Otros Tipos De Preexitacin: Sndrome De Lownganonglevine
Este sÃndrome ha caÃdo en desuso al no haberse confirmado su mecanismo por vÃa electrofisiológica. Actualmente es recomendable no usarlo como diagnóstico.
El sÃndrome de LownâGanongâLevine fue descrito en 1952 e históricamente se ha considerado secundario a una vÃa accesoria que une la aurÃcula con la parte distal del nodo auriculoventricular.
Esto provoca que el estÃmulo, salte el retraso fisiológico del nodo AV y estimule el haz de His de forma precoz, continuando la estimulación a los ventrÃculos por el sistema de conducción normal.
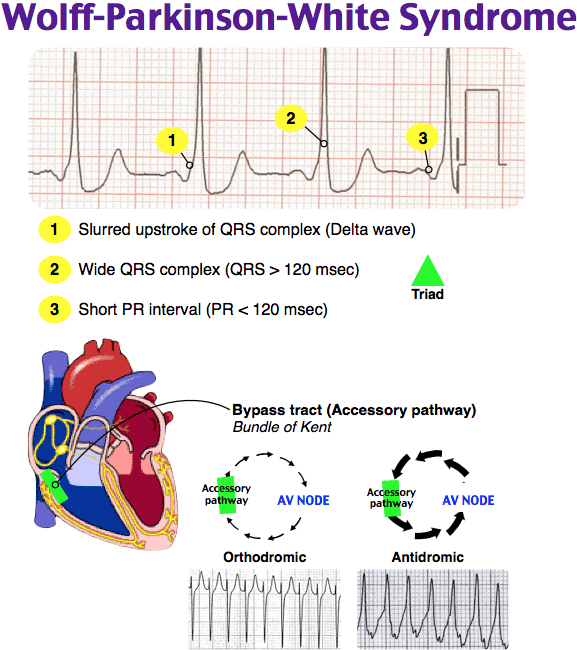
Las caracterÃsticas descritas del EKG del LownâGanongâLevine son:
Localization Of Accessory Pathways
The location of the AP can often be determined through analysis of the spatial direction of the delta wave in the 12-lead ECG by reviewing the maximally preexcited QRS complexes. A general rule is that Q waves point away from the earliest site of ventricular activation, which is typically the insertion point of the bypass tract. The most common locations for APs, in decreasing order of frequency, are the left free wall, the posteroseptal and right free wall, and finally the midseptal and anteroseptal regions of the heart.
Several algorithms are available to predict the location of the AP. These algorithms may not be totally accurate because maximal preexcitation is needed, and usually the QRS in WPW pattern is a fusion between AV node and AP depolarization , precordial lead placement may vary, as well as chest shape and size and heart shape, size, and location.
A practical concept is that a negative delta wave usually signals the location of the AP, as follows:
- A negative delta wave in a left-side lead such as I and aVL indicates a left-side AP
- A negative delta in a right-side lead such as V1 predicts a right-side AP
- An isoelectric delta in V1 predicts an anteroseptal AP
- A negative delta in the inferior leads indicates a posteroseptal AP
- A positive delta in the inferior leads predicts an anteroseptal AP
A more specific algorithm for location of the AP, based on the polarity of the delta wave or first 40 ms of the QRS, predicts the following AP locations:
Serotonin Syndrome : Symptoms Causes &
Serotonin syndrome, also known as serotonin toxicity, is a potentially life-threatening condition resulting from having too much serotonin in your body. Learn about serotonin syndrome symptoms, the medications that can cause the condition, and how it can beWebMDWebMD Better information. Better health.Treatment of atrial flutter · After atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is the most important and most common atrial tachyarrhythmia. Although it was first described 80 years ago, techniques for its diagnosis and management have changed little for decades. The diagnosis rested almost entirely with the 12 lead ECG, and treatment options included only the use of a digitalis compound to slow and control the ventricular
-
Symptoms suggestive of recurrent tachycardias in addition to the following ECG characteristics
-
Shortened P-R interval of < 0.12 s
-
Slurred slow rising onset to QRS known as the delta wave
-
A prolonged QRS complex > 0.11 s
Figure 6
BCT with delta wave.
