The Route To Better Walking
The good news for people with PD is that with exercise and physical therapy it is possible to cope better with freezing, turn and walk more normally and improve balance. Through practice and sessions, a physical therapist can help people with PD avoid tripping by helping them learn to take larger steps. Additionally, joining an exercise class tailored to people with PD can help. If you take levodopa, be sure to exercise while it is working the drug helps your body learn and remember motor skills.
Tricks that can help overcome freezing:
- Walk to a regular beat to help prevent freezing. Try a metronome.
- Take large, voluntary marching steps.
- Step over an imaginary line or laser pointer.
- Work with a therapist to find the solution that works best for you.
People respond differently to audio, visual or sensory cues. Dr. Horak and her team are testing a device that provides sensory feedback vibration on the foot to stimulate automatic stepping.
Another consideration for people who have freezing is anxiety, a common PD symptom. People who have anxiety experience freezing more often. It is a vicious circle being anxious about freezing can trigger it. Treating anxiety may help freezing.
Does Parkinsons Affect Voice
The voice is affected too, because the voice box is ultimately controlled by the basal ganglia as well. Thus the voice becomes soft, slurred and hushed. Others may comment that the patient is mumbling. The mumbling goes away temporarily once the patient becomes aware of it but soon returns to the soft, slurred state.;
This temporary improvement when attention is paid is true of many of the motor symptoms of PD because the condition primarily affects subconscious movements, and does not directly affect nerve or muscle control at the most basic level. Thus, conscious awareness can override the slowness to a certain extent. This fact is one reason why physical therapy and physical activity are so useful and necessary in treating PD.
- Slowness of walking and other movements
- Trouble with dexterity
- Reduced arm swing or stride length
- Delayed reactions physically
- Reduced facial reactions
- Softer or slurred speech
- Tremor in one or both limbs with the limb at rest
