Parkinson Disease: Nursing Process
Notes
Content Reviewers:
Michael Desante is a 67 year old male with a history of . His daughter has been his primary caregiver since his diagnosis, however, as Michaels disease progressed, Michael moved into a long-term care center for further support.
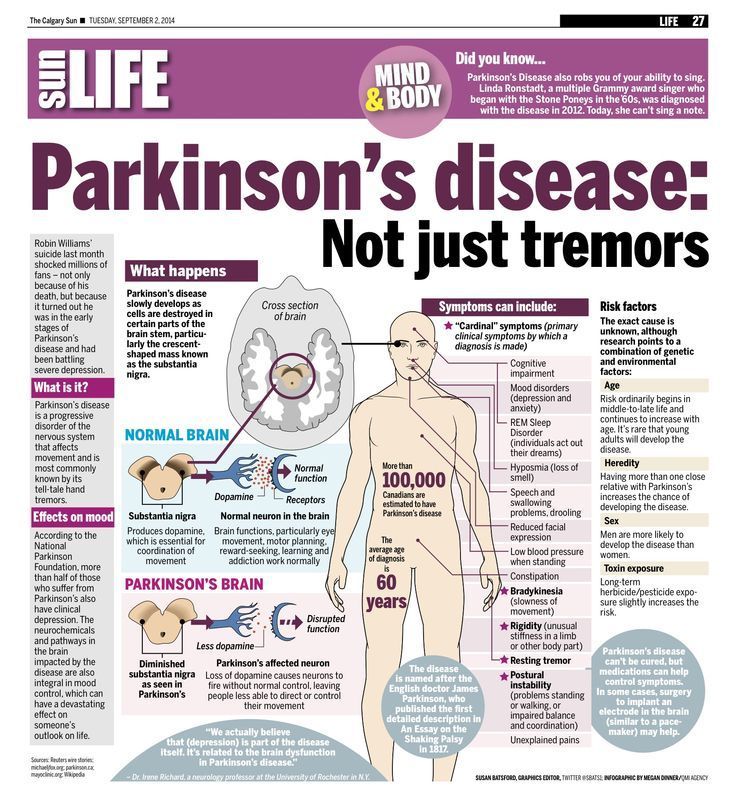
, or PD for short, is a progressive neurological disease that affects movement. Most often, the cause of PD is unknown, but there are some factors that can increase the risk.
Non-modifiable risk factors include increasing age, with a mean age of onset of 57 years as well as male sex and having a family history of PD.
On the other hand, modifiable risk factors include exposure to toxins like pesticides, and a history of . Now, in PD theres degeneration of the dopamine-producing neurons in the of the .
Normally, the helps initiate movements, but also fine tunes the way that movements happen. When these neurons die, the first symptom is a resting , which is an involuntary shaking that presents at rest and decreases with movement.
Most often, resting affects the hands, which is called a pill-rolling because it looks like someone is rolling a pill between their thumb and index finger.
Over time, resting can also involve the feet, tongue, and jaw. In addition, the client can experience bradykinesia, or of .
A more severe form of bradykinesia is , which is when they become unable to initiate a . For instance, the client may feel like their legs freeze up when trying to walk.
General Approach To Management
The primary goal in the management of PD is to treat the symptomatic motor and nonmotor features of the disorder, with the objective of improving the patients overall quality of life. Appropriate management requires an initial evaluation and diagnosis by a multidisciplinary team consisting of neurologists, primary care practitioners, nurses, physical therapists, social workers, and pharmacists., It is also important that the patient and his or her family have input into management decisions.
Effective management should include a combination of nonpharmacological and pharmacological strategies to maximize clinical outcomes. To date, therapies that slow the progression of PD or provide a neuroprotective effect have not been identified., Current research has focused on identifying biomarkers that may be useful in the diagnosis of early disease and on developing future disease-modifying interventions.,
Is Early Diagnosis Possible
Experts are becoming more aware of symptoms of Parkinsons that precede physical manifestations. Clues to the disease that sometimes show up before motor symptoms and before a formal diagnosis are called prodromal symptoms. These include the loss of sense of smell, a sleep disturbance called REM behavior disorder, ongoing constipation thats not otherwise explained and mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression.
