Parkinsons Disease Therapy With Stem Cells: How Can Stem Cells Help
Diverse stem cell types are under scientific investigations, some of which are in clinical trials, for the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based therapies for treating Parkinsons disease. They include:
- Dopamine-producing Embryonic Stem Cells for Parkinsons disease
- Induced pluripotent stem cells for Parkinsons disease
- Neural stem cells for Parkinsons disease
- Stromal Vascular Fraction for Parkinsons disease
- Lab-grown Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Parkinsons disease
Relative Optimism In The Long Haul
Even so, Im more optimistic here than in some other areas of stem cell translational research.
For instance, when we look at the arena of stem cells for COPD, which often includes no actual stem cells, most of what is going on is not approved by the FDA. Some of it is probably illegal. Its not even clear to me how stem cells in most cases would help COPD.
The cell therapy and stem cells for autism space is extremely active even commercially at clinics, yet we mostly dont even know what causes autism and it is a highly heterogeneous collection of conditions. Here again, we have many folks doing stuff they shouldnt too.
Another example is the field of stem cells for heart disease, which has been wracked by controversy and misconduct.
Therapy Workflow For Early To Mid Parkinson’s Disaease
The precise workflow is described in detail on the stem cell- specific pages of BMC, Secretome/Exosomes and PRP . All therapies are divided into phases such as evaluation of the medical history , initial counseling and evaluation of potential, patient-individual benefit of a stem cell therapy , preliminary examinations, diagnostics, consultation on all therapy options, preparation of an individual treatment plan including cost estimate, harvesting of tissue, production of the stem cell product, quality control of the product and application.
Unfortunately, we only treat patients in an early to mid stage of PD and according to the risk-benefit ratio, we cannot treat children or pregnant women. In addition, other factors can also be exclusion criteria.
Also Check: Do All Parkinson’s Patients Get Dementia
Stem Cell Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Stem cell therapy may have the benefit of replacing and repairing damaged dopamine-producing nerve cells within the brain. This has already been found in a study conducted by Neelam K.Venkataramana and colleagues. Seven PD patients aged 22 to 62 years with a mean duration of disease 14.7 ± 7.56 years were enrolled to participate in the prospective, uncontrolled, pilot study of single-dose, unilateral transplantation of autologous bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells . Patients were followed up for 36 months post-transplant, 3 of the 7 patients showed significant improvement in their Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale of 38%.
According to Medical News Today “Currently, the most common therapy uses the drug levodopa to stimulate dopamine production in certain neurons associated with motor skills. These dopaminergic neurons are situated in the nigrostriatal pathway which is a brain circuit that connects neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta with the dorsal striatum. However, levodopa has a wide array of side effects, from physiological to psychological ones. Also, in the long-term, the benefits of such dopamine-regulating drugs are limited. So, scientists must come up with more effective strategies for repairing the brain damage that Parkinson’s disease causes.”
Cell Culture And Phenotype Identification
Fresh umbilical cord samples were obtained from normal spontaneous full-term delivery mothers with written informed consent and reserved in a sterilized phosphate-buffered saline solution processed within 3 h. The cord was rinsed three times to remove the residue blood and clots, cut into 3-cm-long pieces, and rinsed again in a petri dish until the solution became clear. After blood vessels were removed, Whartons jelly was dissected into pieces approximately 0.3 cm3 in size and then transferred into culture vessels, with 10 ml mesenchymal stem cell complete medium at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. The medium was replaced with fresh medium every 3 days after the initial plating. The cultured cells were passaged when cell confluency reached 80%.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Tremors In Parkinson’s Disease
Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair A Parkinsons Disease Model By Inducing Autophagy
Journal: Cell Death and Disease
Institution: Hebei University of Chinese Medicine
Research Areas: Stem cell therapy
Cell Lines: hucMSC
Summary: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can provide neuroprotection in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinsons disease, treatments. However, at the moment, hucMSC applications are limited due to various reasons. In this study, H.-X. Chen with colleagues has shown that Exosomes derived from hucMSC have the potential for effective Parkinsons disease treatment because they can pass the Brain-Blood barrier. Here, HoloMonitor M4 was used to characterize hucMSC cell proliferation and helped to characterize hucMSC self-renewal and reproductive abilities.