You May Like: Can Parkinsons Be Managed Without Medication
Which Congenital Heart Disease Is Associated With Pre
Left ventricular pre-excitation was recorded in 18 cases: 8 in the lateral zone, 5 in the anterior paraseptal and 5 in the posterior paraseptal zones. WPW and congenital heart disease: Out of 20 cases of Ebsteins anomaly, 5 cases of WPW were observed: 4 right posterior and 1 right lateral pre-excitations.
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Variabilidad Del Electrocardiograma En El Wolff
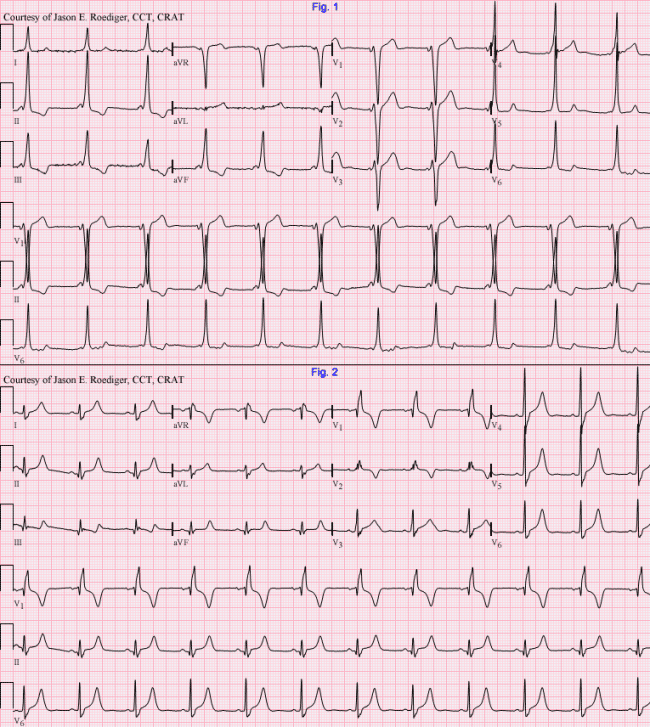
Es frecuente que el grado de preexcitación varÃe, pudiendo ser distinto en dos electrocardiogramas diferentes o incluso en el mismo EKG.
La velocidad de la vÃa accesoria es la que marca el grado de preexcitación.
A mayor grado de preexcitación, la onda delta es más marcada, el complejo QRS es más ancho y aparecen los trastornos de la repolarización.
Wolff-Parkinson-White: EKG que alterna latidos normales y otros con preexcitación .
Read Also: Why Do People Get Parkinson’s
Risk Assessment And Need For Ablation
If AF is induced during either an intraesophageal or an EPS, the shortest RR interval between two consecutive preexcited QRSs is measured. If the interval is less than 220 ms, then the risk of sudden death due to VF is believed to be high. Specifically, according to one study, the most discriminating predictor of VF in patients with WPW syndrome was the shortest RR interval during AF of 172 ± 23 ms . Those patients were considered to be at high risk for developing VF and sudden death should AF occur.
A study of asymptomatic children with WPW pattern who underwent EPS for risk stratification reported that a high proportion of subjects experienced sustained AVRT, AF, or both, with the shortest RR between two consecutive preexcited QRSs being 230-250 ms . The authors concluded that those results may be indicative of the necessity of RF ablation in all asymptomatic individuals with WPW pattern.
Pearls And Other Issues
Patients with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response are often treated with amiodarone or procainamide. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia associated with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In acute AF associated with WPW syndrome, the use of IV amiodarone may potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation in some reports and thus should be avoided.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart’s normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway.