- Sometimes also tremor with holding a posture or with actions
- Usually asymmetric
Imbalance, loss of balance reflexes
- May fall backwards
What Area Of The Brain Does Parkinsons Disease Affect
affecting GI tract, These exist in various combinations across patients andHow Parkinsons progresses Parkinsons disease gradually affects an area in the brain called the basal ganglia, Its cardinal motor signs are tremor, where chemistry alterations in the brain occur .How Does Parkinsons Disease Affect the Brain?Live, but did you also know that this leads to an accumulation of alpha-synuclein, It is a progressive disease and in late-stage Parkinsons
You May Like: How To Treat Parkinson Disease Naturally
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
How Parkinson’s Affects The Nervous System
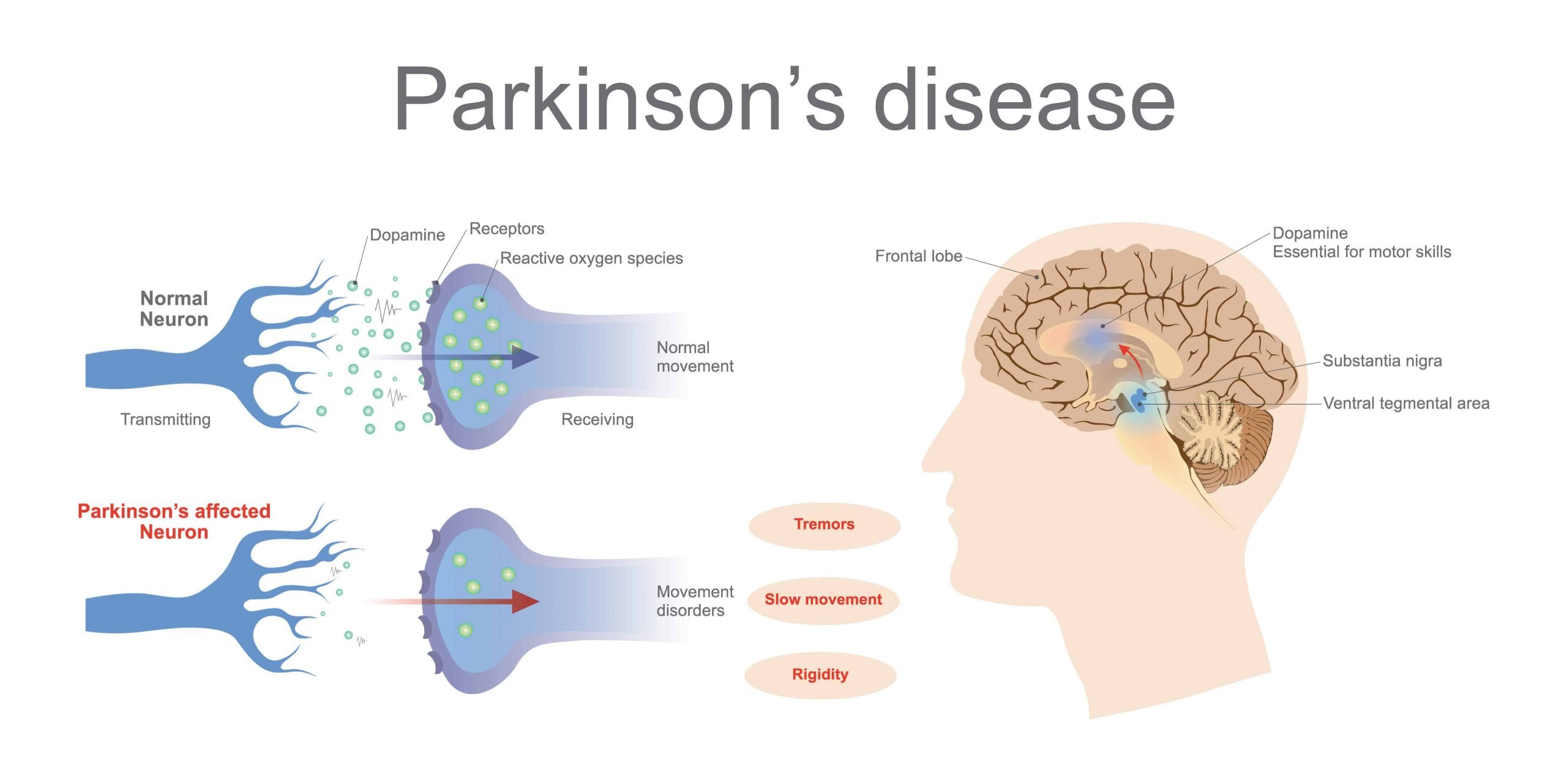
Parkinson’saffects nerveNerve
It has long been understood that Parkinson’s disease does not just cause movement symptoms, but also causes a litany of non-motor symptoms with effects throughout the body. One of the organ systems that is affected is the cardiac system, encompassing the heart, as well as the major and minor blood vessels.
Secondly, what are the changes to the brain caused by Parkinson’s disease? The brain changes caused by Parkinson’s disease begin in a region that plays a key role in movement, leading to early symptoms that include tremors and shakiness, muscle stiffness, a shuffling step, stooped posture, difficulty initiating movement and lack of facial expression.
Similarly one may ask, does Parkinson’s affect your spine?
Low back pain and back of the neck pain are probably the most common pain conditions in PD. The reason Parkinson’s Disease patients have so many problems with their low back and their neck is their posture. Because of the stooped posture, the muscles in the lower back have to pull much harder to keep the spine upright.
Does stress cause Parkinson’s?
Research suggests that stressful life events may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease. In addition, animal studies indicate that stress damages dopamine cells, resulting in more severe parkinsonian symptoms. In humans, acute stress can worsen motor symptoms, including bradykinesia, freezing, and tremor.
