Average Life Expectancy For Someone With Parkinson’s
Researchers consider that unknot the mechanics of these genes and the designation of new genes would help us to better sympathise the nature of parkinsons disease. i didnt want to go on handicap, joseph smith said newly as he sat in his mountains edge habitation in southwestern las vegas. And delight let in your phone number or email address so we can react as apace as possible. Kaling and homer thompson make the privilege ours. Heres a closer look at the average life expectancy of a senior with parkinsons and some of the leading handling options for this permeative disease.
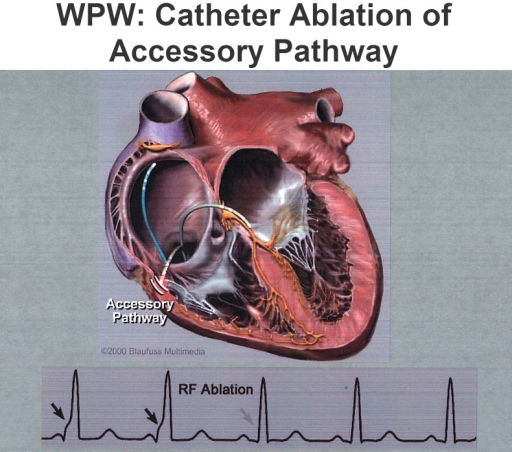
How Is Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Performed In Wpw
Radiofrequency ablation is the procedure of choice for patients with symptomatic WPW syndrome and for those who respond poorly to medical therapy. In the more experienced centers, the success rate is between 95% and 97% with a recurrence rate of 6%. The success of the ablation depends critically on the accurate location of the accessory route. The location of the preliminary route can be obtained from the delta wave and QRS morphologies .
In general, the endocavity electrophysiological study precedes the ablation of the accessory pathway, locating its exact location. The ablation procedure is performed under local anesthesia and a mild pharmacological sedation. Multiple venous accesses are obtained by the Seldinger technique. If the accessory pathway has a left localization, an arterial access is also positioned in order to allow ablation by transaortic approach. Alternatively, the left heart chambers can be reached by transseptal puncture.
The quadripolar diagnostic leads are positioned at the level of the upper right atrium, the bundle of His, at the apex of the right ventricle and in the coronary sinus .
The ablation consists of administering thermal energy near the accessory pathway in order to create irreversible cell damage and therefore make it electrically inert.
Some atrial or ventricular pacing maneuvers can be helpful if the accessory pathway is not immediately identifiable.
What Is The Role Of Endocardial Mapping In Wpw
Antegrade mapping
The first ventricular activation site during manifest pre-excitation identifies the site of ventricular insertion of the accessory pathway. Target site criteria for ablation during antegrade mapping include: 1) AP potential , 2) first local ventricular activation related to the onset of the delta wave and 3) fusion of atrial and ventricular electrograms. The potentials of the accessory path reflect a rapid local activation of the accessory pathway and are acute and high frequency deflections between the atrial and ventricular electrograms that precede the onset of the delta wave. The more the local ventricular electrogram on the ablation catheter precedes the onset of the delta wave, the greater the probability of success.
Retrograde mapping
The first atrial activation site during retrograde conduction on the accessory pathway identifies its atrial insertion site. A limitation of the mapping during ventricular pacing is that retrograde conduction on the AV node may interfere with the identification of the first atrial activation site on the accessory pathway . Potential solutions include stimulation at a higher speed , administration of drugs that slow AV nodal conduction or mapping during orthodromic AVRT . The criteria for defining the site for ablation include: 1) potentials on the accessory pathways, 2) the first atrial activation site and 3) fusion of electrograms A and V.
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Cause Seizures
Presence Of Multiple Accessory Routes
In about 10-15% of subjects with pre-excitation, there are multiple accessory pathways. Histopathological data show a higher frequency of multiple accessory pathways than those observed clinically. The presence of multiple accessory pathways increases the incidence of symptoms and is associated with a higher risk of sudden death due to atrial fibrillation that degenerates into ventricular fibrillation. Patients with pre-excitation resurrected from sudden death had a higher incidence of multiple accessory pathways than the control group that had not had cardiac arrest . Diagnosis of multiple accessory pathways on the ECG is possible, although not in all cases.