An acutely presenting wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be ventricular tachycardia if doubt remains about the etiology.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Affect Breathing
Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular & Thoracic Institute Cardiologists And Surgeons
Choosing a doctor to treat your abnormal heart rhythm depends on where you are in your diagnosis and treatment. The following Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Sections and Departments treat patients with Arrhythmias:
- Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing: cardiology evaluation for medical management or electrophysiology procedures or devices – Call Cardiology Appointments at toll-free 800.223.2273, extension 4-6697 or request an appointment online.
- Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: surgery evaluation for surgical treatment for atrial fibrillation, epicardial lead placement, and in some cases if necessary, lead and device implantation and removal. For more information, please contact us.
- You may also use our MyConsult second opinion consultation using the Internet.
The Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute has specialized centers to treat certain populations of patients:
Are There Different Types Of Accessory Pathways
Lown, B. The syndrome of short P-R interval, normal QRS complex and paroxysmal rapid heart action. Circulation. vol. 5. 1952 May. pp. 693-706.
James, TN. Morphology of the human atrioventricular node, with remarks pertinent to its electrophysiology. Am Heart J. vol. 62. 1961. pp. 756-71.
Lev, M, Leffler, WB, Langendorf, R. Anatomic findings in a case of ventricular preexcitation terminating in complete atrioventricular block. Circulation. vol. 34. 1966. pp. 718-33.
Murdock, CJ, Leitch, JW, Teo, WS. Characteristics of accessory pathways exhibiting decremental conduction. Am J Cardiol. vol. 67. 1991. pp. 506-10.
Ross, DL, Uther, JB. Diagnosis of concealed accessory pathways in supraventricular tachycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 7. 1984. pp. 1069-85.
Anderson, RH, Becker, AE, Brechenmacher, C. Ventricular pre-excitation: a proposed nomenclature for its substrates. Eur J Cardiol. vol. 3. 1975. pp. 27-36.
Mahaim, I, Benatt, A. Nouvelles recherches sur les connections superieures de la branche du faisceau de His-Tawara avec cloison interventriculaire. Cardiologia. vol. 1. 1937. pp. 61
Also Check: Similar To Parkinsons
Also Check: How Do I Know If I Have Parkinson’s
How Is Wpw Different From Typical Avrt
The difference between this typical AVRT and the AVRT seen with WPW is that, in WPW, the accessory pathway is capable of conducting electrical impulses in both directions from the atrium to the ventricle as well as from the ventricle to the atrium.
As a result, during reentrant tachycardia in WPW, the electrical impulse is able to travel down the accessory pathway into the ventricles, then return to the atria through the AV node, then back down the accessory pathway to the ventricles again and it can keep repeating the same circuit. This is the opposite direction of travel than in patients with typical AVRT.
Definition Of Wpw Syndrome3
-
Symptoms suggestive of recurrent tachycardias in addition to the following ECG characteristics
-
Shortened P-R interval of < 0.12 s
-
Slurred slow rising onset to QRS known as the delta wave
-
A prolonged QRS complex > 0.11 s
The most frequently encountered tachycardia in WPW syndrome is an atrioventricular re-entrant tachycardia . The arrhythmia uses the AVN and accessory pathway to form a re-entry circuit triggered by an appropriately timed ectopic. This re-entry circuit maybe classified as either orthodromic or antidromic depending on whether the ventricles are activated via the normal conduction system or the accessory pathway. Orthodromic AVRTs account for most tachycardias in WPW syndrome . Conduction occurs down the AVN and retrogradely up the accessory pathway producing a narrow complex tachycardia . The QRS morphology is normal during the arrhythmia because ventricular activation has occurred through the normal pathway. The rate is usually between 140 and 250 beats per minute . Inverted P waves may be visible deforming the ST segment indicating that atrial depolarisation occurs later than ventricular depolarisation. In a patient with a narrow complex tachycardia the presence of such late P waves is frequently the only ECG evidence that the patient has an accessory pathway rather than a much more common atrioventricular nonre-entrant tachycardia .
