How Can Stem Cells Help Heal This Condition
So, how do Parkinsons disease and stem cells relate? In a nutshell, Parkinsons disease is a degenerative condition. That means the body slowly loses ability over time in direct correlation with the nerve cells it loses. Stem cells constitute one of the viable treatments for Parkinsons disease in that they can replace those cells.
According to recent studies, transplanted cells in studies about stem cells and Parkinsons disease have shown the ability to do the following:
- survive in the brain long after transplantation
- function in similar ways to cells in much younger individuals
- produce long-term links such as that in normal, healthy brains
- grow new axons that send messages throughout the brain effectively, meaning that patients who receive the treatment can function much more normally
With these new treatments, physicians may soon have the power to restore motor function to Parkinsons sufferers, reversing the effects of the disease and eventually curing the disease completely, resulting in a normal brain with the ability to form lasting connections, memories, and thoughts.
Stem cells have another possible use as well: Researchers can use them to create effective models of the brain on which to test new drugs or therapies that may also help reduce or reverse the effects of Parkinsons disease. As with other uses of stem cells, this research is still in its early stages as well.
Ipscs As Disease Model For Parkinsons Disease
The contribution of pharmacogenomics has been heightened through the use of patient-specific iPSC lines and genetic engineering technology to manipulate them. Ever since Yamanakas discovery in 2007 that a handful of transcription factors can reprogram cellular differentiation, iPSCs have been utilized extensively in the study of neurodegenerative disease to direct patient-specific cell fate . While still limited in scope, iPSCs are currently the most robust and phenotypically similar model for PD . Mutations of consequence can now be captured in iPSC lines and directed by small molecules to a DAn fate in PD modelsall within a dish. Displayed openly, the real-time cellular effects of mutation can be physically observed and studied in tandem with control lines to limit genetic background effects of the affected individual similarly, effects of oxidative stress common to PD can also be quantified with broad clinical applications for drug screening without human side-effects. Not surprisingly, it remains difficult to physically confirm the mechanisms of neurodegeneration and neuroprotection implicated by iPSC research as patients neurons are hidden deep within the brain. These effects similarly cannot be perfectly translated into the cellular environment of PD due to some epigenetic effects of aging eliminated in reprogramming protocols.
You May Like: Parkinson Silverware
Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Regenerative medicine in the form of pluripotent stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease patients aims to restore function of the brain cells and dopaminergic cells, replenish neurochemical pathways to improve dopamine release, reactivate neural progenitor cells, grow healthy stem cell-derived dopamine neurons, and signal whole body repair in each individual patient. Although environmental factors and genetic risk factors may play a role in advanced disease, pluripotent stem cell signaling and the reparative sequelae can make a big difference.
Treatments
You May Like: Who Treats Parkinson’s Disease
The Stem Cell Infusion
The stem cell infusion will include the intravenous transplant of 300 million cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells . These cells are only administered by our Medical Director, over the course of a few hours to ensure proper circulation and maximum control over the procedure. The infusion occurs at our facility in our VIP treatment room, with a private adjacent space for resting and recuperation post-treatment.
Phase Iia Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial: Mesenchymal Stem Cells As A Disease
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| Recruitment Status : Active, not recruitingFirst Posted : August 10, 2020Last Update Posted : February 10, 2022 |
Read Also: Is Parkinson An Inflammatory Disease
Does It Work Efficacy Of Commercial Stem Cell Clinics
Commercial clinics do not as a rule publish their results in peer-reviewed journals to demonstrate to the scientific community that the treatments work. Rather, they usually rely on anecdotes from patients as proof of efficacy. Some clinics are tracking their results by measuring variables such as quality of life before or after the procedure. However, without comparing the patients to a similar group who does not receive the treatment, it is hard to know whether any improvement is due to placebo effect or to the treatment itself.
