Learning From Genetic Analyses Of Pd Casecontrol Studies
We analyzed the reports from 12 international studies,,,,,,,,,,,, totaling 5650 persons living with PD in North America, Europe, and Australia. We confirmed that globally only 15% of patients report a family history of PD symptoms, while the remaining 85% of the PD population are classified as sporadic PD . However, the distinction between genetic predispositions in familial and sporadic PD is blurry. No single-gene mutation in PD has a 100% penetrance. Instead, most likely, multiple genetic risk factors act in synergy to increase the chances of both familial and sporadic PD. Such genetic susceptibilities interplay with aging and environmental factors in both familial and sporadic PD.
Fig. 2: The genomics of Parkinsons disease: prevalence and penetrance.
a In the world-wide population of people living with PD, ~85% of PD cases are sporadic and the remaining are familial . b Genetic mutations occur at low and varying frequencies in the PD world population . Data represented as the mean±SEM. c GWAS data suggests risk variants in fPD genes tend to be less prevalent in PD cases . d Single nucleotide polymorphisms in over 44 genomic regions show significant association to PD. Each point presents an independent SNP hit associated with PD.
Understanding The Lrrk2 Mutation
People withLRRK2 Parkinsonâs disease
Most people withLRRK2 Parkinsonâs disease have one normal gene and one mutated gene. This means they have both normal LRRK2 and an overactive version. The overactive LRRK2 causes certain cells in the brain to degenerate, resulting in the development of Parkinsonâs disease.
ESCAPE Bioâs approach
ESCAPE is developing an investigational therapy that only blocks the overactive LRRK2. The therapy is intended to be taken by mouth in pill or capsule form.
The Two Types Of Symptoms Of Parkinson ‘s Disease
The Two Types of Symptoms of Parkinsons DiseaseParkinsons disease , a degenerative nervous system disorder, is more common every day, yet it is still a mystery on what causes it. More than a million Americans have been diagnosed with PD and every year there are 60,000 new cases. Affecting older people, it is the second most common disorder and the condition is expected to increase as the aging population increases. PD essentially is the loss of dopamine-producing neurons. The increase in research
Read Also: What To Buy Someone With Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s Disease Genetic Influence
Recent developments in research gene research has found that genetic influence plays a large role in Parkinson’s disease. Five main genes that are believed to contribute to the disease have been identified and located. These include alpha-synuclein, Parkin, Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase, DJ-1 and SCA2. It has been found that mutations of these genes are some of the underlying causes. In some causes there can be multiple mutations in one gene. The effects of some of these mutations are now understood.
Researchers suspect that genes associated with the late onset of Parkinson’s Disease are susceptibility genes rather than causal genes. It is thought that environmental factors act on these gene, consequently leading to Parkinson’s disease. But the mechanism in which they do so is not yet known. Researchers believe that if they can work out this mechanism, they can disrupt it in some way, and therefore halt the onset of the disease.
The general consensus among researchers is that both genetic influence and environmental factors lead to the onset of Parkinson’s Disease. The mechanisms of the genetic influence of Parkinson’s Disease are still to be understood and much more research is required.
The content of this web site is intended to convey general educational information and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional healthcare advice. More information.
The Burden Of Rare Damaging Variants In Hereditary Atypical Parkinsonism Genes Is Increased In Patients With Parkinsons Disease
Manual curation of OMIM identified 92 Mendelian genes for hereditary parkinsonism.
-
Hereditary parkinsonism genes consist of 17 PARK genes and 75 non-PARK genes.
-
The burden of rare damaging variants in PARK and non-PARK genes was increased in Parkinsons disease.
-
A meta-analysis revealed the enrichment of rare damaging variants in non-PARK genes in Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Reason For Parkinson’s Disease
Genetic Epidemiology Of Pd
More recently, a number of epidemiological studies with differing methodological approaches and study populations have been published and found to support a familial contribution to PD. In case control studies, positive family history was found to be the single greatest risk factor for PD . In family studies, a family history positive for PD was found in 1024% of patients, and the relative risk for PD in first degree relatives of PD patients ranged from 4 to 10. In the largest of such studies, the frequency of PD was 2% in 1458 first degree relatives of 233 PD patients, a significantly higher frequency than the 1% seen in the 7834 first degree relatives of 1172 age-matched controls .
Sequence of exon 4 of the -synuclein gene from a control individual. Sequence of exon 4 of the mutant allele from an individual affected with Parkinson’s disease from the Contursi kindred. Arrows indicate a transition mutation AG resulting in a missense mutation AlaThr at position 53 of the protein.