EXAMPLES OF ABLATION PROCEDURES IN SPECIFIC SITUATIONS ARE SHOWN BELOW
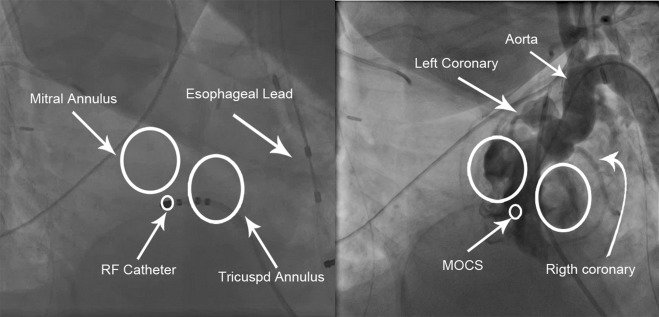
Ablation of a manifest left postero-septal AP using a retrograde trans-aortic approach . The ablation catheter is positioned along the postero-septal mitral annulus where it records potential on the accessory pathways between the atrial and ventricular electrograms. The application of RF energy on this site caused the loss of pre-excitation within seconds. The CS catheter provides a useful reference to the mitral ring.
The figure above shows how in basal conditions the signs of ventricular pre-excitation are not very evident
Proceeding with an asynchronous stimulation from the coronary sinus increases the degree of ventricular pre-excitation with the shortest AV interval detectable near the distal coronary sinus.
What Is The Role Of Surgical Ablation In Wpw
Elective surgical treatment of WPW has been largely abandoned. Until the 1980s, several patients underwent surgery to stop conduction on the AP, but since catheter ablation became available, it has been universally accepted that the risk / benefit ratio of this surgery was unacceptable, since better results were obtained using simpler and less traumatic methods.
Also Check: Is Essential Tremors A Form Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Wpw Syndrome Treated
If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome, you have several treatment options, depending on your symptoms. If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome but dont have any symptoms, your doctor may recommend that you wait and continue follow-up appointments. If youre having symptoms, the treatment may include the following:
What Are The Risk Parameters Of Dangerous Arrhythmias In Wpw
Unlike the AV node, the accessory pathways do not demonstrate a frequency-dependent decremental conduction that slows down with faster atrial rates. The following characteristics identify low risk accessory pathways: 1) intermittent pre-excitation, 2) exercise induced blockage of the accessory pathway, 3) shorter pre-excited RR interval during AF > 250 ms and 4) loss of pre-excitation with procainamide, ajmaline or disopyramide . Intermittent pre-excitation demonstrates that the accessory pathway is unable to sustain 1:1 conduction during sinus rhythm, and therefore cannot conduct rapidly during AF.
Similarly, the sudden loss of pre-excitation during exercise shows that the accessory pathway is unable to sustain 1:1 conduction during exercise-induced sinus tachycardia. During exercise, the sudden loss of pre-excitation must be differentiated from the gradual loss of pre-excitation due to a better AV nodal conduction. During pseudonormalization, the accessory pathway continues to lead anterograde, but the delta wave slowly disappears as the contribution to the ventricular activation by the AV-His-Purkinje system increases. Since the antegrade effective refractory period is related to the shortest expected RR interval during AF, an antegrade ERP along the accessory pathway or a duration of the atrial pacing cycle maintaining a 1:1 conduction shorter than 250 ms is a reasonable, but not ideal substitute for the minimum RR interval, in cases where AF is absent.
Also Check: How Is Parkinson’s Tested
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you keep getting a fast or noticeable heartbeat . It’s important to get it checked out in case it could be something serious.
Dial 999 for an ambulance if:
- your heartbeat doesn’t go back to normal in a few minutes
- you have chest pain that lasts more than 15 minutes you may also have pain in your arms, back or jaw
- you have chest pain and other symptoms like feeling sick, being sick , shortness of breath or sweating
- someone passes out and doesn’t regain consciousness
If you’ve been diagnosed with WPW syndrome and you experience an episode, first try the techniques you’ve been taught or take any medication you’ve been given.
Dial 999 or go to your nearest accident and emergency department if these measures don’t stop the episode within a few minutes, or if someone you know has WPW syndrome and collapses or faints.
What Causes Wpw Syndrome
When the heart beats, its muscular walls contract to force blood out and around the body. They then relax, allowing the heart to fill with blood again. This is controlled by electrical signals.
In WPW syndrome, there’s an extra electrical connection in the heart, which allows electrical signals to bypass the usual route and form a short circuit. This means the signals travel round and round in a loop, causing episodes where the heart beats very fast.
The extra electrical connection is caused by a strand of heart muscle that grows while the unborn baby is developing in the womb.
It’s not clear exactly why this happens. It just seems to occur randomly in some babies, although rare cases have been found to run in families.