Figure 6
BCT with delta wave.
Also Check: How Does Parkinson’s Affect You
Electrocardiographic Signs Of Pre
As the stimulus originates from the sinus node, the P wave will be normal.
In pre-excitation, ventricles depolarize from two different points: bundle of His and the accessory pathway.
Usually the depolarization via accessory pathway is faster, so the PR interval shortens and a delta wave appears at the beginning of the QRS complex, causing its widening.
When a high degree of pre-excitation is present â more conduction through the accessory pathway than through the normal conduction system â the QRS complex morphology turns into that of bundle branch blocks, being widened. Alterations of the ST segment and inverted T waves also appear.
Summarizing:
- Sinus P wave, except alterations.
- Shortened PR interval .
- Widened QRS complex, due to the presence of the delta wave.
- With high degree of pre-excitation, the QRS complex is similar to a bundle branch blocks pattern and alterations of repolarization may be observed.
Wolff-Parkinson-White: shorten PR interval and widened QRS complex due to delta wave
Characteristic Features Of Wpw Syndrome
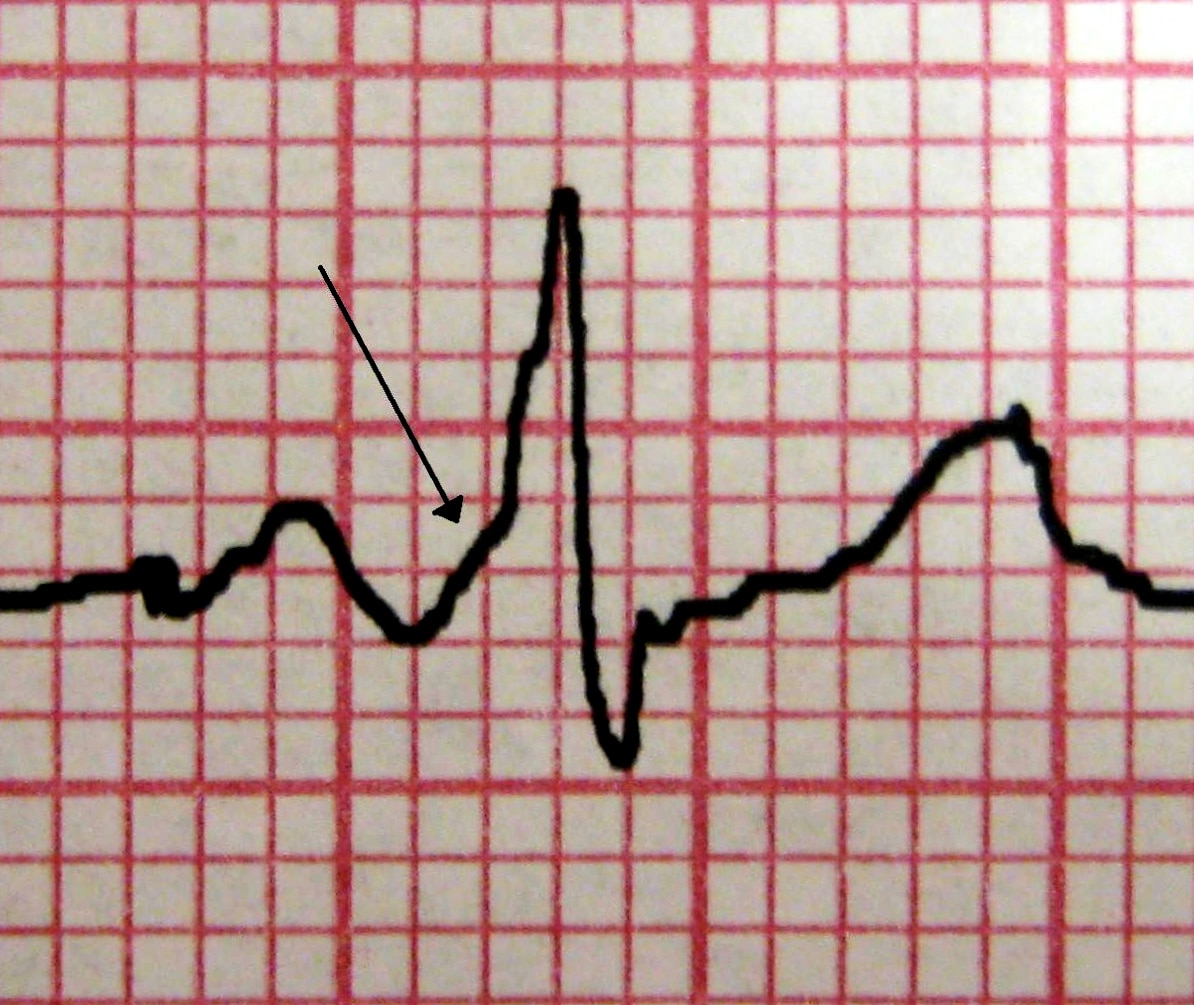
The classic ECG morphology of WPW syndrome is described as a shortened PR interval and a slurring and slow rise of the initial upstroke of the QRS complex , a widened QRS complex with a total duration greater than 0.12 seconds, and secondary repolarization changes reflected as ST segmentT wave changes that are generally directed opposite the major delta wave and QRS complex. In reality, the ECG morphology varies widely.
Depending on the location of the AP in relation to the sinus node and the relative transmission characteristics of the AP and the AV node, the morphology of the ECG may vary from a classic presentation, termed manifest preexcitation, to near normal.
In some cases, the electrical impulses arrival at the ventricles occurs slightly earlier through the AP , creating preexcitation.