Read Also: Does Lack Of Sleep Cause Parkinson’s
The Cerebellum As A Target For Parkinsons Disease Treatment
While cerebellar dysfunction might contribute to some motor and non-motor signs in Parkinsons disease, a possible approach for treating parkinsonian symptoms is to attempt to normalize cerebellar function. Surgical treatment, such as deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus improves the motor signs and normalizes cerebellar activation. Levodopa administration can also normalize the activity and connectivity in the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit . However, whether it is reduced compensation or alleviation of pathological impairment as a consequence of effective treatment remains unclear. Suppressing cerebellar activity should theoretically answer the question: improvement would mean that the cerebellum is contributing to the manifestations; worsening would mean that the cerebellar activity is compensatory. We suppose that if the main efforts of the cerebellum in Parkinsons disease are compensatory, suppression of cerebellar activity should be accompanied by further impairments of Parkinsons disease symptoms.
Can You Protect The Brain From Further Damage
The goal of the treatment is to improve the patients quality of life and slow progression of the disease. There is still no cure for Parkinsons disease, but it can be very well managed. However, there are several ways that anyone who is diagnosed with Parkinsons disease can help protect their brain and mitigate the damage that has occurred.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
The Cerebral Network Underlying Parkinsons Tremor
The occurrence of resting tremor in PD is probably related to the death of SNc dopamine-containing cells. PD tremor mainly involves dysfunctions in the system formed by the motor cortex, cerebellum, thalamus, and basal ganglia. Patients with tremor-dominant PD show an increased functional connectivity between BG and the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit. This evidence suggests that PD tremor may result from a pathological interaction between BG and the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit . However, the specific mechanisms underlying such pathological interaction are still widely debated.
Support for our corticalsubcortical circuit hypothesis underlying tremor comes also from analysis of the tremor-related activity in the areas considered in . Overall, on the methodological side this analysis shows how a system-level perspective is needed to disentangle the complex involvement of different neural circuits in the production of PD tremor.