Considering A Stem Cell Transplant For Parkinson’s What You Need To Know
Imagine if there was a cure for your Parkinson’s disease? This would impact a lot of people as Parkinsons is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease. It is both disabling and therapeutically challenging. Sign me up, right? Not so fast. Stem cells are not a cure for Parkinsons disease though there are many clinics and other facilities who will administer stem cells for cash with the promise of a cure. In this weeks blog we explain stem cell tourism and help folks with the important questions to ask to stay safe.
Recommended Reading: Can Epilepsy Cause Parkinson’s Disease
They Have Alzheimers Brains But No Symptoms A New Wave Of Drug Developers Wants To Know Why
Lopezs dopamine high and the feeling that his brain and body were their pre-Parkinsons selves lasted two days. Then he was back to baseline: no worse, but no better. Still, he said, what we did was stop the deterioration. They gave me another shot at life. Without the cell implants, Lopez said, I think I would be dead now.
At the insistence of the FDA, the procedure at Cornell shot cells into only the left side of Lopezs brain: The agency said that if things went south, it would be twice as bad if Lopez had cell implants on both sides of his brain. I disagreed, Lopez said. I should have had both sides done at once. By requiring two surgeries, he said, the FDA doubled the risk and the cost.
But the first procedure didnt seem to cause harm: no infection, no tumors, no hemorrhaging, no worsening of symptoms. On March 6, 2018, another batch of dopamine cells made from Lopezs skin cells underwent a 20-minute journey from Dana-Farber, not to Manhattan but to Mass. General, which was now equipped to do the surgery. Schweitzer transplanted them into the right side of Lopezs putamen.
This time, Lopez didnt have a Lourdesian experience. No one is quite sure why, but it might be that fresher cells dont give the brain a quick dopamine hit. But they might form enduring synapses. Eventually.
Dont Miss: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
So What Are Stem Cells
Stem cells are cells that have not yet specialized in the body, meaning they have not grown to a particular type of cell with a specific function . A stem cell can become many different cell types in the human body. The process of stem cells become new types of cells is called differentiation. This process is the most important aspect of stem cell therapies, as the cells become the type of cells required for your body to heal. Stem cells are also self-replicating. This allows them to multiply into identical copies of the stem cells that have already gone through differentiation in the body. For example, if stem cells were used to treat a neurological injury, cells administered during treatment could become nerve cells, and then replicate to create exponentially more nerve cells on their own. This drastically increases the effectiveness of stem cell treatments over time.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Don’t Miss: What Is The Sign Of Parkinson Disease
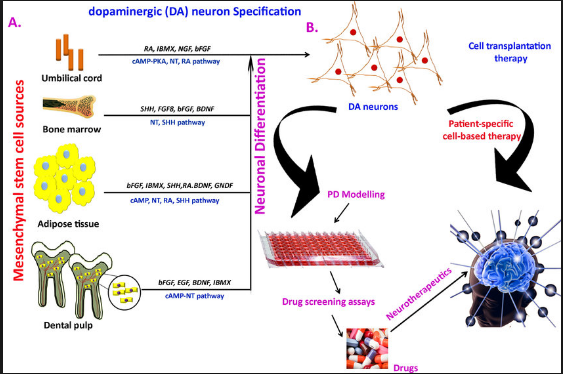
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies For Neurodegenerative Diseases
While there have been significant advances in the symptomatic management of these diseases that improve quality of life and at times survival, the available medications likely only slow the progression of neuronal death by a few months. The idea of using cell therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases has been around for decades, most notably in Parkinson’s Disease where a variety of cell transplant investigations have been performed with success.
According to a recent study conducted by Nathan P. Staff et al,
“The precise mechanism by which MSCs may exert beneficial effects in neurological disease is still being elucidated, but it appears that multiple different mechanisms may contribute. First, MSCs have been shown to secrete neurotrophic growth factors, including glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor , vascular endothelial growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor ,which can be further enhanced under specific culture conditions.Neurotrophic growth factors have been shown to improve neuronal survival in a number of preclinical models of neuron injury, including ALS, PD, and MSA transgenic animalsand nerve injury models. â Second, MSCs strongly modulate the immune system and can aid wound healing, and this mechanism has been exploited in disorders such as graft versus host disease and Crohnâs disease. From a neurodegenerative perspective, it has become increasingly recognized that neuroinflammation plays a significant pathomechanistic role.”