Keywords: HoloMonitor M4, cell proliferation,mesenchymal stem cells
Induction Of Functional Dopamine Neurons From Bmscs
A system to specifically induce dopamine neurons from BMSCs was reported . This system first generates postmitotic functional neuronal cells with a very high efficiency without contamination by glial cells. The resulting neuronal cells are then further induced into dopamine neurons. The induction is achieved by lipofection of a plasmid containing a Notch1 intracellular domain and G418 selection, followed by the administration of a specific combination of trophic factors and cytokines .
Induction of dopamine neurons from MSCs. After NICD introduction, MSCs become similar to NPCs, expressing the NPC markers nestin, GLAST, 3-PDGH, and neuroD. After cytokine stimulation ), cells become postmitotic neurons expressing neuronal markers such as neurofilament, Tuj-1, and MAP-2. The administration of GDNF induces neurons to become dopamine neurons , which are useful in the Parkinsons disease model. Pictures from J Clin Invest 113 17011710 and J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29 14091420 .
When NICD-introduced BMSCs are expanded and then stimulated with trophic factors ) for several days, approximately 96% of the cells extend neurites and differentiate into postmitotic neuronal cells. These cells are positive for the neuronal markers MAP-2ab, neurofilament, and Tuj1, and most importantly, action potentials were recorded in the cells in a patch clamp experiment, suggesting that these induced cells are functional neuronal cells .
You May Like: What Does Azilect Do For Parkinson’s
Stem Cell Clinical Trials For Parkinsons
Previously, some researchers transplanted fetal brain tissue into Parkinsons patients. In some cases, it seemed to produce lasting improvements in symptoms in some patients, but double-blinded studies didnt support this as a generally viable approach.
Where do things stand now?
I found 37 trial listings on stem cells for Parkinsonson Clincialtrials.gov, which sounds like a lot. However, unfortunately, almost none of these are real, robust interventional trials based on solid preclinical data. Many have unknown status, have been terminated, or are using MSCs or mesenchymal cells or bone marrow cells, which doesnt make sense to me. Some are for-profit clinic-type operations too, which is troubling.
What are some of the more promising trials or efforts that will lead to trials? I cant list them all but here are the ones Ive been following most closely:
Overall, while this road is not as straightforward as I thought back in 2010 when I started The Niche, I believe well get there. Whether it is iPSC-based or ESC-based, autologous or allogeneic, I dont know, but its going to happen.
Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Locomotor Function In Parkinsons Disease Mouse Model Through Regulating Intestinal Microorganisms
- 1Department of Neurology, The First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 2Hebei Provincial Engineering Laboratory of Plant Bioreactor Preparation Technology, Shijiazhuang, China
- 3Research Center, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang, China
- 4College of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang, China
- 5Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Disease And Tremors
Recommended Reading: How Long Can Someone Live With Parkinson’s Disease
Stem Cells For Parkinson’s Disease Are Safe And Effective
According the Venkataraman and colleagues, “A subjective improvement was found in symptoms like facial expression, gait, and freezing episodes 2 patients have significantly reduced the dosages of PD medicine. These results indicate that our protocol seems to be safe, and no serious adverse events occurred after stem-cell transplantation in PD patients.”
As stated in a 2005 study held by Brian Snyder,
Stem cells offer the potential to provide a virtually unlimited supply of optimized dopaminergic neurons that can provide enhanced benefits in comparison to fetal mesencephalic transplants. Stem cells have now been shown to be capable of differentiating into dopamine neurons that provide benefits following transplantation in animal models of Parkinson’s disease.