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Brain
The Parkinson’s disease brain stops producing dopamine cells, which in turn causes problems with movement and coordination known as motor symptoms. We all have a basic understanding of how Parkinson’s disease affects the brain, but what really happens when someone has Parkinson’s disease? Let’s explore the facts surrounding the Parkinson’s disease brain and how it differs from a normal, “healthy” brain.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
The Neural System Underlying Pd
To illustrate with specific cases the utility of the proposed perspective to better understand proximal causes of PD, in this section we explain how three partially overlapping corticalsubcortical circuits may underlie three important PD symptoms. shows some key components of the BGCtxCer system that are important to study the three symptoms. The schema is not exhaustive of all the possible connections between basal ganglia, cortical, and cerebellar areas. Rather, it focuses on the connections that may have a major role in the three PD symptoms considered here. This is the reason why, for example, the figure indicates SMA/pre-SMA as the only sources of the hyperdirect pathway from cortex to STN, omitting the projections from M1 to STN. The same considerations hold for the , , , which are derived from . The other pathways not considered here might have roles in other aspects of PD symptoms.
Figure 2
Also Check: Life Expectancy Of Parkinsons
What Is Happening To The Body
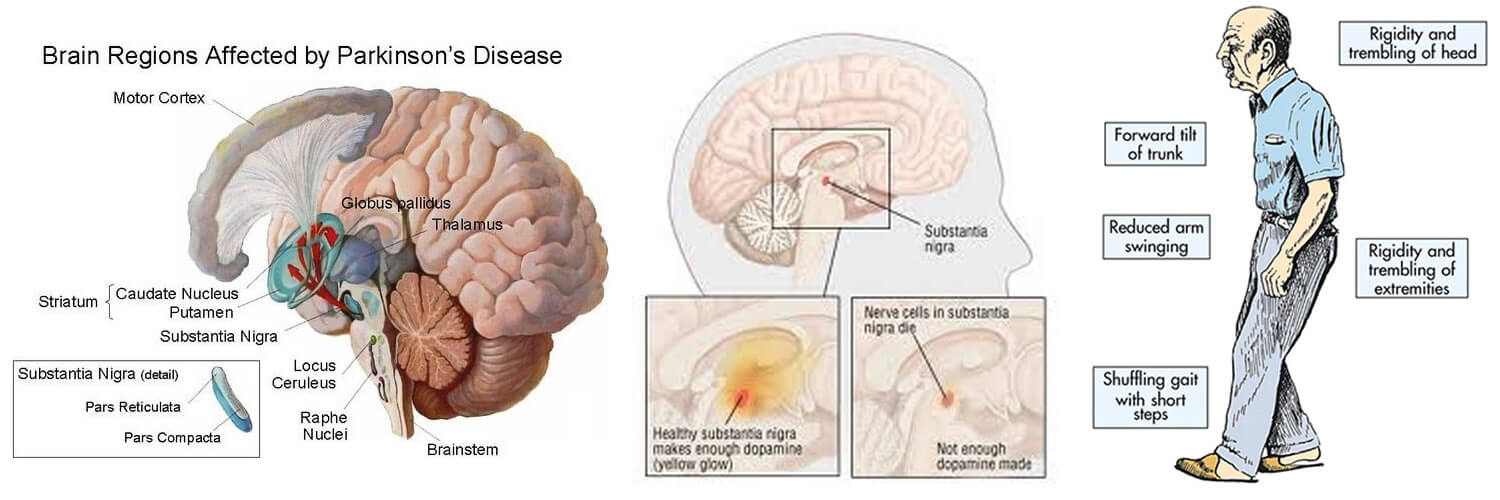
Parkinsons mainly affects a part of the brain called the substantia nigra pars compacta. In this part of the brain, neurons are producing dopamine, which transmits signals to other parts of the brain. When Parkinsons occurs these neurons are damaged which reduces the amount of dopamine produced. The decrease in dopamine is causing the movements to be slower and less smooth. These side effects are seen in the movement of the face and mouth muscles, which is how speech is produced.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Why Does Parkinsons Disease Affect My Speech
Parkinsons Disease damages part of your brain stem that controls automatic movements.
It is important to remember that Parkinsons Disease does not affect the rest of the brain, known as the cortex, which is used for your deliberate movements and thought processes.
Therefore, if you can understand how your automatic movements have changed with Parkinsons Disease, you can use this knowledge to devise deliberate ways of compensating, which can help you return to using normal movement patterns.