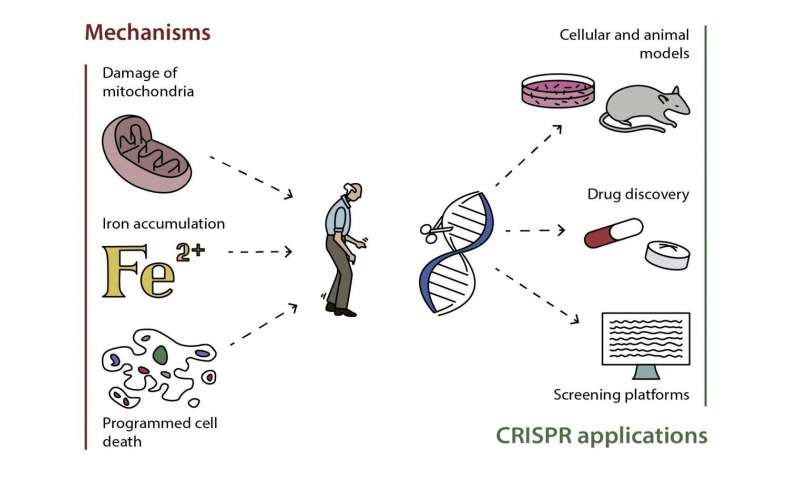
Will Findings From Pd Ipsc Models Translate To Human Clinical Trials
One of the most exciting applications of patient-derived iPSC models of PD is to validate pharmacological treatments before clinical trials. The field is still at the stage of improving human brain tissue engineering, and many different protocols are being tested and developed. However, the need for progress in clinical translation for brain disorders is extremely high, and there is no time to wait for brain tissue models to be perfect. Pioneering iPSC studies pave the road to success and identify limitations which help the community to reach a consensus on the minimal requirements to model brain disorders in vitro most accurately. It seems essential to improve the efficiency of reprogramming and differentiation protocols while trying to make those models as physiological and realistic as possible,. Some concerns are raised that in vitro neuronal development, maturation and function might be too artificial, suggesting that the model may overlook some of the critical processes that occur in vivo. Nevertheless, some defects observed in iPSC-derived neurons have already been confirmed in human postmortem brain tissues,,,,. Although this is very encouraging, it is unclear whether significant in vitro phenotypes that cannot be confirmed in postmortem brain tissue should be disregarded. Most postmortem brains also have technical limitations and may represent later stages of the disease, whereas iPSC models may represent earlier stages, preceding neurodegeneration.
You May Like: What Are The Two Types Of Parkinson’s Disease
Whats The Role Of Genetics In Parkinsons Disease
There are two ways in which gene mutations can affect Parkinsons disease: they can either directly cause the disorder or increase our susceptibility to it . In the latter case, even if you have the associated gene mutation, you may never develop Parkinsons disease.;
Genes that have been linked to Parkinsons disease include:;
- SNCA: gene that provides instructions for making alpha-synuclein, a protein that can be found in large amounts in the brain, and smaller amounts in the heart, muscles and other tissues. At least 5 mutations of this gene have been found to cause Parkinsons disease. These mutations can be inherited but they are extremely rare.;
- PRKN: one of the largest human genes, which provides instructions for making a protein called parkin.
- PINK1: gene that provides instructions for making a protein called PTEN, which is found in high levels in the heart, muscles, and testes.
- LRKK2: gene that provides instructions for making a protein called dardarin. Its active in the brain and other tissues.;
- PARK7: gene that provides instructions for making the DJ-1 protein, which is found in many tissues and organs, including the brain.
- GBA: gene that provides instructions for making beta-glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme active in lysosomes.
- UCHL1: provides instructions for making an enzyme called ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1, which is found in the brain.;
How Environmental Factors And Aging Can Be Recapitulated In Vitro
An obvious limitation of in vitro models is the lack of environmental context. The influence of nongenetic factors is not recapitulated in the basal phenotype of patient-derived neurons. For example, the influence of head trauma of a boxer with sporadic PD will not be recapitulated by default in reprogrammed neurons. An alternative would be to transplant the patient-derived neurons in animals and simulate the trauma on the animal. Similarly, influence of decades of aging of the human brain is difficult to reproduce in vitro in a few months within the boundaries of feasible experimental design. Brains in a dish will always be an imperfect experimental model. However, many tricks can be used to recapitulate the environmental and aging stress in vitro. Table summarizes a list of reagents that have already been used in iPSC neuronal culture to mimic oxidative stress, proteostatic stress, mitochondrial stress, synaptic stress, ER stress, inflammation, and cellular aging. An interesting example is progerin, a truncated form of lamin A associated with premature aging. Increasing the expression of progerin in iPSC neurons can recapitulate at least some aspect of cellular aging in vitro. Human iPSC-derived dopamine neurons overexpressing progerin displayed specific phenotypes such as neuromelanin accumulation. In addition, PD patient-derived neurons revealed disease-related phenotypes that required both genetic susceptibility and induced-aging in vitro.
