Pain Is An Unfortunately Common Problem In Parkinsons Disease
Of course, pain is common in the general population, especially among older people. A recent American study found that pain affected about twice as many people with Parkinsons Disease than those of the same age and gender without PD. About 50% of Parkinsons Disease patients in that study suffered from painful disorders. Men and women seem to be about equally affected. A very well described scenario is the patient who is followed for a painful frozen shoulder for a year or so before a tremor develops leading to a diagnosis of PD. Pain clearly plays a major role in quality of life. Everyone with chronic pain enjoys life less, leading to a vicious cycle in which pain causes depression or isolation which in turn leads to more pain.
Parkinson patients suffer from the same pain problems that other people have, often amplified by the motor dysfunction, but they also have additional pain problems which are unique to PD.
One recent review classified the types of pain Parkinsons Disease patients have into: musculoskeletal, in which the pain results from problems with the muscles , bones or joints dystonic, which is due to abnormal muscle contractions caused by the Parkinsons Disease or the medications used to treat it radicular pain, which is feels like the pain caused by pinched nerves central pain, which is presumed due to abnormalities in the brain, and is a continuously present pain that cannot be explained otherwise and discomfort related to an unpleasant urge to move.
Active Research Into Several Aspects Of Parkinsons Pain
Researchers are working to better understand the mechanisms behind pain in Parkinsons so that it can be more effectively addressed. They are looking for objective measurements, such as brain imaging, to diagnose and monitor pain, and to evaluate response to treatment. And, theyre investigating several drugs and deep brain stimulation for their potential benefits in treating Parkinsons disease pain.
Q Which Pharmacotherapies Are Best For Treating Pain In Pd
Dr. Fleisher: The first step is to make sure that Parkinsons medications are optimized. For example, dystonic or musculoskeletal pain may be caused by Parkinsons motor symptoms when dopamine levels are too low. If the patient is able to keep a pain diary, it may show a clear pattern of pain occurring the hour before each dose or before specific doses, suggesting the need to either increase the dosage preceding the pain episode, increase the frequency of medication dosing, or use adjunctive dopaminergic therapies to achieve more steady dopamine levels throughout the day.
In addition, optimal management of comorbidities that may contribute to pain is needed. The choice of pain medication depends on the pain type.
The first lines of treatment for musculoskeletal pain can be heat and cold packs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs alone or in combination with acetaminophen.
For dystonic pain, adjustment of dopaminergic medications is particularly critical however, if dystonia consistently occurs in 1 particular body part, botulinum toxin injections also can be helpful. The goal of botulinum toxin injection is to weaken the muscle enough to stop the abnormal contractions and twisting, but the patient may lose function in the body part as a result . Thus, patient counseling is important to manage expectations.
You May Like: Parkinson Disease Autosomal Dominant
The Preponderance Of Injury In The Past Of People With Pd
Neck issues or damage can be caused by injuries, but the injury site doesnt have to be local to the neck itself, since it is an integral part of the kinetic chain of the human body – problems anywhere else which affect posture can, in turn, profoundly affect how we tense our necks and cause strains on it by the way we are holding up the head. Ive frequently asked people with Parkinsons Disease to think carefully about any pains and injuries which they might have incurred either before or concurrent with their PD diagnosis. Ive found that the overwhelming majority of us have suffered a prior accident or physical trauma. Injuries to jaw, neck, shoulders, back, hips, knees or feet predominate. All these severely affect posture and hence the kinetic chain and are liable to make our necks prone to permanent strains and stiffness. So in my view, even if chemical cures were invented tomorrow, people with PD would still present with the postural problems, still suffer from the old injuries which have been masked by the narratives of neurology, and would probably quickly decline into pain and problems again, unless these past injuries are properly attended to.