Stem Cells For Parkinsons: Therapy And Tools For A Neurological Disorder
This is a guest post from The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinsons Research . MJFF is committed to the pursuit of a Parkinsons cure and better quality of life for those living with the disease today. Stem cells are valuable tools in that work, helping develop new therapies and learn more about the disease. Find out more about the work they do at www.michaeljfox.org.
Parkinsons disease is a neurological disorder that affects one in 100 people over age 60. The disease causes a variety of symptoms including motor problems such as tremors, muscle rigidity and slowed movement, and non-motor symptoms of cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and autonomic dysfunction. It is estimated that nearly 1 million people in the United States and more than 6 million worldwide have Parkinsons disease. Current treatments can ease some symptoms, but no available therapies stop or slow the progression of the disease.
Scientists are using stem cells to better understand and treat Parkinsons disease.
Stem Cell TreatmentsIn Parkinsons disease , cells that make the chemical messenger dopamine degenerate and die. Introducing new dopamine cells into the brain may help replace what is lost in PD and reduce its symptoms. Such a treatment also could reduce medication side effects. Long-term use of the most commonly prescribed PD medication and progressing disease can lead to dyskinesia or uncontrolled, involuntary movements.
Recommended Reading: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Death
Giving Stem Cells Outside Of The Brain
There are a number of trials looking that the potential of using different types of adult stem cells for Parkinsons happening all over the world. One example is a phase 1/2 trial based in Texas that started in 2015. The study is using stem cells collected from bone marrow, and aims to recruit 20 participants to see if injection of these cells into the blood is safe. It will also collect results on if this type of therapy can improve movement symptoms of Parkinsons, among other measures.
Another study worth note, although not for its scientific merit, is taking a slightly different tack to getting stem cell into the body. In a rather ambitious phase 2/3 trial happening in China, researchers will attempt to give neural stem cells through the nasal track of 12 participants to see if it can cause Parkinsons to go into remission. Personally I dont hold out much hope for the success of this particular trial.
Potential of this type of therapy: Stem cells produce a range of protective factors that could help to protect brain cells and slow the progression of Parkinsons. The pros of this technique are that various types of adult stem cells such as those from bone marrow are easily accessible and the therapy doesnt involve brain surgery so would be less invasive than other therapies in this post. The cons are that these cells will be unable to get into the brain, and the lack of proximity could hamper their effectiveness.
Pluripotent Stem Cell Therapies For Parkinson Disease: Present Challenges And Future Opportunities

- 1The Center for Stem Cell Biology, Developmental Biology Program, Sloan-Kettering Institute for Cancer Research, New York, NY, United States
- 2Developmental Biology Program, Sloan-Kettering Institute for Cancer Research, New York, NY, United States
- 3Neuroscience Graduate Program of Weill Cornell Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, United States
In Parkinsons disease , there are currently no effective therapies to prevent or slow down disease progression. Cell replacement therapy using human pluripotent stem cell -derived dopamine neurons holds considerable promise. It presents a novel, regenerative strategy, building on the extensive history of fetal tissue grafts and capturing the potential of hPSCs to serve as a scalable and standardized cell source. Progress in establishing protocols for the direct differentiation to midbrain dopamine neurons from hPSC have catalyzed the development of cell-based therapies for PD. Consequently, several groups have derived clinical-grade mDA neuron precursors under clinical good manufacture practice condition, which are progressing toward clinical testing in PD patients. Here we will review the current status of the field, discuss the remaining key challenges, and highlight future areas for further improvements of hPSC-based technologies in the clinical translation to PD.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Memory
Clinical Trials For Parkinsons Disease
A search of the worlds larest clinical trial database, ClinicalTrials.gov, reveals there are at least 16 clinical trials worldwide using different types of stem cells in an attempt to find a treatment for Parkinsons disease.