Recommended Reading: What To Know About Parkinson’s Disease
The Genetic Cause Of Parkinson’s Disease
for Parkinsons disease . The real cause of PD is still unknown according to my opinion. Some researchers conclude that PD may cause by a progressive impairment or deterioration certain nerve cells in the brain gradually break down or die. There is considerable controversy surrounding the possibility of a genetic cause of Parkinson’s disease. You have stated that the pathogenesis is multifactorial with genetic predisposition, exogenous and endogenous toxins. To me, the genetic cause
When Should A Person Seek Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is available for some genes related to Parkinsons disease, but testing may not provide useful information to individuals.
For one thing, a wide range of genes may play a role, and it is not possible to test them all. A person may also have a relevant feature but not go on to develop Parkinsons disease.
For example, only around 0.7% of people with symptoms of Parkinsons disease have changes in the LRRK2 gene, and around 0.3% have changes in the PRKN gene, according to a 2020 review.
Finding out in advance if a young person has the gene may help them prepare for the future if there is strong evidence of a family history of the condition. However, the results are unlikely to be conclusive and may cause unnecessary anxiety.
Anyone who is interested in genetic testing should discuss the pros and cons with a doctor and consider genetic counseling if they decide to go ahead.
The Parkinsons Foundation notes that testing is often hard to access. It can also be costly, and health insurance may not cover it. Genetic counseling can be an additional cost.
Don’t Miss: Can Cancer Cause Parkinson’s
What Raises Someone’s Risk For Parkinson’s
It’s a complex picture, but you may be more likely to get Parkinson’s based on:
Age. Since it mostly affects people 60 and older, your risk goes up as the years go by.
Family history. If your parent, brother, or sister has it, you’re a little more likely to get it.
Job. Some types of work, like farming or factory jobs, can cause you to have contact with chemicals linked to Parkinson’s.
Race. It shows up more often in white people than other groups.
Serious head injury. If you hit your head hard enough to lose consciousness or forget things as a result of it, you may be more likely to get Parkinson’s later in life.
Gender. Men get it more than women. Doctors aren’t sure why.
Where you live. People in rural areas seem to get it more often, which may be tied to chemicals used in farming.
Is Parkinson’s Hereditary
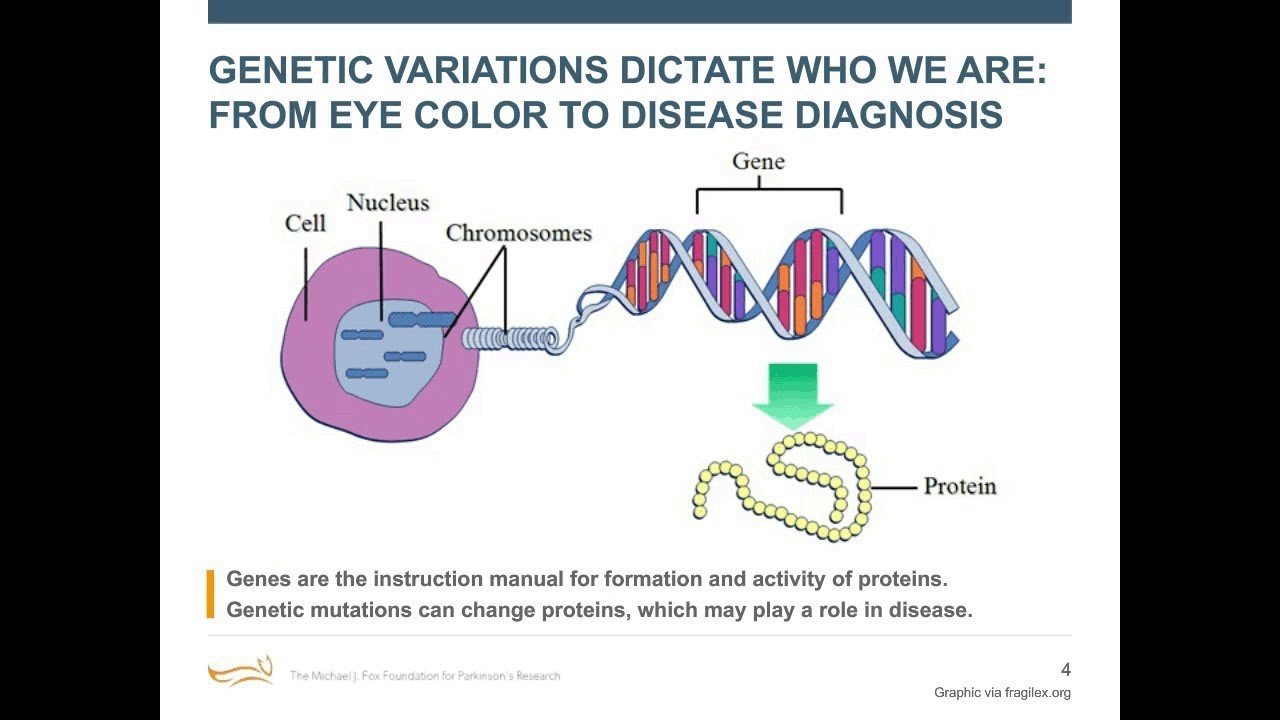
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative condition which affects various parts of the brain; however, most deleterious effects are observed in the substantia nigra a part of the brain which is responsible for balance and movement control. According to latest statistics, this disease affects more than 4 million people globally with a little more than a million in North America alone. In United States, about 60,000 new cases of Parkinson’s disease are identified each year with an incidence rate of 13 per 100,000 of the general population. It is imperative to mention that the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease increases with physiological aging ; but do genetics play a part in this?