Pain In Parkinson’s Disease
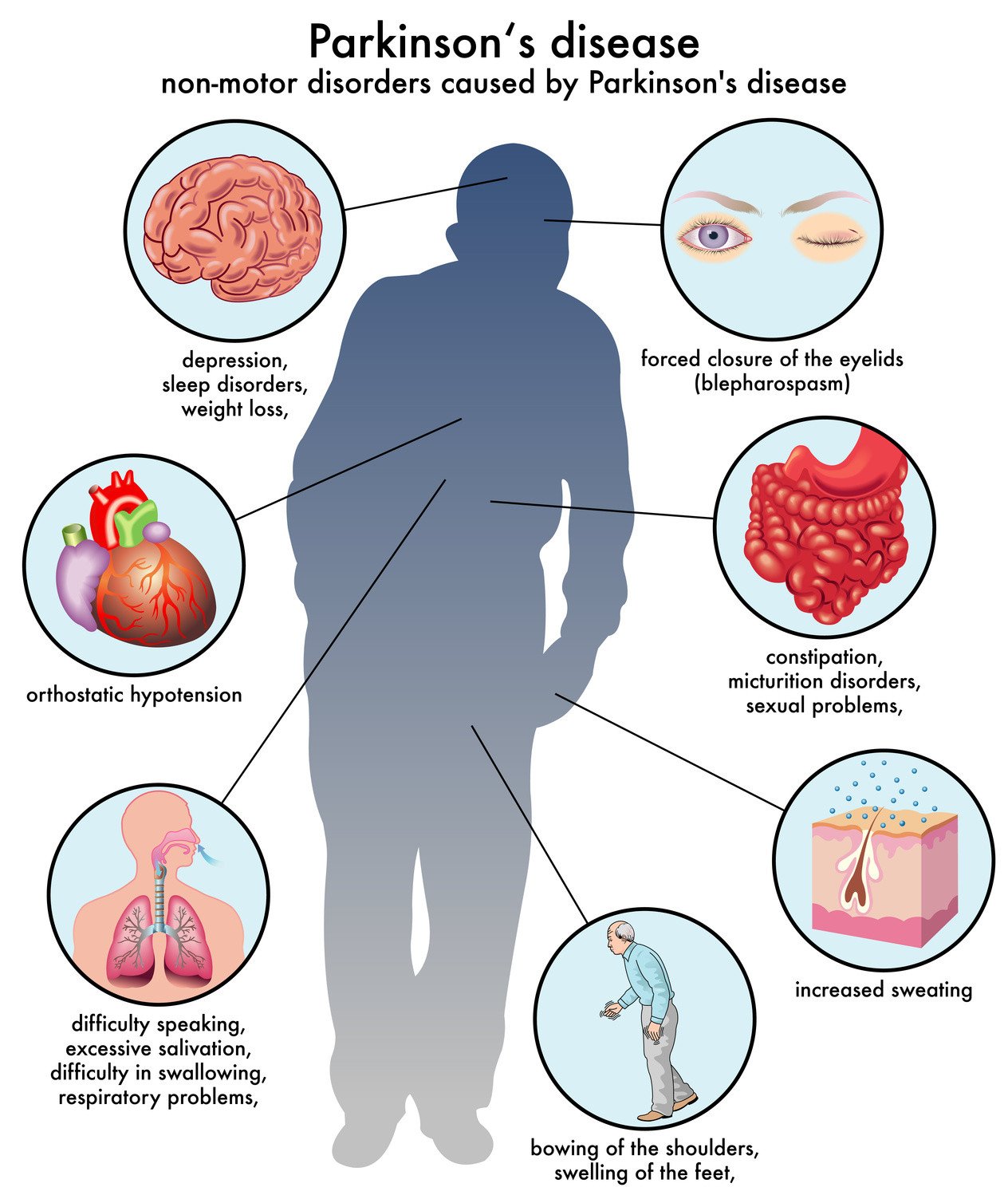
Doctors categorize pain as nociceptive, which refers to pain from tissue damage, or as neuropathic, which refers to pain that arises from the nerves. Some pain is both nociceptive and neuropathic. Most people with PD experience nociceptive pain.
This type of pain is generally localized to a specific area of the body. The most common areas for people with PD to experience pain are the neck, upper back, and the extremities . Neuropathic pain is less common in PD, although it may be caused by akathisia, an extreme restlessness.1
The pain caused by PD can generally be classified by one of five causes:
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Change Your Personality
Natural Treatment For Parkinsons #3 Turmeric And Otherherbs And Spices:
A recent study published in the journal Stem Cell Research & Therapy, foundthat the extracts in turmeric, particularly curcumin and the newly discovered Ar-turmerone,can regenerate a damaged brain and reverse neurological disorders. Researchers said Ar-turmerone is a promising candidate to supportregeneration in neurologic disease. Michigan State University researcherBasir Ahmad also found that a compound in turmeric may help fight Parkinsonsdisease by disrupting the proteins responsible for the disease.
Another study published in the Pharmacognosy Magazine found that tumeric can prevent and evenreverse the toxic effects exerted on the brain from fluoride exposure. Fluorideis a nasty and dangerous heavy metal that destroys brain cells and the intricateworkings of the central nervous system. Fluoride poisoning has also beenimplicated in the development of neurological diseases such as Alzheimers,Parkinsons, ALS and multiple sclerosis. 7
Turmeric is also a very potent anti-inflammatory spice. Because Parkinsons is aninflammation type disease, turmeric will help immensely. A heaped teaspoon ofhigh quality turmeric powder taken 3 times daily in asmoothie will do the trick. Just make sure you combine it with 10-12 blackpeppercorns for enhanced absorption Turmeric is also fat soluble so youll need tocombine it with some coconut oil, red palm oil or fish/krill oil as well.
