How To Deal With The 6 Common Causes Of Leg Pain In Pd
Severe leg pain is a common complaint from people with PD. Lately, it is understood that central pain is common to Parkinsons disease, and can even be the first sign of PD, usually bilaterally. This blog post lists six causes of lower limb pain, and the importance of treating it. Treatments depend on properly identifying the source of pain. Some treatment suggestions are included.
Opening The Medicine Box In The Mind: The Psychology Of Pain
In this 50-minute lecture, Beth Darnall, PhD explains how our experience of pain goes beyond the physical sensation of pain. It has emotional and psychological components that affect our ability to treat pain. She cites research to demonstrate that and shares 13 specific tips to reduce the experience of pain and increase treatment effectiveness. Audience questions follow the lecture.
The Nervous System And Parkinson’s Disease
the hands and fingers, and their use or lack thereof, have key roles either in the rate of degeneration or in progressive symptom reduction. Indeed, if you’ve ever seen one of those grotesque renderings of how the human body is actually represented by the proportion of brain power devoted to each body part , the hands come out as absolutely massive – hands and neurology are very strongly linked!
Therefore hand exercises and finger stimulation are critically important for preventing the ravishes of neuronal atrophy in PD, and also to strengthen “para-sympathetic tone”, enhancing the ability to maintain a relaxed state, so important for people affected by the disease. Indeed, the story of Chris Lacey is intriguing, with reports he is now free from PD symptoms after intensive carving of chess pieces as a hobby.
The importance of hands and fingers is hence profound for those of us who have been diagnosed with chronic disease.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Strengthening Exercises Or Stretching May Be Helpful
Imagine that the spine is like a telephone pole or the mast of a sailboat. If the pole is not exactly upright, even a slight tilt requires a great force to keep it from tilting further and falling. In the human body, this means that the lower back muscles are under great stress. It also means that the tension on the back bones is much increased as well. This worsens whatever problems, like arthritis, that are already present. The same process applies to the neck, although the forces are less great. Strengthening exercises or stretching may be helpful. Almost everyone over the age of 60 has arthritis in their spine. Luckily most dont have pain from it, but those who do will have it worsened by the spine curvature caused by the PD.