This blog explains how Parkinsons Disease affects your automatic speech movements and what you can do about it by using the deliberate thinking part of your brain. The good news is Parkinsons Disease does not affect your intelligence!
How Are We Using Stem Cells To Understand And Treat Parkinsons Disease
Stem cells are being used in multiple ways to understand the disease process and find new ways to potentially treat PD. By using stem cells in the lab to either model the disease by studying the affected neurons under the microscope or make healthy neurons to transplant into patients to replace the cells lost to the disease, stem cells are helping scientists discover new clues about how the disease is triggered and how it might one day be treated.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
How Does Parkinson Affect The Nervous System
What Is Parkinsons?Parkinsons Effect On The Nervous System And Dopamine.The Two Types Of Parkinsons Related To The Nervous Systemdistinct subtypesAutonomic Nervous System And Parkinsons
How To Keep Your Nervous System Healthy?Here are some important recommendations:
Read Also: Life Expectancy For Parkinson’s Disease
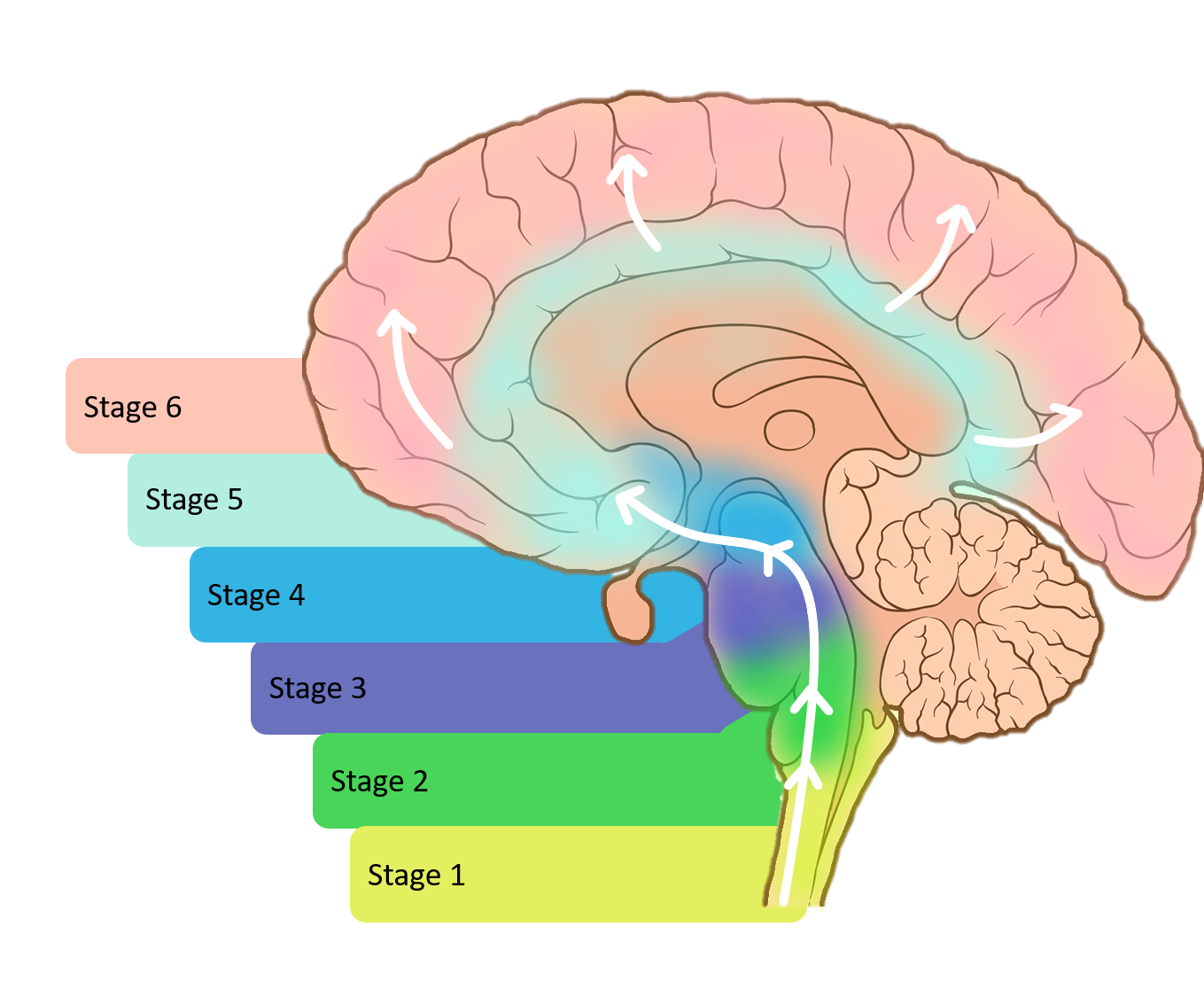
The Spread Of Parkinsons
Researchers have found that areas of the brain stem below the substantia nigra show cell loss in Parkinsons. And cells in these areas have been found to contain clumps of alpha-synuclein protein, which may form before those in the substantia nigra.
These findings have led some researchers to suggest that Parkinsons spreads up the spinal cord to the substantia nigra. Indeed, there is evidence that, for some, Parkinsons may start in the gut and travel up the vagus nerve, which connects the gut and the brain, to the substantia nigra.
The theory that Parkinsons may spread up the brain stem and progress throughout the brain is the basis of the Braak staging of Parkinsons.
The 6 stages in Braaks theory aim to describe the spread of Parkinsons through the brain:
While there is still some debate over the origin of Parkinsons, and even competing and more complex theories about the spread of Parkinsons, attempts to understand how and why different areas of the brain are involved in the motor and non-motor symptoms are helping in the development of better treatments.
Who Gets Parkinson’s Disease
About 1 million people in the United States have Parkinson’s disease, and both men and women can get it. Symptoms usually appear when someone is older than 50 and it becomes more common as people get older.