Don’t Miss: Is There A Test For Parkinson’s
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Who Should Get Genetic Testing
Two groups might consider getting genetic testing, according to Gilbert:
- People with Parkinsons who want to know if they have a mutation they may pass along to their children
- Children and siblings of family members with Parkinsons who want to determine their genetic risk for the disease
Right now its not standard of care for everyone with Parkinsons to get genetic testing, she says. The likelihood that were going to find one of these mutations that is known already is small, and even if you have a mutation associated with Parkinsons, it doesnt mean that youre going to get the disease.
So, at this point, the value of getting tested depends on the individual. Doctors can provide this type of genetic evaluation, or people may turn to direct-to-consumer genetic testing, such as 23andMe. These tests, however, can be limited.
You have to be careful with those panels because theyre not very comprehensive, says Gilbert. They may test for only one or two gene variations.
Currently, 23andMe analyzes DNA from spit samples for a variant in LRRK2 and a variant in the GBA gene associated with the disorder. The company makes it clear that the exam does not diagnose the disease, and there are many other mutations to consider.
Parkinsons patient Paul Cannon, PhD, who works for 23andMe as its Parkinsons research community manager, took the test and found that he had neither of the genetic variations.
Recommended Reading: What Does Early Parkinson’s Feel Like
How Do You Get Parkinsons Disease
There is no known cause of Parkinson’s disease. Scientists and researchers have found that Parkinson’s is caused by a combination of genetics, environmental factors and unknown causes. Patients with Parkinson’s disease have been seen to have low dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, as well as Lewy bodies which can occur after exposure to toxic chemicals and aldehydes.
There is no way to avoid getting Parkinsons, whether or not the disease runs in your family. Some research suggests that avoiding toxic chemicals such as those found in reheated cooking oils and pesticides can reduce your chances of getting Parkinsons, but this isnt always possible. ;
What Role Do Genes Play
Your genes are like your body’s instruction book. So if you get a change in one of them, it can make your body work in a slightly different way. Sometimes, that means you’re more likely to get a certain disease.
There are several genetic mutations thatÂ;can raise your risk for Parkinson’s, each by a little bit. They have a part in about 1 in 10 cases.
If you have one or more of these changes, it doesn’t mean you’ll get Parkinson’s. Some people will, but many won’t, and doctors don’t know why. It may have to do with other genes or something in your environment.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s Disease And Multiple Sclerosis
An Analysis Of Parkinson’s Disease
In definition, Friedman states that Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system symptomized with tremor, slow and muscular rigidity which is common in elderly people. The researcher ex plains that the disease occurs as a result of the malfunctioning of neurons which are vital nerve cells found in the brain. Parkinson’s disease basically affects substantia nigra which are neurons in the brain. When substantia nigra die they produce dopamine. The chemical dopamine is
Genetic Principles And Exceptions Thereof In Familial Pd
The majority of PD cases are sporadic, i.e., only about 10% of patients report a positive family history . Out of the six genes unequivocally linked to heritable, monogenic PD, mutations in SNCA , and LRRK2 are responsible for autosomal-dominant PD forms, and mutations in Parkin , PINK1 , DJ-1 , and ATP13A2 are accountable for PD that displays an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
In general, the inheritance patterns of human disorders are identified by examining the way the disorders are transmitted in the family of the index patient. Such a pedigree analysis requires a careful assembly of the disease records of the family members over several generations, and if possible, examination and sample collection from affected and unaffected individuals from the pedigree. All of the currently known monogenic PD forms are autosomal , which means that they are linked with regions on autosomes .
Pedigree of a PD family that comprises affected members with and without the LRRK2 p.G2019S mutation. Five mutation carriers are unaffected, showing reduced penetrance, two mutation carriers are affected with dystonia, showing variable expressivity, and one affected family member does not have the p.G2019S mutation in LRRK2. Black symbols – affected individuals; white symbols – unaffected individuals; half-filled symbols – individuals with dystonia; + – mutation carriers.
Recommended Reading: What Cold Medicine Can You Take With Parkinson’s
