Cognition In Familial Pd
Recessive forms of familial PD include those with genetic changes in the parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1 genes. These recessive forms of PD are generally characterized by early onset PD, but with a relatively slow progression of symptoms. Systematically collected data on cognition in PINK1 and DJ-1 is limited. A very atypical clinical picture with PD-D and motor neuron disease was reported in a family with a double mutation in DJ-1 and PD-D was reported in two cases with PINK1 deletion mutations., On the other hand, CI in the more common parkin mutation carriers has been examined in some detail . A comparison of parkin, LRRK2 and glucocerebrosidase mutation carriers reported no differences between the three genetic groups on performance of the mini-mental state examination, although GBA mutation carriers subjectively reported more CI. In the relatively large study, early onset PD patients that were either parkin mutation heterozygote carriers, compound heterozygote/homozygyote, or non-carriers were compared on a detailed neuropsychological test battery. There were no significant differences with regard to neuropsychological test performance amongst the three groups . Thus, in autosomal recessive forms of PD there is again a range of reported frequency of CI.
Family History & Genetics
Researchers have been able to identify certain genetic mutations that can increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.;
These are the two types of Parkinsons disease, from a genetic standpoint:
- Hereditary Parkinsons disease: Roughly 15% of all cases of Parkinsons disease are inherited. In these cases, mutations in certain genes are passed down through families and increase the individuals risk of developing this condition.;
- Sporadic Parkinsons disease: On the other hand, cases in which people dont have a family history of Parkinsons disease are referred to as sporadic cases. These cases are in fact the majority. Scientists have found that alterations in certain genes may also play a role in sporadic cases, in addition to other environmental and lifestyle-related factors.
However, the role that these genetic mutations play in the development of the condition hasnt been fully understood yet.;
The Neurochemistry Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease
Across the globe, one out of every 100 individuals over 60 are living with Parkinson’s Disease . In honour; of PD Awareness Month, we’ve decided to highlight the known neurochemistry underlying this debilitating disorder.
Connecting Symptoms to Dopaminergic Circuits
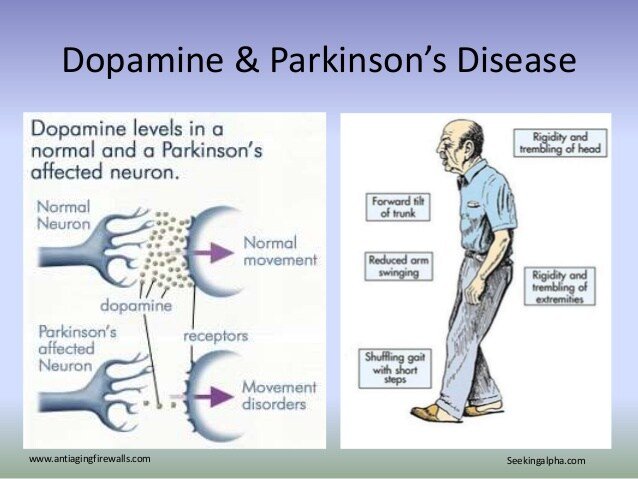
PD manifests itself in a variety of ways in different individuals, but the primary neurological marker is degenerated dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta . These neurons comprise a pathway to the ;basal ganglia, ;an interconnected set of structures in the core of the brain. The basal ganglia are involved in many different behavioral functions, but most notably movement. The dopamine in this pathway speaks to the subcortical brain areas responsible for initiating movement, therefore a lack of dopamine causes PD patients to have rigidity or akinesia. A popular treatment for PD,;L-dopa, is a precursor to dopamine, and helps make up for lost dopamine neurons.
Figure 1. Diagram of the diminished dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra as seen in Parkinsons disease. Courtesy of NIH.
A Closer Look at the Chemistry
Involvement of GABA and glutamate
Related antibodies
Important Customer Notice Regarding Covid-19 Outbreak
Moreover, we hope you and your family, friends and colleagues remain safe and well. We will keep a close monitoring of the situation and will update our efforts accordingly.
If you have any questions or concerns, please contact us.