PD patients also frequently have an aching discomfort in their muscles, particularly in the thighs and shoulders. I think this is due to the rigidity, or stiffness, that is part of the Parkinsons Disease syndrome, but Ive seen many patients with this pain and no apparent stiffness on examination, hence not explained. It is common and it often, but not always, responds to alterations of the usual Parkinsons Disease medications for movement. Exercise and stretching may be helpful as well and should always be tried first before increasing medications.
Pain is a challenge in PD. We cant measure it and often cannot find its cause. It is, however, often treatable, and reducing pain improves quality of life.
Pain In Parkinson’s Disease
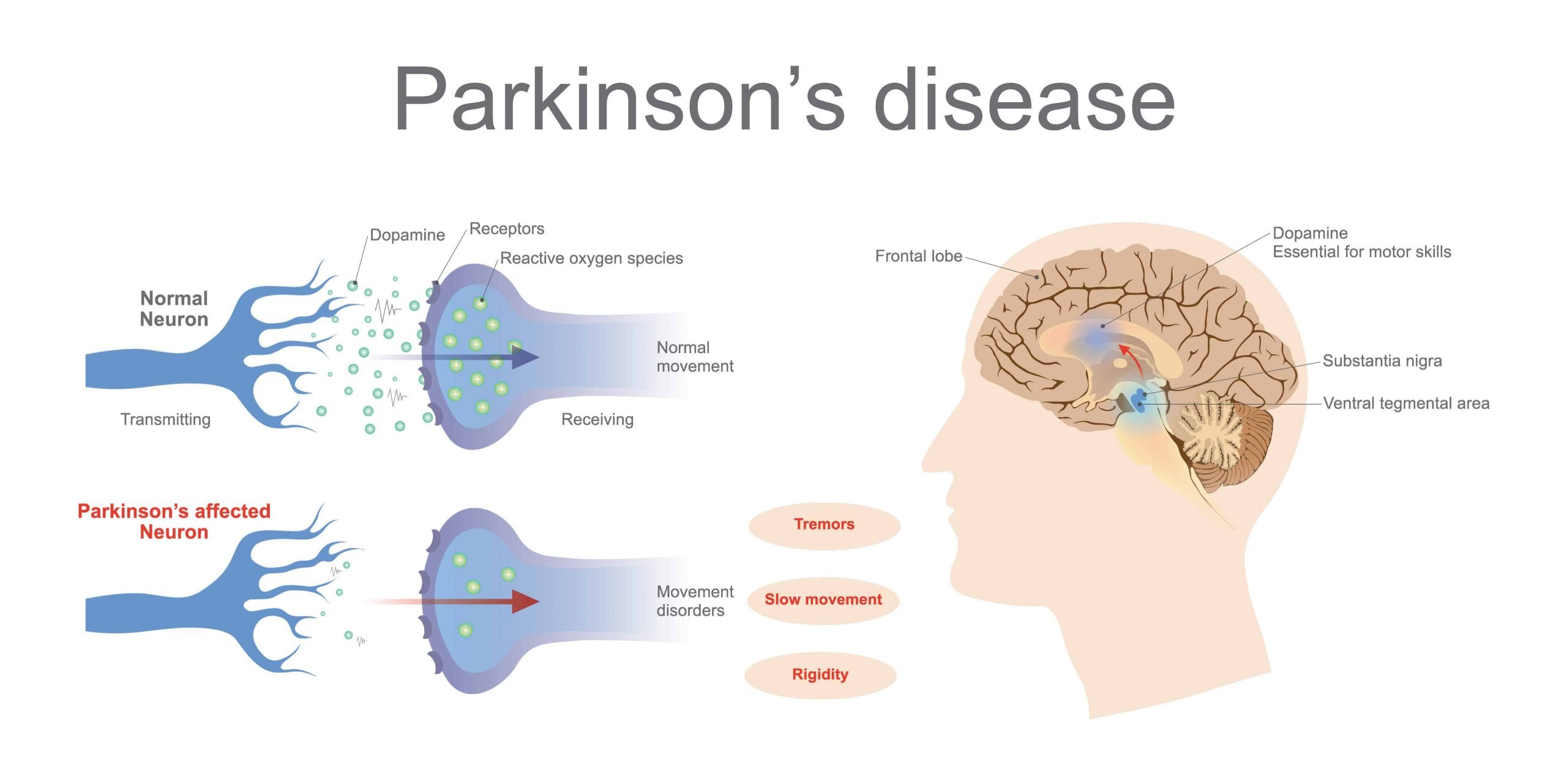
Doctors categorize pain as nociceptive, which refers to pain from tissue damage, or as neuropathic, which refers to pain that arises from the nerves. Some pain is both nociceptive and neuropathic. Most people with PD experience nociceptive pain.
This type of pain is generally localized to a specific area of the body. The most common areas for people with PD to experience pain are the neck, upper back, and the extremities . Neuropathic pain is less common in PD, although it may be caused by akathisia, an extreme restlessness.1
The pain caused by PD can generally be classified by one of five causes:
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Parkinson’s Medication Cost
Approaches To Pain Assessment
When assessing pain in patients with PD, using a validated pain scale that targets symptoms specific to PD whenever possible will more accurately categorize pain type. The first pain tool designed specifically for patients with PD is the Kings PD Pain Scale .4,12 This scale has 14 questions that measure severity and frequency of different types of pain specific to PD. A complementary patient screening tool, the Kings College PD Pain Questionnaire , is designed for assessing whether or not specific pain types are present. All questions on the KPPQ correspond with a specific question on the KPPS. Screening patients with the KPPQ can facilitate identifying pain types that correspond to the KPPS assessment tool.
If unable to assess pain with scales specific to PD, validated general pain scales, such as the Likert scale, can be utilized to determine quality and severity of any type of pain.18 Using PD-specific pain scales may better characterize a patients pain symptoms, however, which may lead to more targeted treatment options.
Social Engagement And Parkinson’s Disease
See the groundbreaking work of Dr Stephen Porges to understand more about this aspect of our Nervous System and its role in wellness and disease, based on the fact that mammals have a more evolved part of the Nervous System specifically designed for purposes of Social Engagement and Social Co-operation.