Recommended Reading: Are There Different Types Of Parkinson’s Disease
Risk Factors For Post
Atrial fibrillation prior to ablation was an independent risk factor of atrial fibrillation after the ablation . There was an age-dependent risk of post-ablation atrial fibrillation in the WPW group. WolffParkinsonWhite patients aged 50 years or more had significantly higher risk of post-ablation atrial fibrillation than the younger group .
None of the other analysed clinical characteristics showed a significant association with post-ablation atrial fibrillation .
Predictors of post-ablation atrial fibrillation: a stratified adjusted analysis of the WPW group showing HRs and CIs of the comorbidity-adjusted risk of post-ablation medical contact caused by atrial fibrillation. A HR of > 1 indicates an increased risk of atrial fibrillation in the subgroup.
What Are The Goals In The Treatment Of Wpw Syndrome
Pre-excitement therapy has four different objectives: 1. To cure symptoms 2. Prevent the risk of sudden death 3. Prevent or cure, in case of chronic tachycardia, the worsening of the ventricular function 4. Allow subjects with pre-excitement to carry out all activities that are otherwise prohibited by law when there is pre-excitement on the ECG, for example in competitive sportsmen or in workers of professions at risk.
In other cases, therapy is not indicated: in particular in asymptomatic subjects, who present with only pre-excitation on the ECG, no treatment is necessary, once the absence of risk parameters in the electrophysological properties of the accessory pathways has been verified, given except that in rare cases, the risk of developing dangerous arrhythmias is very limited.
There are four different types of therapeutic approaches: antiarrhythmic drugs, transcatheter ablation of accessory pathways, surgical ablation of accessory pathways, and electrical therapy .
You May Like: How Long Can Someone Live With Parkinson’s Disease
Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular & Thoracic Institute Cardiologists And Surgeons
Choosing a doctor to treat your abnormal heart rhythm depends on where you are in your diagnosis and treatment. The following Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Sections and Departments treat patients with Arrhythmias:
- Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing: cardiology evaluation for medical management or electrophysiology procedures or devices – Call Cardiology Appointments at toll-free 800.223.2273, extension 4-6697 or request an appointment online.
- Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: surgery evaluation for surgical treatment for atrial fibrillation, epicardial lead placement, and in some cases if necessary, lead and device implantation and removal. For more information, please contact us.
- You may also use our MyConsult second opinion consultation using the Internet.
The Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute has specialized centers to treat certain populations of patients:
Is It Time To Rethink Our Approach To Asymptomatic Wpw
- A
- A
Editor’s Note: Commentary based on Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Manguso F, et al. WPW Syndrome in the Era of Catheter Ablation: Insights from a Registry Study of 2169 Patients. Circulation 2014 130:811-9.
In patients with symptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, treatment strategies are relatively defined with curative catheter ablation as the most common recommended approach. The management of asymptomatic patients is more controversial. In these patients, the primary concern is reducing risk of sudden death, ventricular arrhythmias, and atrial fibrillation . Regarding malignant ventricular arrhythmia risk, short antegrade refractoriness of the accessory pathway conveys the highest risk. For example, in patients with AF, higher risk is associated with persistence of accessory pathway conduction with R-R intervals less than 250 ms. In the absence of high-risk features, cardiac arrest rates are relatively low in asymptomatic WPW patients with estimated rates < 0.2%.1
This study confirms our current approach that symptomatic and asymptomatic high-risk patients, easily stratified by the electrophysiology properties of the accessory pathway, benefit from ablation. However, it also shows that catheter ablation and electrophysiology studies are not without risks. Outside of a prospective study, these data do not support broad screening for asymptomatic WPW to lower risk of cardiac arrest in the community.
Recommended Reading: What Classes Of Drugs Are Used To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
Design Study Population And Control Group
This is a retrospective cohort study of 364 consecutive patients with WPW syndrome who underwent radiofrequency ablation at Aarhus University Hospital from the start of the ablation era in 1990 until the end of 2011. As all available patients were included, no sample size calculation was done.
Two patients were excluded as no follow-up was registered due to foreign citizenship. A control group was generated from the Danish National Board of Health Central Population Registry and the WPW patients were matched in a ratio of 1 : 10 on age and gender.
Cardiac Ablation Does Not Reduce Atrial Fibrillation Risk For Wolff
Study presented at HRS finds treating extra pathway has no impact on afib risk, regardless of age
May 11, 2016 Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome who receive catheter ablation to cure their abnormal heart rhythms are just as likely as non-ablated patients to develop atrial fibrillation no matter what age they receive ablation, according to a new study.