Close
Don’t Miss: Average Life Expectancy With Parkinson’s
Ways To Boost Dopamine
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter thats great to have in abundance. When you do, your brain is flooded with pleasurable feelings and a sense of satisfaction and reward.
While increasing your natural dopamine wont prevent or stop the progression of Parkinsons disease, it might help stave off early symptoms of the disorder. For some people, natural dopamine boosts may be helpful alongside other treatments.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
Can Dopamine Be Used To Treat Parkinsons
If Parkinsons disease is caused by a drop in dopamine, it might make sense that replacing that dopamine would stop the symptoms and halt the progression of the disorder. But its not that easy.
Dopamine from a medication or injection cant penetrate the blood-brain barrier. That makes it an ineffective treatment.
An amino acid called levodopa can help increase levels of dopamine in the brain. If given as a medication, it can cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, levodopa is converted to dopamine.
Levodopa wont replace all of the lost dopamine, but it can help to reduce symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Its particularly helpful with movement control.
Dopamine In Other Diseases
It also plays a role in diseases that arenât related to mental health. One of these is Parkinsonâs disease. Another is obesity, which the American Medical Association classified as a disease in 2013.
Parkinsonâs disease. Dopamine enables neurons in your brain to communicate and control movement. In Parkinsonâs, one type of neuron steadily degenerates. It doesnât have a signal to send anymore, so your body makes less dopamine. The chemical imbalance causes physical symptoms. These include tremor, stiffness, slowness of spontaneous movement, poor balance, and poor coordination. Doctors treat these symptoms with medications that raise levels of this chemical.
Obesity. Most of the time, if you take in more calories than you burn, youâll gain weight. So why canât obese people simply eat less and slim down? The answer isnât that simple. They may face obstacles that others don’t. They could have problems with their natural reward systems. This can affect the amount of food they eat before they feel satisfied. Imaging studies suggest that in people with this condition, the body may not release enough dopamine and another feel-good hormone, serotonin.
Read Also: Yopd Life Expectancy
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms; others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
Also Check: End Stages Parkinsons
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Role In Mental Health
Itâs hard to pinpoint a single cause of most mental health disorders and challenges. But they’re often linked to too much or too little dopamine in different parts of the brain. Examples include:
Schizophrenia. Decades ago, researchers believed that symptoms stemmed from a hyperactive dopamine system. Now we know that some are due to too much of this chemical in certain parts of the brain. This includes hallucinations and delusions. A lack of it in other parts can cause different signs, such as lack of motivation and desire.
ADHD. No one knows for sure what causes attention deficit hyperactivity disorder . Some research shows it may be due to a shortage of dopamine. This problem may be due to your genes. The ADHD drug methylphenidate works by boosting dopamine.
Drug misuse and addiction. Drugs such as cocaine can cause a big, fast increase of dopamine in your brain. That satisfies your natural reward system in a big way. But repeated drug use also raises the threshold for this kind of pleasure. This means you need to take more to get the same high. Meanwhile, drugs make your body less able to produce dopamine naturally. This leads to emotional lows when youâre sober.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Awareness Color
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Severity And Timing Of Neurotransmitter Disruption

The data above suggest that the loss of dopamine occurs prior to the loss of the other neurotransmitter systems in PD, and that increased compensatory neurotransmitter activity initially occurs in regions affected by the deficit in dopamine. Whether such increased activity or a reduced compensatory capacity drives subsequent degeneration remains to be determined, but it is of interest that degeneration of the dopamine system occurs more rapidly in older compared with younger PD patients.
Also Check: What Essential Oils Are Good For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
What Is Dopamines Connection To Parkinsons Disease
For people with Parkinsons disease, dopamine levels are too low. As the dopamine starts to fall, signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease will begin to reveal themselves. That means the smooth, controlled body movements may be replaced by symptoms like tremor or stiffness in limbs. Fluid motions may become slow, shaky, and halted.