Social Engagement involves mainly the Cranial Nerves and their use in social functions such as making sounds and vocal calls for communication, and in facial expressiveness for transmitting emotional states to each other. Dysregulation of this Social Engagement part of our NS seems now to be a principal underlying cause in many chronic conditions, especially in PD, where loss of voice and loss of facial expression are major symptoms. See
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
What Causes Pain In Cases Of Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers
Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers may present with various combinations of back, buttock and leg pain, numbness and muscle weakness, Symptoms are often aggravated by an abnormal asymmetrical gait arising from loss of spatial awareness muscle spasm and loss of limb control. The back pain may arise from irritation within the disc wall but more commonly arises from the pinching of the trapped nerve in the exit doorway from the spinal column. The foramen may be distorted and the nerve is tethered by years of scarring reaction to repetitive bruising, can not evade the pinching by the bulging distorted disc wall or overriding facet joints . The disc may be degenerate and bulging and contribute to the irritation of the tethered nerve. When advanced the compression causes numbness and weakness to develop. The patchy weakness or spasm of the muscles controlling the spinal segments results in asymmetrical loss of control or stiffness of the disc levels and aggravation of the effects of the local pathology at each level and aggravation of symptoms arising at these levels.
Pain: Does Parkinsons Cause Pain Or Does Pain Make Other Pd Symptoms Worse
Is pain a symptom of Parkinsons?
Or do the motor symptoms of PD directly or indirectly cause pain?
Or is pain a symptom of something else? Arthritis? Aging?
Or is pain a result of lack of exercise? Over exercise? Improper exercise form? Improper exercise instruction? Some combination of factors?
Those are interesting questions, but more importantly does pain contribute to the severity of other Parkinsons symptoms?
Is pain a symptom of Parkinsons? If it is, is it a motor symptom or a non-motor symptom?
Do the motor symptoms of PD directly or indirectly cause pain?
Or is pain a symptom of something else? Arthritis? Aging?
Or is it a result of lack of exercise? Over exercise? Improper exercise form? Improper exercise instruction? Some combination of factors?
Does pain contribute to the severity of other Parkinsons symptoms?
If youre looking for a conclusive answer, Ill save you some timethere is no single answer, because pain, like Parkinsons, is as unique to an individual as a fingerprint.
Doctors know that people with Parkinsons experience pain. Estimates of people with PD who experience pain range from between 40% and 85% in various studies of the topic. This significant disparity is most likely due to variances of what qualifies as pain, and how questions about pain experience are worded, as pain can only be reported and measured by the individual experiencing it.
Ranking of the ten most bothersome PD-related symptoms :
| Rank | |
|---|---|
| 3 | 8 |
Additional recommended reading:
Also Check: Tardive Dyskinesia Prognosis
What Is Wrong With Conventional Surgery
The use of multi-level open surgery in Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers including microdiscectomy, decompression, solid or flexible fusion and is an overkill with negative side-effects including blood loss, potential nerve and tissue damage, extended post-operative care and unnecessarily operating on pain-free levels is fraught with aggravation of the current symptom status. It is not as effective as Foraminoplasty in addressing and ameliorating the effects of Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers, rather it runs the risk of increased neurological complications as well as causing the complications of recurrent disc bulging, infection, nerve damage and scarring round the nerve, implant failure, major vessel damage or sexual dysfunction.
Treatment Depends On Properly Identifying The Type
If pain is bilateral always assume it is central pain pain due to PD. In my experience Azilect works great for this type of pain. Other medications which can be employed for this pain as well.
Massage therapy works for all types of leg pain-my favorite therapy but can be costly. Water therapy may also work for all types except central pain. Physical therapy can alleviate dystonia pain, as well as musculoskeletal and radicular pain.
If pain is due to dystonia related to levodopa intake, find out when it occurs—end of dose or at peak dose. Typically adjusting medication doses will resolve problem. However, if dystonia is an initial symptom of PD, initiating treatment with levodopa will resolve. If medication adjustment does not work well for levodopa induced dystonia, another treatment option is DBS . Pain due to dystonia independent of cause can also respond well to Botox injections, as well as centrally acting muscle relaxants. To avoid and alleviate pain caused by stiff muscles, a great treatment option is activity in the form of stretching exercises—any number of activities will do such as tai-chi or yoga. For me when I start having radicular pain shooting down my leg it is time to up my levodopa dosage.
If you are having leg pain make sure to discuss it with your physician.
Don’t Miss: Bryant Gumbel Health Parkinson
Complementary Treatments For Back Pain
Massage therapy and acupuncture are two complementary treatments that are often used for pain. There have been small studies investigating the use of massage therapy and acupuncture for motor symptoms of PD, but more studies are necessary to s determine if they specifically help with PD pain. You can also view a Q+A about complementary treatments in PD.