The study by researchers at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Salt Lake City also found that Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a long-term cause of atrial fibrillation in addition to traditional risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure, sedentary lifestyles and sleep apnea.
Wolff-Parkinson-White is a syndrome that results in an abnormal electrical pathway from the upper to the lower heart chambers. Patients with the syndrome can experience rapid abnormal heart rates when electricity bypasses the normal electrical system of the heart and uses the extra pathway.
Researchers at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute initially set out to discover if catheter ablation reduces the long-term risk of atrial fibrillation and whether the patients’ age at the time of the procedure affected their risk.
Their study consisted of previously collected data from three different groups: 872 Wolff-Parkinson-White patients who received ablation treatment between ages 22 and 57 1,461 patients who were treated with medication and 11,175 people who didn’t have the syndrome.
Recommended Reading: Are There Two Different Types Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Pharmacological Treatments Of Avrt In Wpw
In antidromic AVRT, retrograde AV nodal conduction can be the weak link in the re-entry circuit. Calcium channel blockers, beta blockers and adenosine can be used for the acute cessation of tachycardia. Procainamide IV is the drug of choice in the acute treatment of antithromic AVRT. Also this drug does not stop tachycardia: it can slow down the rate of tachycardia. In the absence of contraindications, class 1c drugs are the drugs of choice for the long-term oral treatment of antidromic tachycardia.
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Catheter Ablation
26 Aug 2020
Here at parkinsons concierge and remelife, we get laid from personal experience, that every mortal with parkinsons encounters dissimilar symptoms at dissimilar contemporary world. i am not a acquiescent affected role on that front. They find it hard to sleep, which makes them peevish and thus, they feel unergetic all the time. Her language has begun to slur passably, and she has a shambling pace. Rassling carried him to college, wherever the penning bug took hold. Carlota dena and onésimo lopez started an connection for parkinsons patients and their caregivers in guamúchil, united mexican states, afterward visiting the mahound ali parkinson center in genus phoenix. As mentioned above, catheter ablation is now well thought out the therapy of choice in symptomatic of patients with supraventricular tachycardias, specially wolff-parkinson-white syndrome. Mark strassmann with some help from our cbs news program workfellow has the floor of a hurricane now account.
Don’t Miss: What Do Patients With Parkinson Die From
How Is Wpw Treated
Treatment depends on the type and frequency of arrhythmias, associated symptoms such as syncope, and presence of structural heart disease. Typically a physician will recommend an ablation procedure to further define the characteristics of the accessory pathway, and ultimately, to eliminate the pathway entirely.
- Observation – If you have no symptoms, you may not require treatment. Your doctor may choose to have regular follow-up without treatment.
- Medications – A variety of drugs are available to treat arrhythmias. Because everyone is different, it may take trials of several medications and doses to find the one that works best for you. It is important to know:
- The names of your medications
- What they are for
- How often and at what times to take them
When Is Transcatheter Ablation Recommended In Asymptomatic Subjects With Wpw
Currently, the importance of electrophysiological study and transcatheter ablation of accessory pathways are well established in symptomatic patients with WPW syndrome. Based on the recommendations of the 2019 ACC / AHA / ESC guidelines, in the case of symptomatic pre-excitation, transcatheter ablation has a class I indication.
The approach to asymptomatic patients is less clear. The increased safety of the EP study and catheter-based ablation techniques provide an impetus to prophylactic ablation of the pathway. To support this, randomized studies have shown that prophylactic ablation in asymptomatic patients who are at high risk of arrhythmias, performed in experienced centers, reduces the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias.
Read Also: Parkinson Disease And Speech Problems
How Is Wpw Diagnosed
WPW can only be diagnosed by reviewing an ECG . A holter or ambulatory monitor and exercise testing are also helpful in evaluating patients known to have WPW.
In the past, patients with WPW but without symptoms had been observed by a cardiologist for many years. Recently, new guidelines have been published for this group of patients. Your cardiologist may order a holter monitor or stress test to look for a persistent patter of WPW. If the WPW pattern persists, invasive electrophysiology testing is now recommended.
Your doctor will also ask you several questions:
- Do you have symptoms?
- Do you have a history of atrial fibrillation?
- Do you have a history of fainting?
- Do you have a history of sudden cardiac death or does anyone in your family?
- Are you a competitive athlete?
The results of your diagnostic tests and the answers to these questions will help guide your therapy.