Dopamine levels may be significantly reduced by the time these symptoms are noticeable. Some of the earliest signs of Parkinsons disease arent as obvious, and they may occur years before the more significant motor problems arise. These symptoms include:
- difficulty concentrating
Read Also: Does Lack Of Sleep Cause Parkinson’s
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Acetylcholine Systems And Pd
There are three main sources of acetylcholine in the brain – striatal interneurons, cortically-projecting Ch4 neurons in the nucleus basalis, and thalamic-projecting Ch5 neurons in the pedunculopontine nucleus ., Striatal interneurons are not affected in PD, but there is ample evidence that the other neuronal groups are affected in PD., On average there is a 40% loss of Ch5 pedunclopontine neurons which correlates with the degree of degeneration in the A9 dopamine cell group, and also with the severity of motor impairment.
Acetylcholine pathways affected in PD and PD-D
The two major acetylcholine nuclei with projections to the forebrain are the nucleus basalis containing Ch4 neurons, located in the basal forebrain, and the pedunculopontine nucleus containing Ch5 neurons, located at the junction of the midbrain and pons. The pedunculopontine nucleus projects to the thalamus and is affected in PD, while the nucleus basalis projects to limbic regions and cortex and is affected in PD-D. Caud=caudate nucleus, GPe=external globus pallidus, GPi=internal globus pallidus, ic=internal capsule, OT=optic tract, Put=putamen.
Also Check: Life Expectancy Parkinson
Parkinson’s Diseasewhat Are The Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Symptoms manifest due to a malfunction of dopamine neurons
The brain is the central control tower that governs the condition of the body. Messages sent out by the brain are transmitted from one nerve cell to the next by neurotransmitters that pass the message on like a baton during a relay race, causing your body to move in reaction to the message. In Parkinson’s disease, levels of dopamine, a neurotransmitter in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra, decrease, causing a loss of control over body movement. It is still not fully understood what causes the amount of dopamine to decrease. Changes in the brain associated with age and, in some cases, changes related to a person’s genes, are presumed to be the cause. Supplementing the deficient dopamine with medication can lessen the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Also Check: Uf Cmdnr
Role Of Other Pathologies
The role of other pathologic findings in causing cognitive impairment in PD remains unclear. As the majority of PD autopsy series have a mean age of cases being >75 years old, the presence of other pathologic findings is extremely common and thus controlling for pathologic changes of aging are critical. While a recent study showed that there is a reduced prevalence of small vessel disease in PD compared to matched controls, the role of vascular changes , including infarcts, is one of the most difficult issues when studying PD-D. One study found that 8/18 PD cases had vascular changes. Lower rates were found in multiple other studies including 2/17 PD-D cases, 2/12 may have had multiple infarcts contributing to the dementia, and 5/40 PD-D cases had significant cerebrovascular disease. In a study of 25 non-demented PD and 25 PD-D cases that excluded concurrent AD or hippocampal sclerosis, PD-D correlated with a the cumulative burden of cerebral white matter disease. So the role of vascular changes remains unclear.
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy , not uncommon in aged controls, was associated with PD-D in one study. CAA had a positive correlation to LRP while vascular pathology was negatively correlated with LRP in a second study. Finally, CAA was more common in PD than controls, and was more common in PD cases with concurrent AD than those without AD.
Interactions With The Gabaergic System
Serotonin exerts a modulatory action on the effects of gamma-amino-butyric acid , which is the main brain neurotransmitter mediating inhibitory signals. Deficiency in brain serotonin results in alterations in the GABAergic system . The use of low doses of diazepam is enough to induce effects in Tph2 / mice, while they are not effective in wild type mice . At the presynaptic level, serotonin inhibits GABA release via 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors and stimulates GABA release via 5-HT3 and 5HT2 receptors. GABA-mediated effects can also be modulated by serotonin at a post-synaptic level through different receptors and mechanisms, as observed in pyramidal neurons from the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus or thalamus . In GABAergic neurons, selective 5-HT1A receptor-mediated signaling paradoxically increases c-fos expression and induces excitation in the prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons . However, the interactions are complex because serotonin also modulates other neurotransmitters. A deeper knowledge of neurotransmitter interactions will provide useful strategies for the therapy of several diseases .
Table 1. Summary reporting the major findings obtained in the different topics.
Recommended Reading: What Do Parkinson’s Patients Usually Die From
