins and other pathogens from blood to the brain, while at the same time allows the entry of water, oxygen, and vital nutrients.
Dopamine agonists can readily cross the blood-brain barrier and act locally by binding to dopamine receptors found on the neurons.
There are two families of dopamine receptors that exist in the brain i.e. D1 and D2, which are subdivided based on genetic and biochemical factors. The D1 family includes D1 and D5 receptors, while the D2 family includes D2, D3, and D4 receptors.
Dopamine agonists bind and activate both families of receptors in other words, they act like dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine agonists have some advantages that preferred them over other Parkinsonians drugs like levodopa. For example they do not need enzymatic reactions for their activities, nor they required other transport substances for reaching the brain. Also, they do not produce any toxic metabolites.
What Are The Benefits Of Dopamine Agonists For Parkinsons Disease
Dopamine agonist effects can make life easier for people with Parkinsonâs disease by treating symptoms. They can reduce movement problems like trembling hands, slow walking, and stiff limbs. Other benefits of dopamine agonists for Parkinsonâs disease include:
Fewer side effects. Levodopa can cause uncontrollable body movements over time. Dopamine agonists are less likely to cause this.
Dopamine agonists are helpful on their own during the early years of Parkinsonâs disease when symptoms may not be severe. People diagnosed with Parkinsonâs disease early in life may start out taking only dopamine agonists. This can reduce the amount of uncontrollable movement that comes with taking levodopa for a long time.
No dietary restrictions. Medications like levodopa can be less potent if youâre eating lots of foods that are high in protein. Your body absorbs dopamine agonists in a different way, though, that doesnât interfere with your diet.
They can help levodopa be more effective. Levodopa or other medications for Parkinsonâs disease can wear off before itâs time for another dose. Dopamine agonists last longer and help manage symptoms when taken alongside levodopa.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Effect On Brain