Effect Of To901317 On Gf To Promote The Differentiation Of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Into Dopamine Neurons On Parkinsons Disease
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology2017
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2015
- Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2008
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2015
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2015
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology2017
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2015
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2015
- Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2008
Also Check: Thc For Parkinson’s Disease
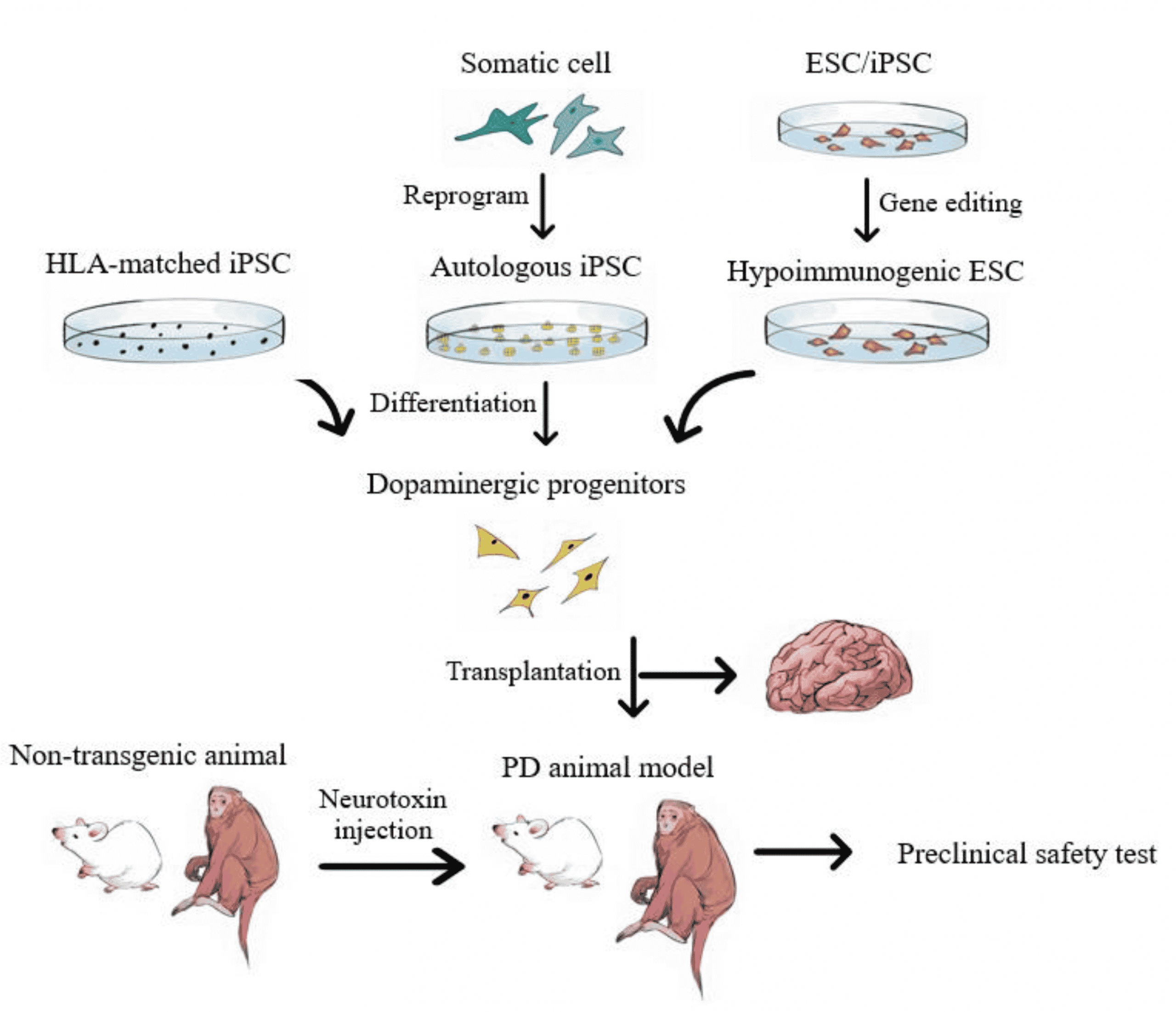
How Would Parkinsons Disease Stem Cell Therapy Work
The basic idea is that human pluripotent stem cells like iPS cells or ES cells would be differentiated in a precise way in the lab.