Additionally, researchers from Kyoto University in Japan are conducting the a groundbreaking study for Parkinsons disease, in which the first patient has been treated with a dose of 2.4 million cells.
Conventional Parkinson Disease Therapies Vs Stem Cell Therapy
Parkinsons Disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder caused by selective and gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons. These neurons are spread throughout the brain, however, the most effected region is the substantia nigra. The symptoms of Parkinsons Disease are mainly tremor and rigor. At later stages the illness is characterized by more severe symptoms like speech disorder, depression or even dementia. Currently, there is no cure for Parkinsons disease. Nevertheless, there are few hormone replacement-based therapies which tackle the symptoms only. These pharmacological treatments are effective to control the symptoms of PD to a certain degree, with side effects, but are unable to stop neural degeneration, let alone replace dead dopaminergic cells.
Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinsons DiseaseANOVA IRM Germany, © DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00080
Stem cell research has allowed ANOVA, a German Stem Cell Clinic in the heart of Europe near Frankfurt/Main airport, to offer a novel treatment with a new therapeutical approach: The ANOVA Stem Cell Secretome is a cell free and promising treatment option for AD. , whether you wish to apply for a treatment, or simply receive more information.
Read Also: Can You Reverse Parkinson Disease
The Next Generation Of Trials
Studer was part of the initial studies involving fetal tissue in the 1980s and 1990s, and knew from the start that the work was more of a proof of principle than a solution for people with Parkinsons. For me it was clear that a fetal transplant isnt a long-term solution because of ethical, legal and practical issues. Because this procedure requires 4 to 12 fetuses per patient, there was no way they could treat thousands, let alone tens of thousands, of people that way. Instead, Studer turned to stem cells.
Immunosuppression is a particularly important element of BlueRocks approach, because it relies on a single cell line that cannot be adjusted to more closely resemble the recipients own tissues. A group led by stem-cell scientist and neurosurgeon Jun Takahashi at Kyoto University in Japan is attempting to provoke a lesser immune response by pairing transplant recipients with cells that are less likely to be rejected. The researchers are using cell-surface proteins, called major histocompatibility complexes , that are recognized by the adaptive immune system and can have varying levels of compatibility from one person to another. Rather than using frozen cell lines, Takahashi and his colleagues are creating a fresh batch of MHC-matched cells for each transplant.
Modulatory Effects Of Mscs On Pd
Recently, dysregulation of the autophagy system has been identified in the brains of PD patients and animal models of the condition, suggesting a potential role for autophagy in PD . In PD models, MSCs have been demonstrated to improve a-syn clearance and regulate autophagy-lysosomal activity . MSCs may activate autophagy signaling through upregulation of Beclin-1 , a key positive regulator of mammalian autophagy. The secretome of MSCs has been found to contain numerous components associated with autophagy signaling in cell-based experiments through induction of autophagy-related genes, including beclin-1 , Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein-like 1 and Autophagy related 12 . The secretome of MSCs drives PI3K/Akt activation and modulates different signaling pathways to improve nutrient absorption, cell growth, metabolism, and proliferation .
According to several investigations, MSCs exhibit immunomodulatory effects after infiltrating to injury sites in response to particular chemotactic recruitment and releasing numerous growth and immunoregulatory factors, so they can alleviate inflammation and improve tissue healing . Therefore, MSC-based cell therapy has been used to modulate inflammation and accommodate tissue regeneration in treating many neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative illnesses such as Parkinson’s disease .
You May Like: How Does Smoking Lower The Risk Of Parkinson Disease
Why We Believe This
Stem cells have the potential to develop into every kind of cell found in the body.
This means that stem cells could be used to treat a wide range of conditions, including Parkinsons, where new cells could be used to repair and replace damaged tissue.
Scientists have been able to turn stem cells into dopamine-producing nerve cells the type of brain cells affected in Parkinsons.