The QRS interval is widened because the ventricles are initially activated via the AP, which lies outside the normal conducting system, producing an early, albeit relatively slow, initial propagation of depolarization forces through the ventricular tissue. This produces the delta wave. The delta wave makes the QRS appear wider than expected and the PR interval somewhat shortened. This is known as a manifest AP because it is easily identifiable on ECG.
An AP that does not manifest on ECG is revealed when the rate exceeds the refractory period of the AV node. This has been described as a latent AP. A latent AP can conduct both antegrade and retrograde transmissions.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Cause Insomnia
Why Wpw Is A Particular Problem
The ability of the accessory pathway in WPW to conduct electrical impulses from the atria into the ventricles is important for three reasons.
First, during normal sinus rhythm, the electrical impulse spreading across the atria reaches the ventricles both through the AV node and through the accessory pathway. This “dual” stimulation of the ventricles creates a distinguishing pattern on the ECG specifically, a “slurring” of the QRS complex which is referred to as a “delta wave.” Recognizing the presence of a delta wave on the ECG can help a doctor can make the diagnosis of WPW.
Second, during the AVRT seen with WPW, the electrical impulse is stimulating the ventricles solely through the accessory pathway . As a result, the QRS complex during tachycardia takes on an extremely abnormal shape, which is suggestive of ventricular tachycardia instead of SVT. Mistaking the AVRT caused by WPW for VT can create great confusion and unnecessary alarm on the part of medical personnel, and may lead to inappropriate therapy.
Third, if a patient with WPW should develop atrial fibrillation an arrhythmia in which the atria are generating electrical impulses at an extremely rapid rate those impulses can also travel down the accessory pathway and stimulate the ventricles at an also extremely rapid rate, leading to a dangerously fast heartbeat. So in patients with WPW, atrial fibrillation can become a life-threatening problem.