Research into these and other early symptoms holds promise for even more sensitive testing and diagnosis.
For example, biomarker research is trying to answer the question of who gets Parkinsons disease. Researchers hope that once doctors can predict that a person with very early symptoms will eventually get Parkinsons disease, those patients can be appropriately treated. At the very least, these advances could greatly delay progression.
Also Check: Are There Different Types Of Parkinson’s
Department Of Veterans Affairs
Through the VA Health Care program and their pensions, the VA offers veterans multiple avenues of assistance with medical equipment, assistive technology and home modification. The avenue best pursued depends on whether or not the individual with Parkinsons Disease was exposed to herbicides during their military service. For those individuals not exposed, they are most likely to receive assistance from the Aid and Attendance pension benefit, VD-HCBS or the HISA Grant. For those veterans with PD who were exposed, VA Health Care will cover the cost of much assistive technology and medical equipment.Another option for veterans comes not from the VA but from a non-profit organization with a veteran-specific program called Heroes at Home. This program is intended to assist in making home modifications and typically provides free labor for modifications but does not cover the cost of materials.
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease

There is no specific diagnostic procedure to diagnose PD. However, the following are helpful to come up with the diagnosis:
- Medical History Taking
- Physical Examination
- Single Photon Emission CT scan -this form of imaging shows the blood flow to tissues and organs
- Dopamine transporter scan this imaging is often used to confirm the diagnosis of PD. It is not typically requested as medical history and physical examination are often conclusive.
You May Like: How Old Can You Be To Get Parkinson’s Disease
Differences In Home Health Nursing Care For Patients With Parkinsons Disease By Stage Of Progress: Patients In Hoehn And Yahr Stages Iii Iv And V
Yumi Iwasa
1Department of Nursing, Graduate School of Health Sciences, Kobe University, Tomogaoka, Suma-ku, Kobe, Hyogo 654-0142, Japan
2Akebi Home-Visit Nursing Station, Hosoe, Shikama-ku, Himeji, Hyogo 672-8064, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disease with no radical cure. In Japan, patients above stage III on the Hoehn and Yahr scale are eligible for public medical expense subsidies. When calculated using the Japanese population, the adjusted prevalence of the disease is 166.8 per 100,000 individuals .
It is important for patients with PD in long-term medical treatment to receive physical therapy to maintain bodily functions and pharmacotherapy, centering primarily on L-Dopa, to achieve symptomatic relief both of these efforts require effective care protocols. When provided by nurses, programs that involve counseling, medication information, and collaboration with local organizations during hospitalization and discharge are known to be effective for supporting patients with PD. In the West, PD nurse specialists perform these roles and, in recent years, efforts to improve these nursing activities have resulted in studies and surveys leading to the creation of nursing practice guidelines . Due to the need to enhance the effectiveness of nursing care provided to patients with PD, the movement to maintain and further improve the quality of care is increasing globally.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants and Collected Data
3. Results
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
This study will be conducted in accordance with the good clinical practice guidelines promulgated by the International Conference on Harmonization, the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act. The NICE-PD study protocol and communication materials have been approved by the local ethics committee . The study is registered with the ClinicalTrials.gov registry . The trial results will be reported according to the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials 2010 guidelines .
When a patient meets the inclusion criteria, informed consent will be obtained by the research team after the team explains the procedures and requirements of the study, how subjects confidentiality will be maintained, and any potential hazards/risks. Each patient will sign an informed consent form in person at the baseline visit before baseline assessment takes place. The researcher will sign the informed consent immediately after the patient has signed it. The researcher provides a copy of the signed informed consent form to each participant and keeps a copy in the participants study file.
When important changes are made to the study protocol , the principal investigator will notify relevant parties about these changes, and a copy of the revised protocol will be sent to these parties . Furthermore, the updated protocol will be included in the trial registry.