James* Was Diagnosed With Parkinson’s In 2011 His Pain Has Worsened As His Condition Has Progressed
When I was diagnosed with Parkinson’s, I initially felt little to no pain. It’s only now, in the advanced stages of the condition, that I’ve started feeling pain, coupled with the normal ageing process.
One of the worst pains I experience is dystonia and dyskinesia of the upper body, especially in my neck and head. It usually starts with a pulsing headache, followed by jerking of the muscles in my face, neck, upper torso and hands. It’s particularly severe in my arthritic finger and my neck. It can be severe to mild, often very distressing, and can last up to 2 hours.
I also have mild to moderate, uncontrollable movements or swaying associated with dyskinesia. It’s more prominent when I’m sitting down at a table or working on my laptop. Strangely, I feel this pain at its worst when I’m on the phone, or trying to explain something, or if I’m feeling over-excited or anxious which is when I become severely dyskinetic. There’s now a dull, continuous pain in my neck, caused through the movement, which gets sharper during bouts of the symptom.
I also experience pain when standing, mostly during a ‘wearing off’ period. My knees pull towards each other and the pain is so severe that I can’t walk. Luckily it only lasts a minute or 2, but the pain can be distressing.
To ease the pain, I take paracetamol as and when, occasionally co-codamol, and very occasionally an anti-inflammatory, for the arthritis. I previously tried cannabis oil but it was of no benefit to me.
Read Also: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinson
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Pain Presentation And Assessment In Pd
Most epidemiological data are based on questionnaires which were not specifically validated for PD patients so that results have to be interpreted with caution. The Kings Parkinsons disease pain scale is to date the only questionnaire that is specifically calibrated and validated for PD and is highly recommended to qualitatively and quantitatively assess pain and to ascribe the pain pathophysiologically. The scale contains seven different pain domains comprising musculoskeletal pain, chronic pain , fluctuation-related pain, nocturnal pain, oro-facial pain, discolouration or oedema/swelling and radicular pain as well as 14 sub-categories . This assessment tool is based on the pain classification according to Ford but also considers pain types of other classifications such as motor fluctuations or visceral pain .
In addition, there are some specific pain syndromes in PD which have to be kept in mind, including the so-called coat-hanger pain that occurs in cases of pronounced orthostatic dysregulation and although it is more frequent in multisystem atrophy it can occur also in PD and is often associated with strong headache and neck pain . Furthermore, pain due to constipation which is frequent in PD can cause abdominal pain.
Read Also: Weighted Blanket Parkinson’s
Opening The Medicine Box In The Mind: The Psychology Of Pain
In this 50-minute lecture, Beth Darnall, PhD explains how our experience of pain goes beyond the physical sensation of pain. It has emotional and psychological components that affect our ability to treat pain. She cites research to demonstrate that and shares 13 specific tips to reduce the experience of pain and increase treatment effectiveness. Audience questions follow the lecture.
The Parkinsons Disease News Today Forums Are A Place To Connect With Other Patients Share Tips And Talk About The Latest Research Check Them Out Today
PD pain can resemble pain from other disease processes, especially as the patient ages and faces a multitude of other pain-causing conditions such as arthritis, spine degeneration, poor muscular conditioning, and such. In my case, PD pain is distinguished by the following:
- The progression of body pain correlated with the progression of the disease over time.
- Levodopa, a dopaminergic therapy, successfully reduces the pain.
- The pain is worse during off periods.
My PD pain also has a particular characteristic: stinging , irritating tingling, burning, and muscle heaviness with increased pain on movement. This pain happens over large regions of the body and varies in severity. At its worst, it can last several days and reach level 7, inducing spontaneous tears.
PD with episodic chronic pain is disabling in several ways. First, high levels of pain obstruct clear thinking. Second, high levels of pain induce the fight-or-flight response, which interferes with emotion management. Third, the amount of energy necessary to manage it is very tiring . Chronic PD pain entails much more than body symptoms.
I have been a communicator most of my life, but it remains a struggle to find words that describe the unique character of PD pain. If you experience PD pain, please share your descriptors in the comments. Together we may find a common dialogue that will help others.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Akinetic Crisis And Pain

This type of pain may occur in the advanced stages of Parkinsons. Its brought on by akinetic crisis, which is a rare and sometimes dangerous complication of Parkinson’s.
Akinetic crisis involves a worsening of Parkinsons symptoms, which can include severe rigidity, a complete loss of movement, fever and difficulty swallowing. People with Parkinsons who have akinetic crisis pain say that they feel pain in their muscles and joints, and experience headaches. Some people also experience whole-body pain.