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Read Also: Parkinson Facial Expression
Pain Management In Patients With Parkinsons Disease: Challenges And Solutions
This review focuses on the diagnosis and management of Parkinson-related pain. It reviews the incidence and prevalence of PD, general pain and PD-related pain, the pathophysiological pathways of pain in PD, physiological pathways of pain relief, measurements of pain, clinical diagnosis of PD-related pain, and treatment strategies.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Im In Pain But I Dont Want To Take Carbidopa/levodopa Yet Because My Doctor Says It Will Only Work For Five Years Any Advice
It is true that as time passes and your disease progresses, you will have to take higher doses to replace the dopamine your body can no longer produce. However, the rate of dopamine loss is different for everyone. What your doctor may be telling you is that after taking carbidopa/levodopa for some time, you may begin to experience side effects like dyskinesia. It is important to understand that while you may experience this unwanted side effect, for example, you still benefit from the carbidopa/levodopa. If you believe your pain is Parkinsons-related, and you have already tried other medications and complementary therapies without relief, it is probably time to try carbidopa/levodopa.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Mitochondrial Dysfunction
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Types Of Parkinson’s Pain
Most of the time, discomfort in muscles and joints is secondary to the motor features of Parkinsons lack of spontaneous movement, rigidity, and abnormalities of posture what is known as musculoskeletal pain. The most commonly painful sites are the back, legs, and shoulders and it is usually more predominant on the side more affected by parkinsonism.
But there are many other categories of pain associated with Parkinsons disease. Radicular or neuropathic pain is experienced as a sharp pain that can start in the neck or lower back with radiation to arm or leg respectively and is often associated with numbness or tingling, or a sensation of coolness in the affected limb. It is usually secondary to a pinched nerve due to something like a slipped disc.
Dystonia related pain occurs as its name suggests, at times of dystonia most often experienced in the foot, neck or face and arm at different points in the dosing schedule, particularly the off phase when there is not enough dopamine replacement but can uncommonly also occur at peak-dose times. It can be one of the most painful symptoms those with Parkinsons can face.
Akathisia pain is experienced as restlessness, a subjective inner urge to move, an inability to stay still and the inherent feelings of discomfort that it brings. It is primarily experienced in the lower limbs and can often be relieved by walking around.
Read Also: What Is Life Expectancy Of Parkinson’s Patients
What Is Special About Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers
Parkinsons Syndrome is a condition where the important nuclei below the brain become dysfunctional resulting in impaired communication and transmission of nerve impulses to and from nerve fibres throughout the body. Consequently some cognitive processes, eyesight focus, muscle control or strength may deteriorate. This often presents in a haphazard fashion with increasing stiffness of the joints and muscles and intention tremor most noticeable in the hands. Fine movements and writing ability deteriorate, The gait deteriorates as seem as a shuffling pattern with small steps with a quickening of gait as power is mustered and spasm is overcome, Whilst there is a downhill trend the process of deterioration may arrest for periods.
Seldom does this process directly generate nerve pain such as sciatica. Back or Neck pain and pain referred in to the arm or leg may arise in Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers as part of the Degenerative Disc Disease seen in the rest of the population and with the same pathologies disc protrusions, nerve entrapment / scarring / tethering, Lateral Recess Stenosis, Axial Stenosis, Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis, vertebral slippage, Instability, Failed Back Surgery or failed chronic pain management.
Q Are There Any Alternative Therapies That Are Effective For Pain In Pd
Dr. Fleisher: Although alternative therapies may be helpful, there is little evidence-based research to support their use. Certainly massage therapy, anecdotally, seems to be helpful for managing pain. Small studies suggest that acupuncture might improve sleep in patients with PD, but data on the effects on pain in PD is lacking. Larger, more well-controlled and reproducible studies of these therapies are needed.
Patients frequently ask about the effects of medical marijuana in managing PD, including pain symptoms. Several studies have looked at efficacy of marijuana in PD and have found that it probably is ineffective for most PD symptoms.11 However, we just dont have enough evidence to know for sure. The most rigorous study of medical marijuana in PD showed a trend toward worsening tremor.11,12
For most people, stress and anxiety worsen tremor, and anything that relieves anxiety will improve tremor. Thus, modalities such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness training will improve tremor. Similarly, medical marijuana may improve tremor in certain people by temporarily reducing anxiety and stress, but the evidence has not borne this out yet.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinsons Deadly