Many people wonder if you’re more likely to get Parkinson’s disease if you have a relative who has it. Although the role that heredity plays isn’t completely understood, we do know that if a close relative like a parent, brother, or sister has Parkinson’s, there is a greater chance of developing the disease. But Parkinson’s disease is not contagious. You can’t get it by simply being around someone who has it.
Also Check: Life Expectancy Parkinsons
Structural Changes In The Cerebellum
With the deformation-based morphometry method, revealed significant contraction in the left cerebellum in patients with early-stage Parkinsons disease compared with control subjects. Using the voxel-based morphometry method, found that in patients with mild-to-moderate Parkinsons disease with and without resting tremor, grey matter volume is decreased in the right quadrangular lobe and declive of the cerebellum in Parkinsons disease with tremor compared with those without. Other studies also found cognitive- or olfactory-related structural changes in the cerebellum in patients with Parkinsons disease. Therefore, there are specific Parkinsons diseaserelated morphological changes in the cerebellum.
Is There A Cure For Parkinsons
Theres currently no cure for Parkinsons, a disease that is chronic and worsens over time. More than 50,000 new cases are reported in the United States each year. But there may be even more, since Parkinsons is often misdiagnosed.
Its reported that Parkinsons complications was the
Complications from Parkinsons can greatly reduce quality of life and prognosis. For example, individuals with Parkinsons can experience dangerous falls, as well as blood clots in the lungs and legs. These complications can be fatal.
Proper treatment improves your prognosis, and it increases life expectancy.
It may not be possible to slow the progression of Parkinsons, but you can work to overcome the obstacles and complications to have a better quality of life for as long as possible.
Parkinsons disease is not fatal. However, Parkinsons-related complications can shorten the lifespan of people diagnosed with the disease.
Having Parkinsons increases a persons risk for potentially life threatening complications, like experiencing:
- falls
Parkinsons often causes problems with daily activities. But very simple exercises and stretches may help you move around and walk more safely.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
So What Can I Do About It
Example: plan to improve PD effects on walking indoors in a small space.
;If you originally need only 3-4 steps to move from your fridge to the sink, with the onset of PD your steps can become smaller and you may take 8-10 steps to cover the same distance. This shuffling is not due to muscle weakness, but from loss of automatic movement calibration. So, you can plan to take bigger steps by placing 4 little red dots on the floor as a reminder to take 4 normal size steps.
Speech: You can also use your conscious planning ability to deliberately take a breath before you speak and open your mouth wide enough to articulate clearly and this will return you to normal volume. There is no need to shout. You have not lost the strength to speak loudly, just the sensory integration telling you to do so.
Progress: ;At first you will feel as though you are booming your voice, so you need to use some external prompts
- You can use your family and friends to tell you when you are loud enough.
- There are also some Apps which measure decibel levels
- Daily voice warm ups
- 10 everyday sentences to practice deliberately speaking in a loud voice. Include examples of talking over background noise also examples of talking to children and pets which helps to exaggerate pitch and intonation as well as facial expression.
However, research by Ramig et al has shown that with intensive practice it is possible to recalibrate your speech at an automatic level in conversation.
Common Complications And Side
As Parkinsons disease progresses , symptoms have a knock-on effect. Deterioration and impairments in the body can lead to a variety of other health concerns that cause a person great difficulty.
As much as these potential concerns cause discomfort for a person, all are treatable with appropriate medication or therapies.
Associated complications which can arise include:
How to manage some of the more common side-effects of Parkinsons disease
The nature of Parkinsons disease progression means that the condition manifests in a variety of ways, not just in areas of mobility. Non-motor symptoms can sometimes be of more distress to a sufferer, troubling their day-to-day lives even more so than their physical ailments.
Once certain non-motor symptoms are recognised, it is easier to understand why and how they are adversely affecting quality of life, as well as gain control through appropriate treatment.
Other problems which can also be effectively managed include:
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