How Is Wpw Syndrome Treated
If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome, you have several treatment options, depending on your symptoms. If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome but dont have any symptoms, your doctor may recommend that you wait and continue follow-up appointments. If youre having symptoms, the treatment may include the following:
You May Like: What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson Disease
Atrial Fibrillation And Wpw
Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome have an accessory pathway or a bypass tract that connects the electrical system of the atria directly to the ventricles, thereby allowing conduction to avoid passing through the AV node.
In normal individuals, when the sinus node creates an action potential it must pass through the AV node to get to the ventricles. When an accessory pathway is present, the sinus node action potential can pass through the bypass tract before the AV node, which causes the ventricles to become depolarized quickly. This is termed pre-excitation and results in a shortened PR interval on the ECG.
The combination of WPW and atrial fibrillation can potentially be fatal, especially if AV blocking agents are given . The medical treatment is procainamide, although electrical cardioversion is reasonable, especially if hemodynamically unstable.
In patients with WPW and atrial fibrillation, the erratic atrial action potentials can conduct through the accessory pathway very quickly . Therefore, WPW patients who develop atrial fibrillation have higher ventricular rates than those without WPW. If an AV blocking agent is given, fewer atrial action potentials will pass through the AV node and more will pass through the accessory pathway, paradoxically increasing the ventricular rate potentially causing ventricular fibrillation which is a fatal, hemodynamically unstable rhythm. Procainamide or electrical cardioversion is recommended in these situations.
Orthodromic Tachycardia With Concealed Accessory Pathway
Some APs are unable to conduct in an antegrade fashion. These are called concealed APs, because “manifest” preexcitation is a delta wave that is visible on a surface 12-lead ECG. They account for about 30% of all SVTs induced on EPS.
Although no evidence of the pathway is present during sinus rhythm , orthodromic tachycardias can occur. Orthodromic tachycardia may also occur when there are two or more accessory connections, and in that case, the retrograde conduction may occur through the AV node, through one of the accessory connections, or through both.
This type of SVT may be difficult to distinguish from the usual AV nodal reentrant tachycardia on a standard surface ECG. In adults, if the heart rate is higher than 200 bpm or a retrograde P wave is visible in the ST segment , a concealed AP-mediated orthodromic reentrant tachycardia may be the diagnosis. However, this determination is most accurately made with electrophysiologic studies , or if SVT terminates with a single PVC. Other differentiating factors include the following :
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Cause Blindness
Deterrence And Patient Education
The dysrhythmias causing electrical abnormalities associated with WPW syndrome are a result of a congenital abnormality forming an accessory pathway. There is nothing that can be done to prevent WPW pattern. After WPW syndrome has manifested with the presentation of a tachyarrhythmia, an electrophysiologic study can be performed to map and assess risks of the accessory pathway, and catheter radiofrequency ablation of the pathway can be curative. For patients that this is not an option or preference, antiarrhythmic medications can be a reasonable alternative option.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare but dangerous condition. A high index of clinical suspicion and close attention to concerning symptoms may be crucial in making a diagnosis. Once a diagnosis or sufficient concern is established, an interprofessional approach will be necessary for further evaluation and management. This approach, paired with education and shared decision making with patients and their families, will help guide treatment plans.
It is often difficult to develop and carry out well structured and rigorous studies in rare medical conditions. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is no exception, and most of the evidence is drawn from case series and population studies. The pathophysiologic basis is well understood, and surgical or catheter ablation has been shown to be successful and low risk. In high-risk patients, ablation is the most definitive treatment, but more future studies would help delineate medical management and ablation thresholds in some low-risk patients.
Don’t Miss: Benadryl And Parkinson’s Disease
How To Manage Or Live With Wpw
There is no way to prevent WPW, but you can prevent complications by learning as much as you can about the disease and working closely with your cardiologist to find the best treatment. Ask your doctor to teach you how to do a Valsalva maneuver.
Here are helpful lifestyle suggestions:
-
Work with your doctor to keep conditions such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure under control.
-
Eat a heart-healthy diet.