Recommended Reading: Antipsychotic Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
- Tremor. The presence of tremors is one of the triad symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Tremors usually start in the limbs, most commonly in the hands and fingers. They are likely to occur when the body is at rest and relaxed. Pill-rolling tremors are common in Parkinsons disease patients. It is characterized by the rubbing of thumb and forefinger back and forth.
- Bradykinesia. One other main symptom of PD is slow movements or bradykinesia. Individuals with PD display a distinctive slow and shuffling gait. Slowness in movements often make it more difficult for people with PD to complete activities of daily living.
- Rigidity . Muscle stiffness is also a common sign of PD. It may occur in any part of the body and may lead to dystonia or uncontrolled painful muscle cramps.
- Impaired posture and balance. Most people with PD often have a stooped posture.
- Loss of automatic movements. Unconscious movements such as blinking, smiling, and swinging of hands when walking may be reduced in people with Parkinsons disease.
- Anosmia. Loss of the sense of smell may occur even years before the diagnosis of PD.
- Speech changes. Changes in speech may also be noted in people with PD. Their speech may become soft, fast, slur, and their tone may become monotonous.
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion and exclusion criteria for patients are kept purposefully broad in order to represent the full diversity of the PD spectrum and thus generate results that apply to real clinical practice. All patients with PD, regardless of disease severity or disease duration, male and female, aged 18years or older at the time of PD diagnosis are eligible. We will only exclude patients for the following reasons:
-
Lack sufficient knowledge of the Dutch language to complete questionnaires
-
Have received care from a PDNS in the past 2 years
-
Have a score < 18 on the Mini Mental State Examination and < 12 on the Frontal Assessment Battery
-
Have a type of atypical parkinsonism caused by medication , a metabolic disorder , encephalitis, or a neurodegenerative disorder
-
Residing in a nursing home or another type of residential care facility
-
Have any other medical or psychiatric disorder that, in the opinion of the researcher, may compromise participation in the study
Dont Miss: Similar To Parkinsons
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease A Disability
Pharmacological Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
There is currently no proven disease-modifying or neuroprotective therapy for PD. A summary of previous neuroprotection trials is given in a recent review article. Current evidence-based treatment for PD is symptomatic and mainly based around dopaminergic replacement or modulation . The evidence base is summarised in recent guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors are all licensed for use as initial therapy in PD. Anticholinergics are no longer routinely used due to the risk of cognitive decompensation.
Pharmacological therapies currently used for initial and adjunctive treatment of motor symptoms in Parkinsons disease
- Selegiline hydrochloride
- Rasagiline mesylate
The enzyme monoamine oxidase B breaks down dopamine in the brain. MAO-B inhibitors prevent this breakdown, thus increasing the amount of dopamine in the brain and reducing the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
MAO-B inhibitors to treat the symptoms of PD can either be used alone or with levodopa. In early PD, they can delay the need for starting levodopa. Later in the disease, they can be given with levodopa, to enhance and prolong the effects to levodopa, thus reducing the wearing off phenomenon. When taken in combination with levodopa, it may allow the dose of levodopa to be reduced.
How Nursing Plus Of Broward Can Help
At Nursing Plus of Broward, we understand the symptoms of Parkinsons Disease are unique to each person and can vary in severity. Since early signs and symptoms of PD are sometimes dismissed as the normal effects of aging and there are currently no blood or laboratory tests that diagnose Parkinsons Disease, it can be difficult to diagnose accurately early on in the course of the disease. Since many other diseases have similar features, physicians may not diagnose Parkinsons until the later stages of PD when symptoms progress and become more prominent.
As a slowly progressive disorder, its impossible to know what course the disease will take for you or your loved one. We understand how it can be emotionally and physically exhausting for families to not only cope with the news, but with the added responsibilities of caring for a loved one with Parkinsons Disease. With a skilled team on your side, you and your loved ones will have the support needed to achieve the optimal function possible while continuing to live in the comfort of their home.