This process produces human dopaminergic neurons, the cell type lost in Parkinsons disease.
These cells would then be transplanted into the proper location in the brains of patients and take the place of the lost cells. In Parkinsons specific neurons are lost in the substantia nigra so that generally is one prime target for transplantation but not the only one.
The hope is that these new cells would be functional and not cause problems. What are the risks? For example, if the transplanted cells produce too much dopamine or in the wrong place, they can cause trouble like movement disorders called dyskinesias beyond or different from what the patients are already facing with Parkinsons in terms of movement issues.
Note that the underlying cause of Parkinsons isnt well-understood. Its thought to be a combination of environmental and genetic factors, leading to dopaminergic neuron death. Such a brain environment could eventually damage or kill transplanted dopaminergic neurons too. This represents another possible challenge.
Modulatory Effects Of Mscs On Pd
Recently, dysregulation of the autophagy system has been identified in the brains of PD patients and animal models of the condition, suggesting a potential role for autophagy in PD . In PD models, MSCs have been demonstrated to improve a-syn clearance and regulate autophagy-lysosomal activity . MSCs may activate autophagy signaling through upregulation of Beclin-1 , a key positive regulator of mammalian autophagy. The secretome of MSCs has been found to contain numerous components associated with autophagy signaling in cell-based experiments through induction of autophagy-related genes, including beclin-1 , Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein-like 1 and Autophagy related 12 . The secretome of MSCs drives PI3K/Akt activation and modulates different signaling pathways to improve nutrient absorption, cell growth, metabolism, and proliferation .
According to several investigations, MSCs exhibit immunomodulatory effects after infiltrating to injury sites in response to particular chemotactic recruitment and releasing numerous growth and immunoregulatory factors, so they can alleviate inflammation and improve tissue healing . Therefore, MSC-based cell therapy has been used to modulate inflammation and accommodate tissue regeneration in treating many neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative illnesses such as Parkinsons disease .
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Tremor Is Associated With Parkinson’s
What Do We Know About Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is the second most common type of neurogenerative disease, affecting over 10 million people, or approximately 1% of the population worldwide, over the age of 65.
Parkinsons disease is characterized by a progressive loss of muscle control leading to bradykinesia , rigidity, resting tremor and postural instability.
As symptoms worsen, it may be difficult to walk, talk, and perform simple tasks. Non-motor symptoms can include anxiety, depression, psychosis, and dementia.1,2
The main pathological feature of Parkinsons disease is the significant loss of dopamine neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta.
The loss of the dopaminergic neurons is linked to the formation and accumulation of Lewy bodies. Dopamine is a chemical that acts as a messenger between brain cells. It plays a role in how we move, what we eat, and how we learn.
The substantia nigra, a tiny strip of tissue on both sides of the base of your brain produces dopamine. When the brain cells in the substantia nigra start to die, dopamine levels drop.