This type of pain can be brought on if you abruptly stop taking Parkinsons medication, or if you develop an infection, both of which can cause Parkinson’s symptoms to suddenly get worse. Akinetic crisis requires urgent medical help. If it looks like someone is experiencing akinetic crisis, call 999.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Do All Parkinsons Patients Develop Dementia
Although dementia is a hallmark of Alzheimers disease, dementia may occur in Parkinsons disease affecting approximately 70% of the patients.
Dementia describes a set of symptoms that cause is a significant loss in brain function. It produces a greater impact on patients on patients with Parkinsons than in Alzheimers patients as they have to deal with motor and cognitive impairment.
Alzheimers affect memory and language in general terms. Still, in Parkinsons, it affects problem-solving capacity, speed of thinking, memory, and they run with mild cognitive impairment.
Notably, Parkinsons disease dementia is a common thing among patients with this condition. The vast majority of them may experience some form of cognitive impairment over time.
Though it is a unique process for each person, several risk factors may lead to dementia symptoms and dementia itself.
- Increasing age.
- Exposure to psychological stress
- Low education level and low socioeconomic status
Disease duration has as well a direct correlation with the development of dementia on these patients. The more time the patient has this disease, the risk of developing dementia increases.
Also, Parkinsons dementia has a direct correlation with Lewy bodies. Most people develop dementia as a progression of the disease rather than having Parkinsons and Alzheimers. Nonetheless, a doctor with a neurology specialist should examine the patient to give an assertive diagnosis to the condition.
Why Pain Occurs In Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons is a brain disease that is caused by the death of cells responsible for dopamine production. Dopamine is a chemical messenger that plays an important role in body movement. It is mainly concentrated in the substantia nigra part of the brain. When its production ceased in the brain, the body experience abnormal movement .
In addition to the substantia nigra, dopamine can also be found in other regions of the brain like thalamus, basal ganglia, insula, and anterior cingulate cortex. These regions are typically associated with pain perception. The presence of dopamine in these areas suggests that, in addition to its main role in the movement, dopamine may also involve in the modulation of pain sensation within the brain .
In fact, recent research shows that a low level of dopamine in some of these regions contribute to develop pain in the body. This evidence strongly suggests that apart from motor symptoms, a low level of dopamine also causes pain. And this could be the likely reason why people with Parkinsons feel pain in their body .
But most clinicians think that Parkinsons disease symptoms are the actual cause of pain. The pain is directly linked to the intensity of symptoms, the more strong the symptom the more pain will be felt .
For example, rigidity is one of the major symptoms in Parkinsons patients. Those patients who have high rigidity are tended to experience more pain than those who have less.
Don’t Miss: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Pain Diagnosed Assessed And Treated
Diagnosing and treating pain in people with Parkinsons can be difficult and often, common ways of reducing pain, such taking painkillers or doing regular, gentle exercise may not help.
Usually, your doctor or Parkinsons nurse specialist will be able to help you to manage the more common types of pain, such as shoulder pain and headaches. Certain other types of pain, however, such as pain caused by involuntary movements or burning mouth, may need the help of your Parkinsons specialist.
Completing a Kings Parkinsons Disease Pain Questionnaire and showing it to your heath-care professional will help them to understand the pain you are suffering from1. Completing the 24-hour Hauser2 diary, a home diary designed to assess your motor symptoms, over the same period of time, would further help your doctor or Parkinsons nurse to better understand the pain you are experiencing and to treat it more quickly.
To ensure Parkinsons pain is assessed and diagnosed efficiently, a specific scale has been designed. Kings Parkinsons Pain Scale 1 is a validated scale which covers the common types of Parkinsons related pain. Your Parkinsons specialist might use this scale to help understand the type of Parkinsons pain you have even better and assess what needs to be done to help you further.
References:
Second Type Of Leg Pain Is Caused By Dystonia
When related to levodopa, it usually occurs as a wearing off but can also occur at peak dose. In most cases this leg pain is unilateral and has direct correlation to medication intake. When pain is due to dystonia, it is more common in early morning. This type of leg pain is usually accompanied by toes curling and foot abnormally posturing.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Drug Treatments Are Commonly Prescribed For Pain
Dopamine agonists are often the neurologists first weapon to alleviate Parkinsons-related pain. Levodopa is used to treat many types of pain due to Parkinsons because it treats the motor symptoms such as rigidity and dystonia that are causing them. Other medicines called analgesics can also be used to treat pain. When talking with your doctor, it is critical to let her know about all of the medications you are taking including over the counter drugs, herbs, vitamins and mineral supplements. Without complete information, your doctor may prescribe a drug that could have serious adverse effects.