The trained team at Nursing Plus of Broward can help with any of the following:
A few of the daily tasks we can help with include:
Also Check: New Treatment For Parkinson’s
Inpatient Management Of Parkinsons Disease
Patients with PD are often admitted to hospital for other reasons, but the unique challenges of the condition mean that outcomes related to PD are often suboptimal. Many hospitals have an alert system to inform members of the PD team of admission to allow proactive in-reach consultations. It is essential that antiparkinsonian medications are given on time and in correct dosage, as sudden reduction or withdrawal of medication can lead to severe morbidity or even mortality due to parkinsonismhyperpyrexia syndrome. Dopamine blocking drugs must not be given. When patients with PD cannot take their usual oral medications, we recommend that an equivalent dosage be given via nasogastric tube. If this is not possible, or enteral medication is contraindicated, cautious use of rotigotine patch can be helpful.
Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
Currently, Parkinsons disease has no cure. However, treatments are extremely helpful in managing its signs and symptoms.
You May Like: Do All Parkinson’s Patients Get Dementia
Home Care Plan For Stage Five
Round the clock care is likely to be required at stage five. Most tasks will require some form of assistance. Cavendish Homecare can help you to decide on the best plan for caring for yourself or a loved one. This includes palliative home care.
We pride ourselves on being able to deliver care thats professional,organised and efficient, plus tailored to an individuals needs. Our flexiblepackages can be adapted if circumstances change. Get in touch with us today.
Neurodegeneration With Brain Iron Accumulation
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation patients present with a progressive extrapyramidal syndrome associated with iron deposition in the basal ganglia. The two main syndromes are outlined here, although there are additional syndromes including neuroferritinopathy and aceruloplasminemia. The most common of the NBIA disorders is pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration , resulting from mutations on the PANK2 gene, accounting for 50%. The classic syndrome manifests in early childhood with a combination of pyramidal and extrapyramidal features . PKAN can also rarely present in early adulthood. There are typical MRI findings, with a central hyperintensity with surrounding low signal on T2 images in the globus pallidus, giving the so-called eye-of-the-tiger sign .
The second main type of NBIA is PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration . When onset occurs in infancy, PLAN causes progressive motor and mental retardation with cerebellar ataxia, seizures, and pyramidal signs. However, onset can occur later in life which leads to an atypical syndrome that may mimic PD, with rest tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia and a good response to levodopa. However, patients also exhibit additional features including eye-movement abnormalities and pyramidal signs .
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Cause Seizures
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is an idiopathic illness, which means that its cause is unknown.
The signs and symptoms it present are caused by the loss of nerve cells in the part of the brain called substantia nigra.
This part of the brain is responsible for the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that links the brain and nervous system to coordinate body movements.
Loss of dopamine results in uncoordinated body movements, thereby producing the signs and symptoms of the disease.
Though the exact cause of Parkinsons disease is still unknown, there are possible explanations that may be responsible for the condition, such as:
- Genetics. Studies have shown that a minority of cases of PD have genetic involvement.
- Environmental factors. Exposure to pesticides, herbicides, and industrial pollution is now being looked at as a possible cause of PD. However, the results are still inconclusive.
- Presence of Lewy bodies. Lewy bodies are clumps of substances in the brain cells. These are often seen in people with Parkinsons disease. The studies about them are still inconclusive, but researchers believe that these substances hold useful information to what causes PD. Researchers are also focusing into alpha-synuclein found in the Lewy bodies.
The following are the associated risk factors in developing Parkinsons disease:
Pathogenesis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of mechanisms have been implicated in PD pathogenesis, with -synuclein aggregation central to the development of the disease. Multiple other processes are thought to be involved, with several studies suggesting that abnormal protein clearance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation play a role in the onset and progression of PD. However, the relationship between these pathways remains unclear.
Recommended Reading: Stabilizing Spoon For Parkinsons
Also Check: What Foods Should Parkinson’s Patients Avoid
Complications Of Parkinsons Disease