When the level of dopamine gets to low, you will begin to experience symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease and currently available therapeutic approaches only treat the symptoms of the disease
Mscs And Their Differentiation Ability
The possibility of MSC plasticity and transdifferentiation was initially described following in vivo experiments in which transplanted donor bone marrow-derived cells differentiated into glial cells in the recipient brain . While some studies suggested that MSCs are plastic based on their expression of cell-specific markers, the functions of the transdifferentiated cells were not clearly demonstrated in other cases. Moreover, questions have been raised regarding the interpretation of transdifferentiation of infused cells into neuronal lineage cells because some investigators have suggested that the transdifferentiation observed was rather a result of fusion between infused bone marrow cells and the host brain cells . Despite this uncertainty, accumulating evidence supports the broad differentiation of MSCs both in vivo and in vitro. Based on the frequency and ratio of MSCs integrated and differentiated into the host tissue, fusion alone cannot explain all of the phenomena observed after MSC infusion. Furthermore, experiments using a Cre-lox system clearly demonstrated that MSCs can transdifferentiate into epithelial cells in vivo without fusion . In vitro differentiation of MSCs provides further evidence for MSC transdifferentiation because there are no preexisting differentiated cells to be fused at the beginning of induction under culture conditions.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Disease Cause Personality Changes
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
In 2007, the process for generating iPSCs was first reported, offering a new avenue for the development of a stem cell-based treatment for PD . iPSCs are generated by the reprogramming of an adult somatic cell into a stem cell, through the expression of a number of transcription factors that could induce pluripotency . The iPSCs derived in this way can be differentiated into dopaminergic neurons using protocols similar to those used with ESCs, which could serve as the basis of a useful cell-based treatment for PD . The potential advantage of iPSC-derived over ESC-derived grafts is that it would be possible to generate autologous grafts, by using a patients own fibroblasts to produce a neural grafting product, negating the requirement for immunosuppression that will be necessary with ESC-derived grafts. However, there are other biological and logistical challenges faced with the iPSC approach, which are discussed below.
iPSC-derived neural grafts have been trialed in primates with MPTP-induced nigral toxicity, with promising results . The neural progenitors grafted ultimately extended neurites into the striatum, did not form any tumors, and resulted in improved motor function at two years. As with the ESC-approach, clinical trials in humans are on the horizon and will begin in the next couple of years .
The Challenges Of Hmsc Cell
Previous clinical studies using MSCs in the treatment of PD in humans have provided promising preliminary data. In an open-label study in 2010, autologous bone marrow -derived MSCs with a dose of 106 cells per kilogram body weight were stereotactically administered unilaterally into the sublateral ventricular zone in seven patients with PD. Three patients were reported to have improved PD symptoms. In 2012, the same research group started another open-label study using allogeneic BM-derived MSCs with a dose of 2×106 cells per kilogram of body weight and stereotactic administration bilaterally into the sublateral ventricular zone into eight patients with PD and eight with advanced symptoms of PD recognized as PD plus. The group reported persistent improvement of symptoms in PD patients and transient improvement of symptoms in PD plus patients.
Currently, seven clinical trials using MSCs for PD treatment are in progress with highly variable set up . There is a distinct lack of consistency between clinical trials, such that these studies are difficult to compare with one another in order to pinpoint what needs to be improved upon in future studies. In the following sections, we highlight the sources of variability in MSC-based PD therapy in an effort to draw attention to the need for increased standardization in this field.
Table 2 Clinical studies involving MSC therapy in Clinicaltrials.gov website.
Read Also: When Was Michael J Fox Diagnosed With Parkinson’s
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies For Neurodegenerative Diseases
While there have been significant advances in the symptomatic management of these diseases that improve quality of life and at times survival, the available medications likely only slow the progression of neuronal death by a few months. The idea of using cell therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases has been around for decades, most notably in Parkinsons Disease where a variety of cell transplant investigations have been performed with success.
According to a recent study conducted by Nathan P. Staff et al,
The precise mechanism by which MSCs may exert beneficial effects in neurological disease is still being elucidated, but it appears that multiple different mechanisms may contribute. First, MSCs have been shown to secrete neurotrophic growth factors, including glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor , vascular endothelial growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor ,which can be further enhanced under specific culture conditions.Neurotrophic growth factors have been shown to improve neuronal survival in a number of preclinical models of neuron injury, including ALS, PD, and MSA transgenic animalsand nerve injury models. â Second, MSCs strongly modulate the immune system and can aid wound healing, and this mechanism has been exploited in disorders such as graft versus host disease and Crohnâs disease. From a neurodegenerative perspective, it has become increasingly recognized that neuroinflammation plays a significant pathomechanistic role.
